Methods of Payment in International Trade: Documentary Collections
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Kari Crane explains the concept of documentary collections (D/C) in international trade as a payment method for exporters. She outlines the process, which involves banks acting as intermediaries to ensure payment for goods. The video details the steps of using documentary collections, including shipping goods, presenting documents, and obtaining payment. Kari highlights the conditions under which D/Cs are suitable, such as having a strong relationship with the importer and operating in a stable country. She also emphasizes the importance of selecting the right payment method to minimize risk. For more information, viewers are encouraged to download a free Trade Finance Guide.
Takeaways
- 😀 Documentary collections (D/C) are a payment method where banks handle the collection of payment and documents between exporters and importers.
- 😀 The exporter’s bank sends the documents to the importer’s bank along with payment instructions, facilitating the exchange of goods for payment.
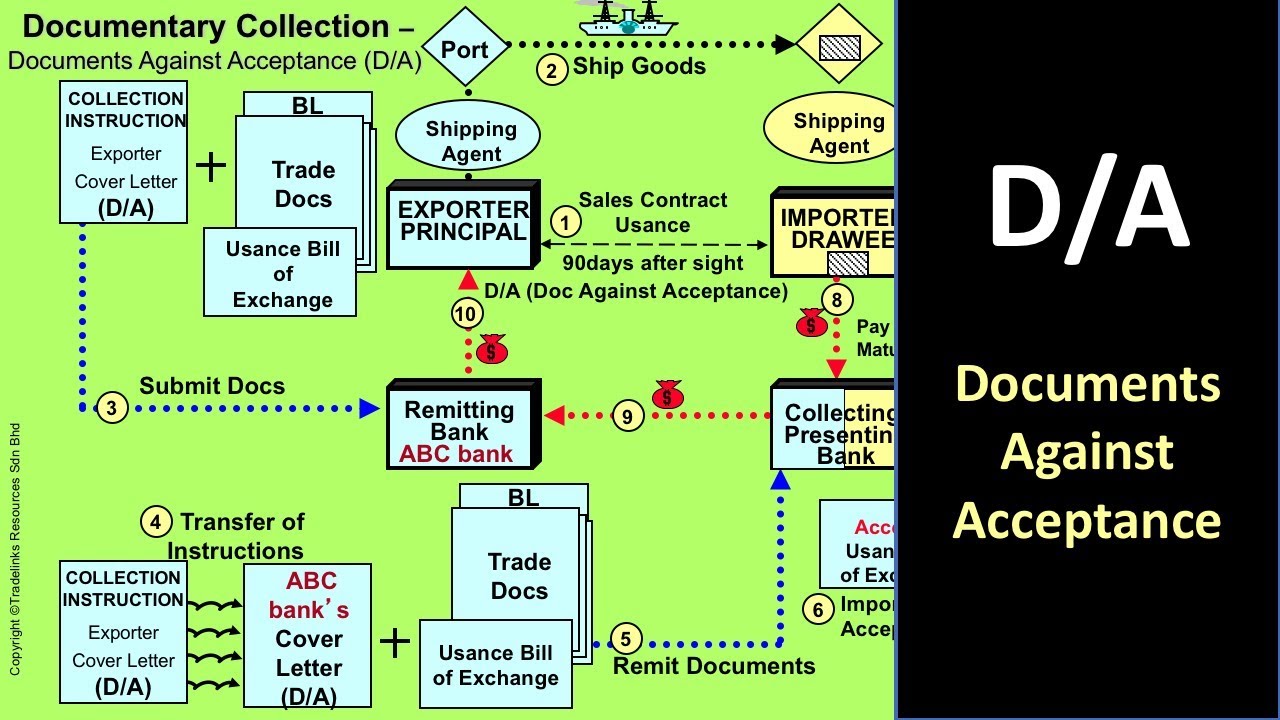
- 😀 D/Cs involve using a bill of exchange (draft) that requires the importer to pay either at sight or on a future date.
- 😀 Banks act as agents but do not verify documents or assume risk in documentary collections.
- 😀 Documentary collections are less complicated and cheaper than letters of credit, but offer less protection for the exporter.
- 😀 The exporter retains control of goods until the importer pays or accepts the draft.
- 😀 D/Cs are not recommended if the exporter has concerns about the buyer’s ability or willingness to pay.
- 😀 Documentary collections are suitable when there is an established relationship between the exporter and importer.
- 😀 Exporters should use D/Cs when the importing country is politically and economically stable.
- 😀 The typical seven-step process for D/Cs includes shipping goods, presenting documents, transferring funds through banks, and receiving payment.
- 😀 To learn more about D/Cs or explore other payment methods, exporters can download a free Trade Finance Guide and access a wealth of export resources.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of documentary collections in international trade?
-The main purpose of documentary collections is to facilitate payment for products between the exporter and importer through banks, minimizing risk and ensuring the buyer's needs are accommodated.
What are the five primary methods of payment in international trade?
-The five primary methods of payment in international trade are open account, advance payment, letter of credit (LC), documentary collections, and cash in advance.
How does a documentary collection (D/C) work?
-In a D/C, the exporter sends documents to the importer's bank through their own bank, along with instructions for payment. The payment is made by the importer to the bank, and the bank then remits the funds to the exporter in exchange for the documents.
What role do banks play in documentary collections?
-Banks act as intermediaries in documentary collections, facilitating the transfer of documents and payment between the exporter and importer, but they do not verify the documents or take on any risk.
What is a bill of exchange in the context of documentary collections?
-A bill of exchange, or draft, is a document used in documentary collections that requires the importer to pay the specified amount either immediately (at sight) or on a future date.
Why are documentary collections considered less expensive than letters of credit?
-Documentary collections are less expensive than letters of credit because they involve fewer steps and less complexity, and there is no need for the bank to verify the documents or take on risk.
What are the risks involved for the exporter when using documentary collections?
-The primary risk for the exporter is that there is little recourse if the importer does not pay. The exporter relies heavily on the established relationship with the importer.
When should documentary collections be used?
-Documentary collections should be used when the exporter and importer have a well-established relationship, the exporting country is politically and economically stable, an open account is too risky, and a letter of credit is unacceptable to the importer.
What are the seven steps in the documentary collection process?
-The seven steps are: 1) Exporter ships goods and receives documents, 2) Exporter presents documents to the bank, 3) Exporter’s bank sends documents to the importer’s bank, 4) Importer’s bank releases documents to the importer upon payment or acceptance of the draft, 5) Importer uses documents to obtain goods and clear them at customs, 6) Importer makes payment, 7) The banks transfer funds, and the exporter is credited.
What should an exporter do if they want to learn more about documentary collections or other payment methods?
-Exporters can download a free Trade Finance Guide and access hundreds of articles about exporting from the Shipping Solutions blog.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

5 Payment Methods for International Trade

5 Payment Methods in International Trade Upload

Methods of Payment in International Trade for Export & Import (2020)

Introduction to Documentary Collections Trade Finance in the Spotlight

Choosing an Export Payment Method: Cash-in-Advance
How Documents Against Acceptance works in International Trade
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)