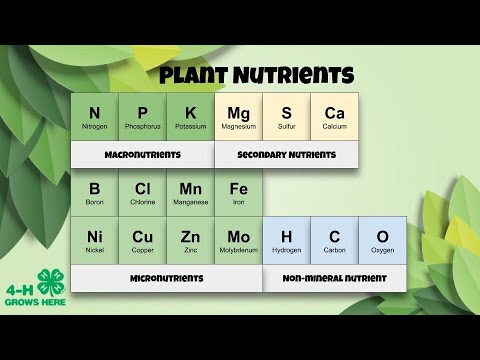
UNSUR HARA MAKRO DAN MIKRO LENGKAP : NITROGEN, FOSFAT, KALIUM, BORON, KALSIUM, SULFUR, ZINK, SILIKA
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses the importance of essential macro and micro nutrients for plants, focusing on Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K), Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg), Sulfur (S), Iron (Fe), Manganese (Mn), Zinc (Zn), Copper (Cu), Boron (B), and Silicon (Si). It explains the roles of each nutrient in plant growth and their sources, highlighting how these elements contribute to the plant’s overall health, structure, and resistance to diseases. The speaker also touches on how fertilizers can supplement these nutrients and ensures proper plant development for optimal yield.
Takeaways
- 😀 Micronutrients are essential for plants, just like macronutrients, to support their growth and development.
- 😀 Micronutrients help enhance plants' immunity, resistance to diseases, and improve overall health.
- 😀 There are two main types of essential nutrients for plants: macronutrients and micronutrients.
- 😀 Macronutrients include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur.
- 😀 Micronutrients, though required in smaller quantities, are equally important for plant vitality.
- 😀 Zinc, copper, and boron are examples of micronutrients that plants need for various functions.
- 😀 Boron plays a critical role in plant reproduction, particularly in pollen tube formation and seed production.
- 😀 Copper is necessary for plant photosynthesis and the formation of chlorophyll.
- 😀 Silica is a key micro-nutrient for monocot plants, such as rice and corn, as it strengthens cell walls.
- 😀 Silica enhances plant resistance against pathogens and helps to reinforce the cell structure.
- 😀 Silica can be found naturally in soil or provided via registered liquid silica fertilizers.
Q & A
What are macronutrients and micronutrients in the context of plant growth?
-Macronutrients are elements that plants require in large quantities for healthy growth, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and calcium. Micronutrients, on the other hand, are elements needed in smaller amounts but are equally crucial, such as iron, zinc, and silica.
Why are macronutrients essential for plant growth?
-Macronutrients are critical because they play vital roles in plant development, including promoting healthy root growth, boosting overall plant vigor, and aiding in photosynthesis and energy storage.
What specific role does nitrogen play in plant growth?
-Nitrogen is essential for plants as it helps in the formation of chlorophyll, which is necessary for photosynthesis. It also aids in protein synthesis, which is vital for cell growth and overall plant health.
How does phosphorus contribute to plant development?
-Phosphorus is key in energy transfer within plants. It helps with root development, flowering, and fruiting. It is also involved in the formation of nucleic acids and enzymes necessary for growth and metabolism.
What is the significance of potassium for plants?
-Potassium helps regulate various plant processes, including water uptake, enzyme activation, and photosynthesis. It also enhances the plant's resistance to diseases and improves drought tolerance.
What are micronutrients, and why are they important for plants?
-Micronutrients are elements required by plants in small amounts, yet they are crucial for various biochemical processes, such as enzyme activation and nutrient absorption. Examples include iron, zinc, copper, and silica.
How does iron function as a micronutrient in plants?
-Iron is involved in chlorophyll formation and is a key component of enzymes involved in energy production and nitrogen fixation. It is essential for photosynthesis and overall plant metabolism.
What is the role of silica in plant health, especially for monocots?
-Silica strengthens the cell walls of plants, particularly monocots like rice, corn, and onions. This reinforcement makes plants more resilient to pathogens and environmental stress.
How do plants absorb silica, and what are its sources?
-Plants absorb silica primarily from the soil, where it is naturally present. It can also be provided through specialized fertilizers, such as liquid silica, which are often registered with agricultural authorities.
What is the difference between monocot and dicot plants in terms of their need for nutrients?
-Monocots, like rice and corn, have a higher demand for silica compared to dicots. This is because monocots rely on silica to reinforce their cell walls, whereas dicots have different structural requirements.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)