Linear Programming - Graphical Solution | Don't Memorise
Summary
TLDRThis video explains how to solve linear programming problems, focusing on graphical solutions for problems with two variables. The presenter walks through finding optimal solutions using a coordinate plane and the corner point method, emphasizing how to graph linear inequalities and identify feasible regions. The optimal solution is determined by evaluating the objective function at the corner points of the feasible region. The video also covers key concepts like feasible regions, bounded and unbounded regions, and how to apply the corner point method to maximize or minimize an objective function.
Takeaways
- 😀 Linear programming aims to find the optimal solution to a problem by maximizing or minimizing an objective function.
- 😀 An optimal solution is the maximum or minimum value of the objective function that satisfies the constraints.
- 😀 Problems with two variables can be solved graphically using a coordinate plane.
- 😀 For problems with more than two variables, the simplex method is typically used for solving.
- 😀 When solving graphically, only the first quadrant is considered, as decision variables must satisfy the non-negativity constraint.
- 😀 To graph inequalities, equations corresponding to the inequalities are first written and then plotted based on their x and y intercepts.
- 😀 The feasible region is determined by the common area where all constraints are satisfied.
- 😀 The feasible region is bounded by the lines representing the constraints, and the optimal solution lies at one of the corner points.
- 😀 The corner point method is used to find the optimal solution by evaluating the objective function at the corner points of the feasible region.
- 😀 The objective function is evaluated by substituting the corner points into the function to find the maximum or minimum value.
- 😀 In the example, the optimal solution is found at point C, where the value of the objective function (Z) is maximum.
Q & A
What is an optimal solution in linear programming?
-An optimal solution is the maximum or minimum value of the objective function for the given linear programming problem.
What is the primary method to solve linear programming problems with two variables?
-The primary method to solve linear programming problems with two variables is graphing, where the problem is solved by plotting the constraints and finding the feasible region.
How are linear inequalities graphically represented in a coordinate plane?
-Linear inequalities are first converted into equations, and then the x and y intercepts are found to draw the corresponding lines on the coordinate plane.
What is the significance of the feasible region in solving linear programming problems?
-The feasible region is the area where all the constraints of the linear programming problem are satisfied. It represents all possible solutions that meet the given constraints.
What method is used to find the optimal solution in a linear programming problem once the feasible region is determined?
-The corner point method is used, where the optimal solution is found by evaluating the objective function at the corner points of the feasible region.
How do you find the corner points of the feasible region?
-The corner points are found by determining the intersection points of the constraint lines that define the boundaries of the feasible region.
What is the purpose of evaluating the objective function at the corner points?
-Evaluating the objective function at the corner points helps to determine which corner point yields the maximum or minimum value, thus identifying the optimal solution.
What is the process of graphing a linear inequality, as demonstrated in the example?
-First, write the corresponding equations for the inequalities, find the x and y intercepts, and then plot the lines on the graph. The feasible region is then determined by identifying the area where all constraints are satisfied.
What happens when the feasible region is unbounded in a linear programming problem?
-If the feasible region is unbounded, it means the optimal solution might not exist, or it could approach infinity, which is common in optimization problems that don't have clear constraints limiting the solution.
Why are the corner points specifically chosen in the corner point method?
-The corner points are chosen because, according to linear programming theory, the optimal solution to a linear programming problem always lies at one of the corner points of the feasible region.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
PROGRAM LINIER - METODE GRAFIK - RISET OPERASI

Linear Programming dengan Metode Grafik

MK Kuantitatif - Linier Programming Metode Simpleks

ILLUSTRATING SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES || GRADE 8 MATHEMATICS Q1
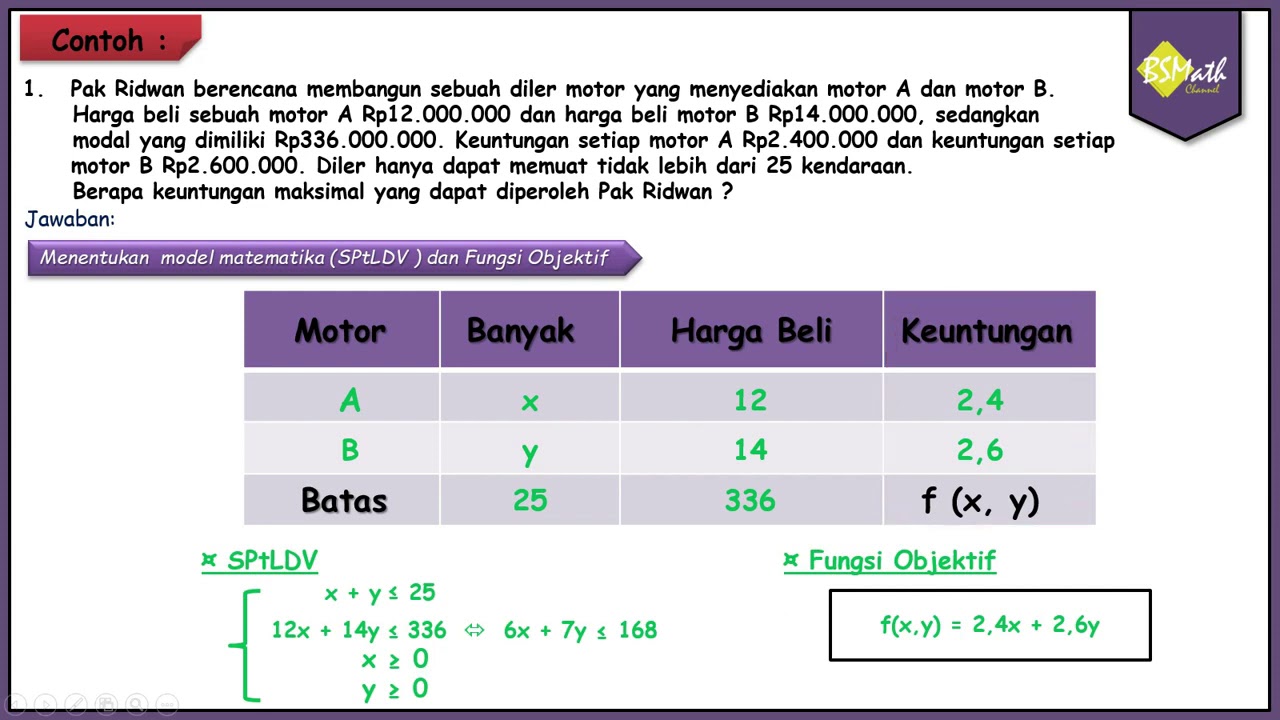
Menyelesaikan Permasalahan Program Linear Menentukan Nilai Optimum dengan Metode Uji Titik Pojok

How to Solve a Linear Programming Problem Using the Graphical Method
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)