Planos Anatômicos e Eixos de Movimento: Introdução à Anatomia parte 2
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Professor Natália Reinecke explains the concepts of anatomical planes and axes of movement. The video introduces the three primary anatomical planes: sagittal (dividing the body into right and left), frontal (dividing the body into front and back), and transverse (dividing the body into top and bottom). It also discusses the corresponding axes of movement: lateral-lateral, anterior-posterior, and longitudinal, which facilitate movements like flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation. The content is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of how the body moves in space, using clear, relatable examples to help students grasp these concepts.
Takeaways
- 😀 Anatomical planes are imaginary cuts that help describe the body in three dimensions and are essential for studying anatomy and interpreting medical images like CT scans.
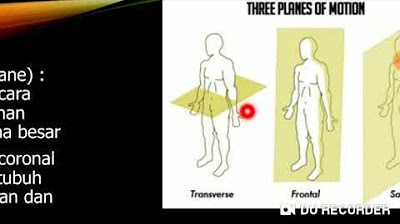
- 😀 The main anatomical planes are the sagittal plane, frontal (coronal) plane, and transverse plane.
- 😀 The median sagittal plane divides the body into equal right and left halves, while the other sagittal planes are parallel to this one.
- 😀 The frontal plane divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) parts.
- 😀 The transverse plane divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) parts.
- 😀 Anatomical planes are crucial for describing body movements along specific axes of motion.
- 😀 There are three primary axes of motion: lateral-lateral (transverse), antero-posterior (sagittal), and longitudinal axes.
- 😀 The lateral-lateral axis runs horizontally and perpendicular to the sagittal plane, facilitating movements like flexion and extension.
- 😀 The antero-posterior axis runs from front to back, perpendicular to the frontal plane, and enables movements like abduction and adduction.
- 😀 The longitudinal axis runs vertically from top to bottom and is crucial for rotational movements around the body.
- 😀 The script emphasizes how anatomical planes and axes work together to describe how the body moves in relation to its structure.
Q & A
What are the anatomical planes?
-Anatomical planes are imaginary cuts that divide the body into different sections. These planes help describe the body in three-dimensional terms and are essential for studying anatomy and interpreting medical images, such as CT scans.
What is the sagittal plane, and how does it divide the body?
-The sagittal plane is a vertical plane that divides the body into two equal halves: the right and left sides. It runs from front to back, and the median sagittal plane specifically divides the body into two symmetrical halves.
What are the other types of sagittal planes?
-The other sagittal planes are parallel to the median sagittal plane, dividing the body into similar right and left portions, but they are not necessarily symmetrical. These planes are known as parasagittal planes.
What does the frontal plane do, and how does it divide the body?
-The frontal plane, also called the coronal plane, is a vertical plane that divides the body into front (anterior) and back (posterior) portions. It cuts the body from side to side.
What is the transverse plane, and how does it divide the body?
-The transverse plane is a horizontal plane that divides the body into upper (superior) and lower (inferior) portions. It cuts across the body horizontally, from top to bottom.
What is the difference between the transverse plane and the other anatomical planes?
-The key difference is that the transverse plane is horizontal, dividing the body into upper and lower parts, while the sagittal and frontal planes are vertical and divide the body into right/left and front/back sections respectively.
What are the axes of movement, and how are they related to anatomical planes?
-Axes of movement are imaginary lines around which body movements occur. They are associated with anatomical planes because movements happen within these planes and around these axes.
What is the lateral-lateral (transverse) axis, and which movements occur around it?
-The lateral-lateral axis, also called the transverse axis, runs from side to side of the body. It is perpendicular to the sagittal plane and allows for movements of flexion and extension, such as bending or straightening a limb.
What is the antero-posterior axis, and what movements does it facilitate?
-The antero-posterior axis runs from front to back of the body. It is perpendicular to the frontal plane and enables movements like abduction and adduction, which are the movements of a limb away from or towards the body's midline.
What is the longitudinal axis, and what movements occur around it?
-The longitudinal axis runs vertically from top to bottom of the body. It is perpendicular to the transverse plane and allows for rotational movements, such as turning the head or twisting the torso.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Movimentos do corpo humano. Anatomia e Cinesiologia | Anatomia etc

Introdução à Anatomia: posição anatômica e termos de relação | Anatomia etc

Acidentes Ósseos: Sistema Esquelético | Anatomia etc

Planos e Eixos Anatômicos | WEBVET
ANATOMI GERAK MANUSIA (BAG. 1) : ISTILAH ARAH, BIDANG ANATOMIS DAN SUMBU ANATOMIS.
Anatomy: Planes & Axes (NEW VERSION IN DESCRIPTION)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)