O que é Bioenergética
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of bioenergetics, focusing on how the human body generates, stores, and transfers energy for survival. Key topics include glycolysis and glycogenolysis (breakdown of glucose and glycogen), glyconeogenesis and glycogenesis (formation of glucose and glycogen), and the energy provided by macronutrients. The video also discusses the ATP-CP, glycolytic, and oxidative energy systems, detailing how the body uses these systems depending on activity levels. Emphasizing the importance of ATP, the body’s primary energy molecule, the video explains how energy is synthesized and degraded under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions.
Takeaways
- 😀 Bioenergetics studies the transformation, storage, production, and transfer of energy in the human body, essential for survival and specific conditions.
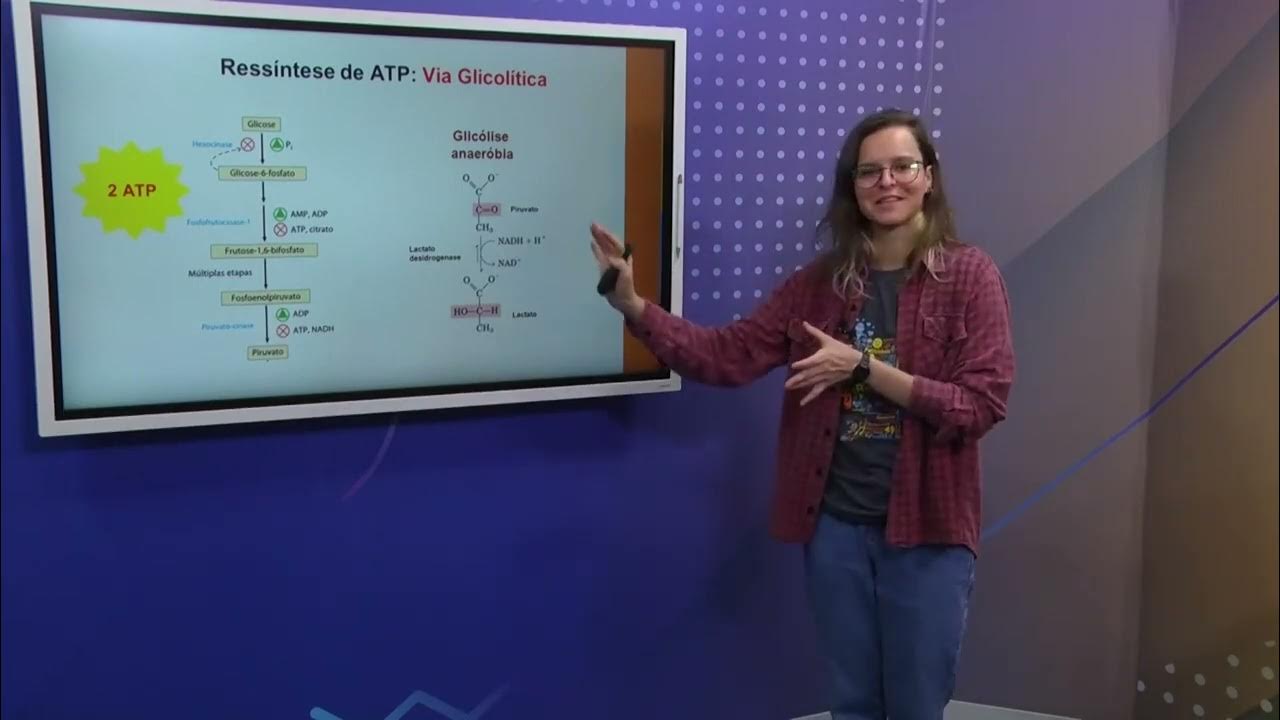
- 😀 Glicolysis is the breakdown of glucose, while glycogenolysis breaks down glycogen into glucose-1-phosphate, primarily in the muscles and liver.
- 😀 Anabolism processes like glycogenesis refer to the formation of glycogen, and gluconeogenesis is the formation of glucose from non-glucose substrates like pyruvate and amino acids.
- 😀 Carbohydrates and proteins provide around 4–4.5 kcal per gram, while lipids provide 8–9 kcal per gram, highlighting lipids as the most energy-dense macronutrient.
- 😀 For energy to be used, macronutrients must be broken down into substrates, such as glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids.
- 😀 The body uses multiple energy systems: ATP-CP for quick energy, the glycolytic system for glucose-based energy, and the oxidative system for more prolonged energy use.
- 😀 These energy systems are integrated, meaning they work together, and their dominance depends on factors like physical activity, stress, or rest.
- 😀 The body's energy storage includes glycogen (from carbohydrates), triglycerides (from fats), and proteins in the form of amino acids.
- 😀 ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the primary energy carrier, consisting of adenine, three phosphate groups, and ribose, a five-carbon sugar.
- 😀 ATP is continuously synthesized and degraded to provide energy for cellular functions, with anaerobic and aerobic processes involved depending on oxygen availability.
Q & A
What is bioenergetics?
-Bioenergetics is the study of how living organisms handle energy transformation, storage, production, and transfer to support their survival. It is crucial for understanding how the human body uses energy for various processes.
What role do macronutrients play in bioenergetics?
-Macronutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids are key sources of energy for the body. They need to be broken down into smaller substrates, like glucose, amino acids, or fatty acids, to be used as energy for bodily functions.
What is glycolysis, and how does it relate to energy production?
-Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose into smaller molecules, releasing energy. It is an essential process in bioenergetics, providing energy for the body, especially during physical activity.
How is glycogen related to energy storage and usage?
-Glycogen is the stored form of glucose in the body, particularly in muscles and the liver. It can be broken down into glucose through glycogenolysis when the body needs quick energy, such as during exercise.
What is the difference between glycogenesis and gluconeogenesis?
-Glycogenesis is the process of forming glycogen from glucose, while gluconeogenesis refers to the formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate substrates like pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, or amino acids.
What are the energy contents of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids?
-Carbohydrates and proteins provide about 4-4.5 kcal per gram, whereas lipids provide 8-9 kcal per gram, making lipids more energy-dense.
What is the ATP-CP system, and when is it used?
-The ATP-CP system is a quick energy system that uses adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and creatine phosphate to provide immediate energy for short bursts of activity, like sprinting or lifting heavy weights.
How does the glycolytic system contribute to energy production?
-The glycolytic system uses glucose as an energy source and is activated after the ATP-CP system. It helps provide energy for activities lasting a bit longer but still requires quick energy, like moderate-intensity exercise.
What is the oxidative system, and why is it important?
-The oxidative system provides a large amount of energy over longer periods of time by utilizing oxygen to metabolize carbohydrates, fats, and sometimes proteins. It is essential for prolonged activities like endurance exercise.
How are the three energy systems integrated in the human body?
-The three energy systems—ATP-CP, glycolytic, and oxidative—work together in the body. Depending on the activity or situation, one system may predominate, but all three contribute to energy production simultaneously, with no clear-cut switches between them.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Curso Fisiologia do Exercício Aplicada - Bioenergética ATP - Aula 01

EGRAD BEDU 202154 FISIOLOGIA GERAL E DO MOVIMENTO PARTE 2

GCSE Physics Revision "Energy Transfer by Appliances"
EGRAD BEDU 202352 PROJETO DE ENSINO ASPECTOS FISIOLOGICOS DO EXERCICIO FISICO PARTE 1

Bioenergética e Introdução ao Metabolismo #1 (reedição)

Bill Nye The Science Guy - S03E05 - Energy - Best Quality
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)