Umidade relativa do ar
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the concept of atmospheric pressure and how it relates to the partial pressures of gases, specifically water vapor. It covers the relationship between water vapor and the air's ability to retain it, influenced by temperature and volume. The concept of relative humidity is introduced as the ratio of actual water vapor to the maximum the air can hold at a given temperature. The video also discusses the saturation of air, how temperature affects relative humidity, and how water vapor remains relatively constant while saturation pressure increases exponentially with temperature.
Takeaways
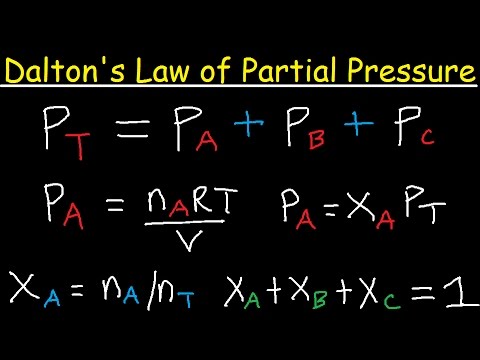
- 😀 Dalton's law of partial pressures states that each gas in the atmosphere exerts pressure independently of others.
- 🌫️ Water vapor is a key gas in the atmosphere and exerts its own pressure, known as actual vapor pressure.
- 💧 The vapor pressure is higher in areas with a larger quantity of water vapor, leading to higher pressure on surfaces.
- 🌡️ Air can only retain a certain amount of water vapor, and this limit depends on the air's temperature.
- 📉 According to the ideal gas law, at constant pressure, the volume of air is directly proportional to its temperature.
- 🔥 Air volume changes with temperature, expanding or contracting, which impacts the amount of water vapor it can hold.
- 🌧️ The saturation vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by water vapor when the air is fully saturated.
- 💨 Relative humidity is defined as the amount of water vapor in the air relative to the maximum it can hold at a given temperature.
- 🌞 For example, 80% relative humidity means the air holds 80% of the maximum possible water vapor it can at that temperature.
- 🌡️ Relative humidity is more influenced by temperature changes than by the actual water vapor content.
- 🔄 The saturation vapor pressure increases exponentially with temperature, which inversely affects relative humidity.
Q & A
What is the atmospheric air composed of?
-Atmospheric air is composed of a mixture of gases, as described by Dalton's law of partial pressures.
What does Dalton's law of partial pressures state?
-Dalton's law states that each constituent of the atmosphere exerts its own pressure on a surface, independent of the presence of other gases.
How does water vapor contribute to atmospheric pressure?
-Water vapor is one of the gases in the atmosphere and, on its own, exerts a pressure known as the real or current vapor pressure.
How does vapor pressure differ in two environments with equal volume?
-In two environments of equal volume, the environment with a greater amount of water vapor will exert a higher vapor pressure on the surface.
What is the limit to how much water vapor air can retain?
-Air has a limit to the amount of water vapor it can hold, which is determined by temperature and is governed by the ideal gas law.
What does the ideal gas law suggest about the relationship between volume and temperature?
-According to the ideal gas law, under constant pressure, the volume of a mass of air is directly proportional to its temperature.
What happens to the volume of air when the temperature changes?
-As the temperature of the air changes, its volume either expands or contracts accordingly.
What is the concept of relative humidity?
-Relative humidity refers to the amount of water vapor present in the air compared to the maximum amount the air can hold at a given temperature.
What does an 80% relative humidity indicate?
-An 80% relative humidity means that the air contains 80% of the maximum amount of water vapor it can hold at a specific temperature.
How does the saturation of water vapor in the air relate to temperature?
-The saturation pressure of water vapor increases exponentially with temperature, meaning that the amount of vapor the air can hold rises significantly with temperature.
How does relative humidity change with temperature?
-Relative humidity is inversely proportional to air temperature, meaning that as the temperature increases, the relative humidity typically decreases, assuming the amount of water vapor remains constant.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

HUKUM DALTON | KIMIA "Tekanan Parsial"

ATMOSPHERIC GAS CONCENTRATION AND INTRODUCTION TO ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE

Hidrometeorologia - parte II
Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure Problems & Examples - Chemistry

Simplest Way To Understand Boiling Point Elevation & Vapor Pressure Depression

Nyomás | Pascal törvénye | Hidrosztatika
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)