PROJEÇÕES CARTOGRÁFICAS
Summary
TLDRThis video focuses on understanding different types of cartographic projections used in map-making, including cylindrical, conical, and azimuthal (or planar) projections. The video explains how maps are created and how these projections distort the Earth's surface, highlighting their pros and cons. It delves into the historical context of projections like Mercator's, which presents an Eurocentric view, and Peters' projection, which prioritizes the size of continents in a more equitable way. The video aims to provide viewers with a comprehensive understanding of map projections and their implications in representing the world.
Takeaways
- 😀 Cartography is the science of map-making, and the professional who creates maps is called a cartographer.
- 🌍 Maps represent the Earth's surface (or part of it) on a flat surface, such as paper or a computer screen, using a scale.
- 📏 Every map involves some level of distortion, as it's impossible to represent the Earth's 3D surface perfectly on a flat plane.
- 🌐 There are three primary types of map projections: cylindrical, conical, and azimuthal (also known as planar).
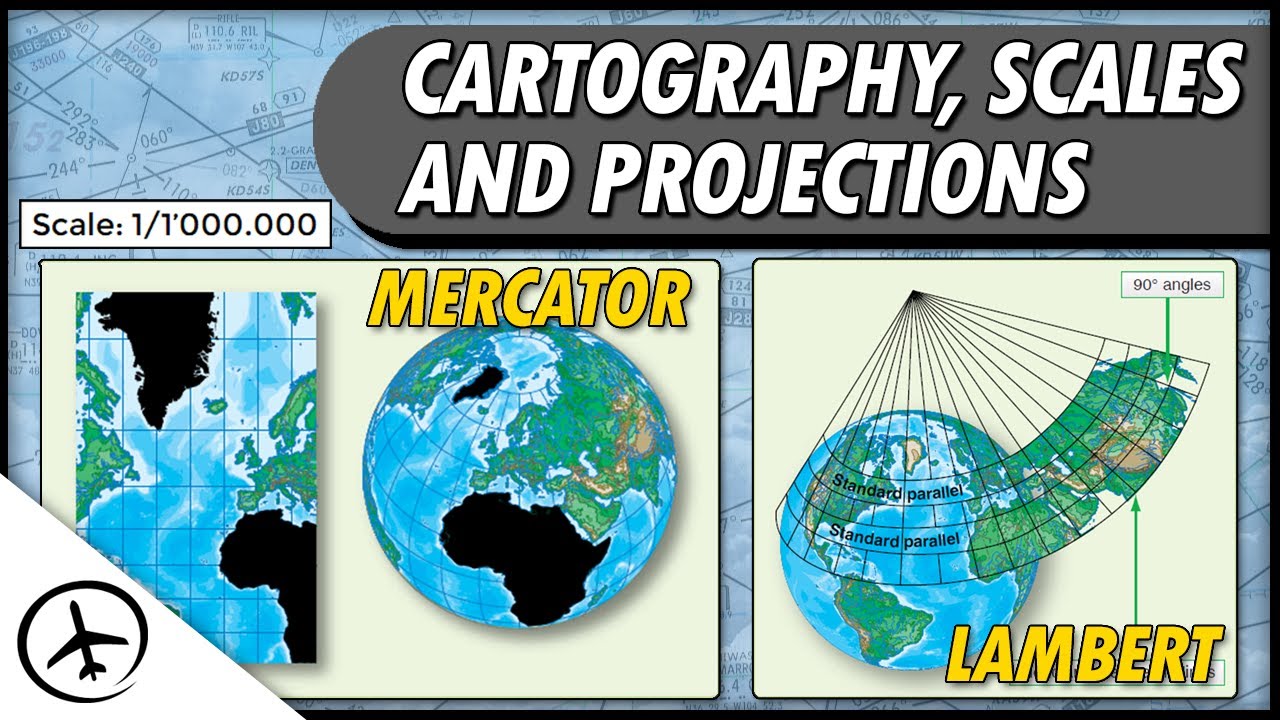
- 🗺️ The cylindrical projection is the most widely used and helps create world maps like the Mercator projection.
- 🌍 The Mercator projection distorts areas at higher latitudes, making regions like Greenland appear much larger than they are in reality.
- 📜 The Mercator projection was designed to maintain shapes and angles, but it distorts the sizes of continents, presenting Europe as larger than it is.
- 🌍 The Peters Projection (created by Arno Peters) presents continents more accurately in terms of their sizes, but distorts their shapes.
- 🌍 Unlike the Mercator projection, the Peters Projection centers on continents like Africa and South America, highlighting underrepresented regions.
- 🌍 The conical projection uses a cone to represent the Earth, and it's best suited for showing areas between the tropics and polar circles with minimal distortion.
- 🌐 The azimuthal (or planar) projection is most accurate for polar regions but causes significant distortions in areas further away from the poles.
- 🔑 It's important to understand the differences between the three projections, as they each emphasize different aspects of the Earth’s surface.
Q & A
What is cartography?
-Cartography is the science of creating maps. It involves the process of representing the Earth's surface, or a part of it, on a flat surface like paper or a computer screen.
Who is a cartographer?
-A cartographer is a professional who specializes in creating maps. They use various techniques to represent geographical areas accurately on different media.
What are the three most commonly used map projections?
-The three most commonly used map projections are the cylindrical, conic, and azimuthal projections.
What is a cylindrical projection?
-A cylindrical projection represents the Earth as if it were wrapped around a cylinder. It is the most common projection used for world maps, like the Mercator map, but it distorts the size of landmasses at higher latitudes.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the cylindrical projection?
-The cylindrical projection allows for the representation of the entire Earth's surface at once and works well for low latitudes, but it severely distorts high latitudes, making areas like the poles appear much larger than they are.
Why is the Mercator map considered eurocentric?
-The Mercator map places Europe at the center and distorts the sizes of other continents to highlight Europe. It emphasizes a European-centric view of the world.
How does the Peter's projection differ from the Mercator projection?
-The Peter's projection prioritizes the accurate representation of the size of continents, especially in the Global South, while distorting their shapes. In contrast, the Mercator projection preserves shapes but distorts sizes, especially in polar regions.
What is the main feature of the Peter's map?
-The Peter's map highlights the relative sizes of continents, especially Africa and South America, making them appear larger than in the Mercator map, which showcases an eurocentric view with Europe at the center.
What is the conic projection, and when is it used?
-The conic projection is used to represent medium latitudes, using a cone to project the Earth's surface. It minimizes distortion in these areas but only represents one hemisphere at a time, causing distortion in other regions.
What is the azimuthal (or planar) projection, and how is it different from the other projections?
-The azimuthal projection places a flat plane on the Earth's surface to represent a specific region, often used for polar areas. It provides accurate representation of these regions but distorts other areas of the planet.
What are the key differences between the cylindrical, conic, and azimuthal projections?
-The cylindrical projection represents the entire Earth but distorts high latitudes. The conic projection is best for medium latitudes, representing one hemisphere at a time. The azimuthal projection is ideal for polar regions but distorts areas farther from the poles.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)