Palm Oil Refining: Part 1
Summary
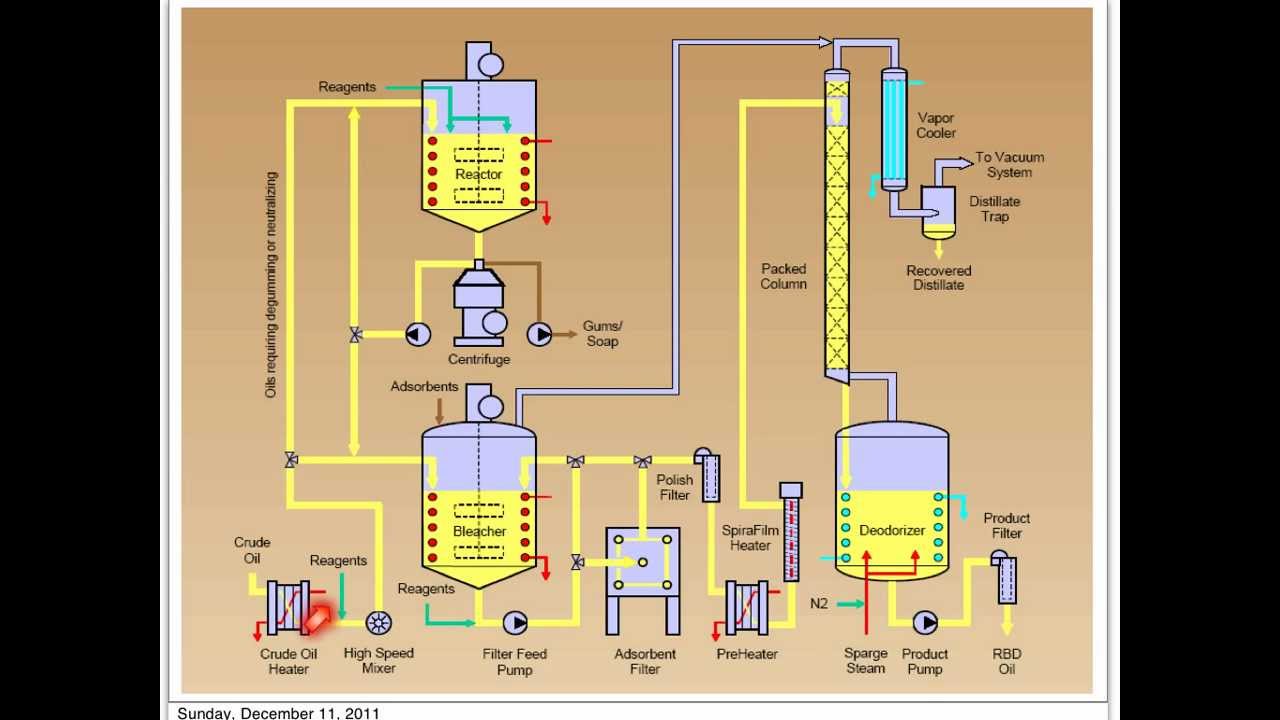
TLDRIn this lecture, Professor Abdul Karim from University Science Malaysia discusses the process of edible oil refining, focusing on crude palm oil and crude palm kernel oil. He explains the steps involved in refining, such as degumming, bleaching, and deodorization, to remove impurities like free fatty acids, phosphatides, and pigments. The differences between physical and chemical refining processes are highlighted, with physical refining being more common in Malaysia. The goal is to produce high-quality palm oil while minimizing waste and chemical usage. The lecture also covers the refining equipment, like the deodorizer column used for steam distillation.
Takeaways
- 😀 Crude palm oil (CPO) contains 95% triglycerides (desired oil part) and 5% non-triglyceride components such as free fatty acids and phosphatides.
- 😀 The goal of edible oil refining is to remove undesirable components (like FFAs and gums) while minimizing damage to the triglycerides.
- 😀 The refining process involves two main methods: physical refining (using high-temperature steam distillation) and chemical refining (using alkaline solutions).
- 😀 Physical refining is most suitable for oils with high FFAs and low phosphatides, such as palm oil, and does not produce soapstock.
- 😀 Chemical refining, on the other hand, is more suitable for oils with low FFAs and higher phosphatides and produces soapstock as a byproduct.
- 😀 Physical refining includes steps such as degumming (to remove phosphatides), bleaching (to remove pigments), and deodorization (to remove FFAs and volatile compounds).
- 😀 Chemical refining includes the neutralization of FFAs with sodium hydroxide, followed by bleaching and deodorization, resulting in soapstock as a byproduct.
- 😀 In physical refining, the degumming step is crucial, as it reduces phosphatides to a low level, improving oil quality without producing soapstock.
- 😀 Physical refining results in higher oil yield and less chemical usage, reducing the need for waste treatment compared to chemical refining.
- 😀 In Malaysia, physical refining is preferred for palm oil, with over 95% of palm oil production using this method due to its efficiency and adaptability to palm oil's characteristics.
Q & A
What is the primary goal of the edible oil refining process?
-The primary goal of edible oil refining is to remove non-triglyceride components such as free fatty acids, gums, oxidation products, and trace elements from crude palm oil, in order to produce high-quality refined oil.
What are the key components found in crude palm oil?
-Crude palm oil consists primarily of around 95% triglycerides, which are the actual oil, and approximately 5% non-triglyceride components, including free fatty acids, phosphatides (gums), oxidation products, and trace elements like copper and iron.
Why is it important to remove phosphatides (gums) during refining?
-Phosphatides (gums) need to be removed during refining because they cause the oil to be viscous and can lead to the formation of soap stock, which results in oil losses and reduced oil quality.
What are the differences between physical refining and chemical refining?
-Physical refining uses steam distillation to remove free fatty acids and other volatile compounds, while chemical refining uses alkali solutions to neutralize free fatty acids and produce soap stock, which needs to be separated. Physical refining is generally more suited for oils with high free fatty acid content, while chemical refining is better for oils with higher phosphatide content.
What is the role of the deodorization process in refining?
-Deodorization is a high-temperature steam distillation process that removes volatile fatty acids, residual mono- and diglycerides, and other small compounds like aldehydes, ketones, and sulfur compounds, helping to reduce unwanted odors and improve oil quality.
Why is the removal of free fatty acids (FFA) crucial in the refining process?
-Free fatty acids (FFA) need to be removed because they contribute to the acidity of the oil and can result in undesirable flavors, odors, and a decrease in the shelf life of the final product.
What byproducts are produced during the refining of crude palm oil?
-The byproducts of refining crude palm oil include free fatty acid distillates, which can be further processed into chemicals or soap, and soap stock, which is a byproduct of the chemical refining process.
What is the significance of the bleaching process in oil refining?
-The bleaching process removes pigments, oxidation products, and other impurities, improving the color and stability of the oil, which enhances its overall quality.
What types of oils are typically refined using physical refining?
-Physical refining is typically used for oils that have a high free fatty acid content but relatively low phosphatide content, such as palm oil and coconut oil.
Why is physical refining preferred in Malaysia over chemical refining?
-Physical refining is preferred in Malaysia because it is more efficient for palm oil, as it provides higher oil yields, reduces chemical usage, and minimizes waste treatment problems. It is also less prone to oil losses, particularly in oils with high free fatty acid content.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)