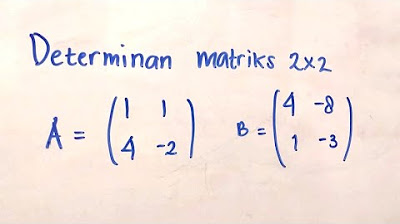Matematika SMA - Matriks (5) - Determinan Matriks 2x2, Invers Matriks 2x2 (A)
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, viewers are introduced to the fundamentals of matrix operations, specifically focusing on 2x2 matrices. The tutorial covers the calculation of determinants and inverses, providing clear explanations and step-by-step examples to ensure understanding. The presenter explains how to compute the determinant using a simple formula and demonstrates how to find the inverse matrix, including handling special cases. The video also features practice problems, allowing learners to apply the concepts. A friendly and engaging tone is maintained throughout, encouraging viewers to like, share, and subscribe for more content.
Takeaways
- 😀 The tutorial is about learning matrices, specifically determinants and inverses of 2x2 matrices.
- 😀 To receive notifications for new videos, viewers are encouraged to subscribe and click the notification bell on the channel.
- 😀 Determinants and inverses can only be calculated for square matrices, and this video focuses on 2x2 matrices.
- 😀 The formula for the determinant of a 2x2 matrix is: |A| = a * d - b * c, where the matrix is [[a, b], [c, d]].
- 😀 The inverse of a 2x2 matrix is calculated by taking 1 over the determinant and multiplying it by the adjoint of the matrix.
- 😀 The adjoint of a 2x2 matrix is found by swapping the diagonal elements and changing the signs of the off-diagonal elements.
- 😀 If the determinant of a matrix is zero, the matrix does not have an inverse.
- 😀 In the exercise, the determinant of matrix A (6, 3, 4, 5) is calculated as 18, and for matrix B (-1, -5, 2, -3) it is 13.
- 😀 The inverse of matrix A (7, 9, 3, 4) is calculated to be 1/28 times the adjoint matrix, resulting in the inverse matrix [[4, -9], [-3, 7]].
- 😀 The inverse of matrix B (-13, -5, 20, 18) is calculated to be 1/4 times the adjoint matrix, resulting in the inverse matrix [[8, -13], [-5, -21]].
- 😀 The third exercise involves solving for x in an equation involving the transpose and inverse of matrices, ultimately finding x = 4.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is about learning matrix operations, focusing on determinants and the inverse of 2x2 matrices.
What is the formula for calculating the determinant of a 2x2 matrix?
-The determinant of a 2x2 matrix with elements [a, b; c, d] is calculated as: det(A) = (a * d) - (b * c).
What does the term 'adjoint matrix' refer to in the context of finding the inverse of a matrix?
-The adjoint matrix (or adjugate) of a 2x2 matrix is formed by swapping the elements a and d, changing the signs of b and c, and then multiplying the resulting matrix by 1/determinant(A).
What happens if the determinant of a matrix is zero?
-If the determinant of a matrix is zero, the matrix does not have an inverse, as the inverse is undefined for such matrices.
How do you calculate the inverse of a 2x2 matrix?
-To calculate the inverse of a 2x2 matrix [a, b; c, d], you first calculate the determinant, then find the adjoint matrix by swapping a and d, changing the signs of b and c, and finally multiplying by 1/determinant.
What is the inverse of a 2x2 matrix with the elements [7, 9; 3, 4]?
-The inverse of the matrix [7, 9; 3, 4] is calculated as 1/(7*4 - 9*3) multiplied by the adjoint matrix, which results in the matrix [4, -9; -3, 7]. The final result is [1/28, -27] multiplied by the adjoint matrix.
How do you calculate the determinant of the matrix [6, 3; 4, 5]?
-To calculate the determinant of the matrix [6, 3; 4, 5], use the formula det(A) = (6 * 5) - (3 * 4), which equals 30 - 12 = 18.
What steps are involved in solving for the inverse of a matrix with elements [(-1), -3; -5, 2]?
-First, calculate the determinant: det(A) = (-1) * 2 - (-3) * (-5) = -2 - 15 = -17. Then, compute the adjoint matrix by swapping the elements a and d, changing signs for b and c, and multiply by 1/determinant. The final result is [1/-17] * adjoint matrix.
What is the significance of the adjoint matrix in calculating the inverse?
-The adjoint matrix plays a crucial role in calculating the inverse because it transforms the original matrix in a way that, when multiplied by 1/determinant(A), results in the inverse matrix.
What is the purpose of the problem involving matrix A and matrix B with the condition that A^T = B^-1?
-The purpose of this problem is to find the value of 'x' in a system where matrix A transpose (A^T) equals the inverse of matrix B (B^-1), using matrix operations and the given conditions to solve for the unknown variable.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)