Double Fertilization (Angiosperms) | Plant Biology
Summary
TLDRIn this video, we explore the fascinating process of double fertilization in angiosperms (flowering plants). The process involves two fertilization events: one forms the zygote, and the other creates the endosperm. The video explains the structure of flower parts involved, such as the gynoecium and androecium, as well as the detailed steps of fertilization. It covers how pollen reaches the ovule, how the sperm cells fertilize the egg and polar nuclei, and the subsequent development of the embryo and endosperm. This process is crucial for the development of seeds and plant growth.
Takeaways
- 😀 Double fertilization is a process in flowering plants (angiosperms) that involves two fertilization events.
- 😀 The first fertilization results in the formation of a zygote, and the second results in the formation of the endosperm.
- 😀 The female reproductive organs of a flower are called the gynoecium, which contains the pistil.
- 😀 The pistil consists of the stigma, style, and ovary, and the ovary holds the ovules.
- 😀 Ovules are surrounded by two integument layers and contain a tissue called the megasporangium.
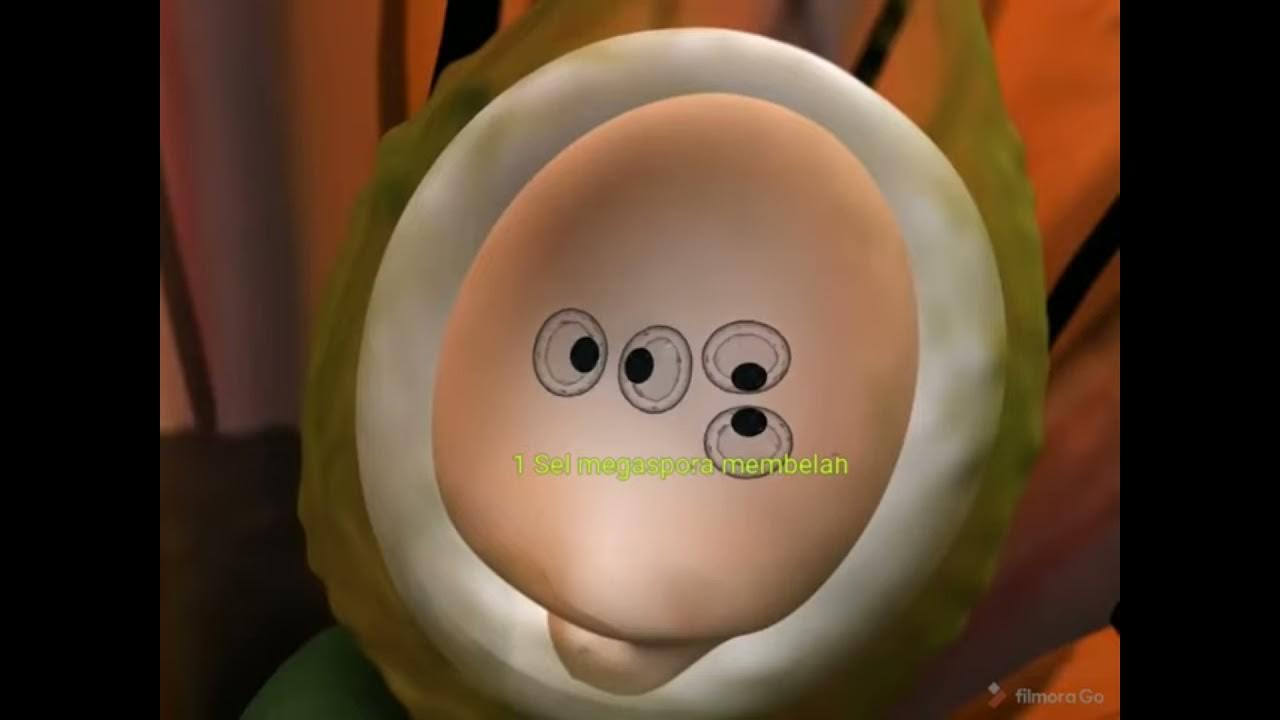
- 😀 The megasporocyte undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid megaspores, with only one surviving to undergo mitotic divisions.
- 😀 The embryo sac forms eight nuclei, including three antipodal cells, two synergid cells, one egg cell, and two polar nuclei.
- 😀 The male reproductive organs, the androecium, are composed of stamens that produce pollen grains.
- 😀 A pollen grain contains a generative cell and a tube cell, and it lands on the stigma to begin the fertilization process.
- 😀 The tube cell grows down the style and into the ovule, guided by chemicals from synergid cells.
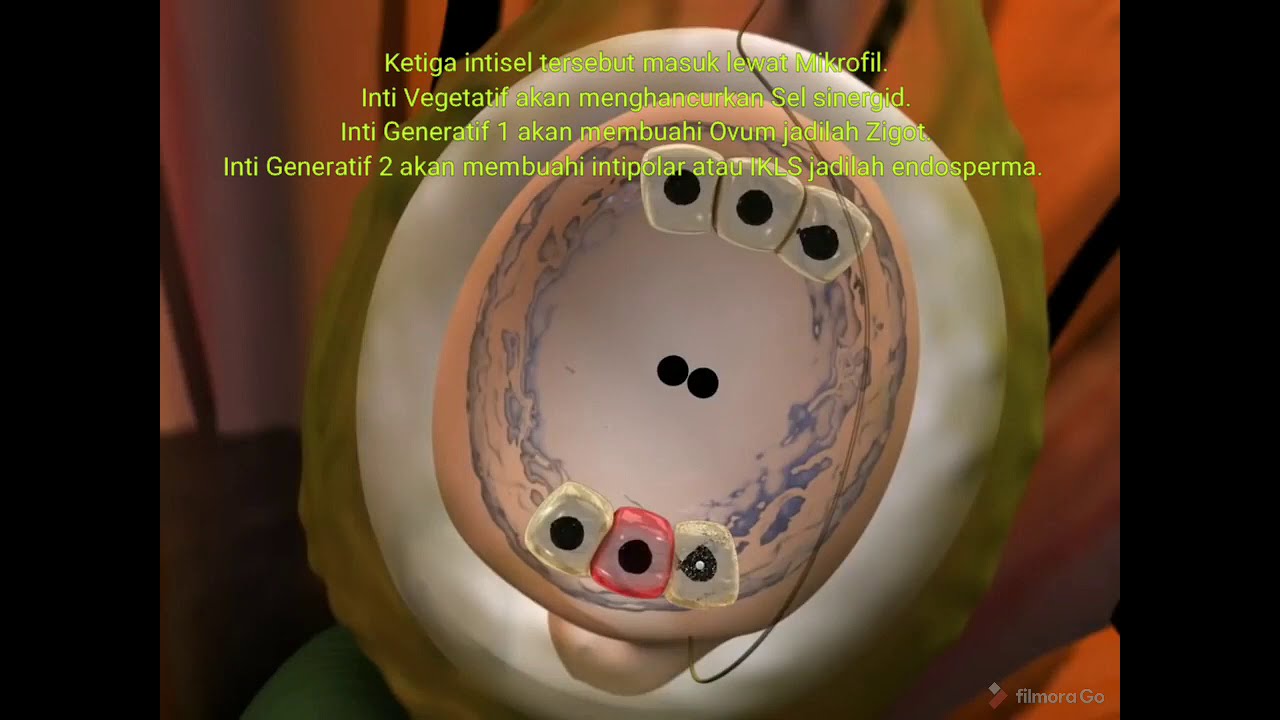
- 😀 Double fertilization occurs when one sperm cell fuses with the egg cell to form a zygote, and the second sperm cell fuses with the polar nuclei to form the triploid endosperm.
- 😀 The zygote undergoes embryogenesis to develop into an embryo, while the endosperm provides nourishment to the embryo.
Q & A
What is double fertilization in angiosperms?
-Double fertilization is a unique process in angiosperms (flowering plants) where two fertilization events occur: one results in the formation of the diploid zygote, and the other leads to the creation of the triploid endosperm.
What are the main parts of the flower involved in double fertilization?
-The key parts of the flower involved in double fertilization are the gynoecium (female reproductive organs) and androecium (male reproductive organs). The gynoecium consists of the pistil, which includes the stigma, style, and ovary. The androecium is made up of stamens, which produce pollen.
What is the function of the pistil in double fertilization?
-The pistil, located in the gynoecium, contains the stigma, style, and ovary. The ovary houses the ovules, which are essential for fertilization. It is in the ovules where the fertilization events occur.
How does a pollen grain fertilize the egg cell?
-The pollen grain, containing a generative cell and a tube cell, lands on the stigma and germinates. The tube cell grows through the style, reaching the ovule, where one sperm cell fuses with the egg cell, forming the diploid zygote.
What is the role of the endosperm in double fertilization?
-The endosperm, formed from the fusion of one sperm cell with the two haploid polar nuclei, is a triploid tissue that provides nourishment to the growing embryo during its development.
What is the megasporocyte, and what is its role in fertilization?
-The megasporocyte, also known as the megaspore mother cell, is the original cell inside the ovule that undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid megaspores. One of these survives and develops into the embryo sac, which contains the egg cell and polar nuclei.
How does the pollen tube find its way to the ovule?
-The pollen tube grows down through the stigma and style, guided by chemicals secreted by the synergid cells near the micropyle of the ovule. These chemicals direct the tube to the embryo sac, where fertilization occurs.
What happens to the synergid cells during double fertilization?
-The synergid cells are located near the micropyle and help guide the pollen tube. When the pollen tube reaches the embryo sac, it causes the death of one of the synergid cells, which then provides space for the sperm cells to enter the ovule.
What are the antipodal cells, and where do they go in the embryo sac?
-The antipodal cells are three nuclei formed from the division of the megaspore. They move to the chalazal end of the embryo sac and do not play a direct role in fertilization but are part of the overall structure of the embryo sac.
What happens after double fertilization is complete?
-After double fertilization, the diploid zygote develops into an embryo through embryogenesis, while the triploid endosperm provides nutrition for the growing embryo. The other cells in the embryo sac degenerate.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Video Reproduksi Tumbuhan

Plant Reproduction in Angiosperms

IPA Kelas 9 : Sistem Perkembangbiakan Tumbuhan (Part 3 : Pembuahan Ganda pada Tumbuhan Angiospermae)

Angiosperm (flowering plant) Life Cycle
Pembuahan Ganda pada Angiospermae

Tumbuhan Berbiji Terbuka dan Tertutup || SPERMATOPHYTA || Materi Biologi Kelas 10 || Utak Atik Otak
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)