All Chemistry Explained in 17 Minutes
Summary
TLDRThis engaging and humorous chemistry video takes viewers through the fundamental concepts of chemistry, from the structure of atoms to the periodic table. Using relatable analogies and references to modern technology, it explains atomic models, chemical reactions, and periodic trends like electronegativity and atomic radius. The video also dives into the history of atomic theory, from the ancient Greek philosophers to modern quantum mechanics, making complex ideas accessible. With clear explanations and a fun narrative, the video makes chemistry both approachable and fascinating for viewers, setting the stage for more in-depth exploration in the second part.
Takeaways
- 😀 Chemistry is the study of matter and its transformations, which can be chemical or physical.
- 😀 Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons form the nucleus, while electrons form the outer electron cloud.
- 😀 The atomic model has evolved over time, starting with Democritus' idea of indivisible atoms to more complex models involving quantum mechanics.
- 😀 Matter can undergo both physical changes (e.g., water changing states) and chemical reactions (e.g., hydrogen and oxygen forming water).
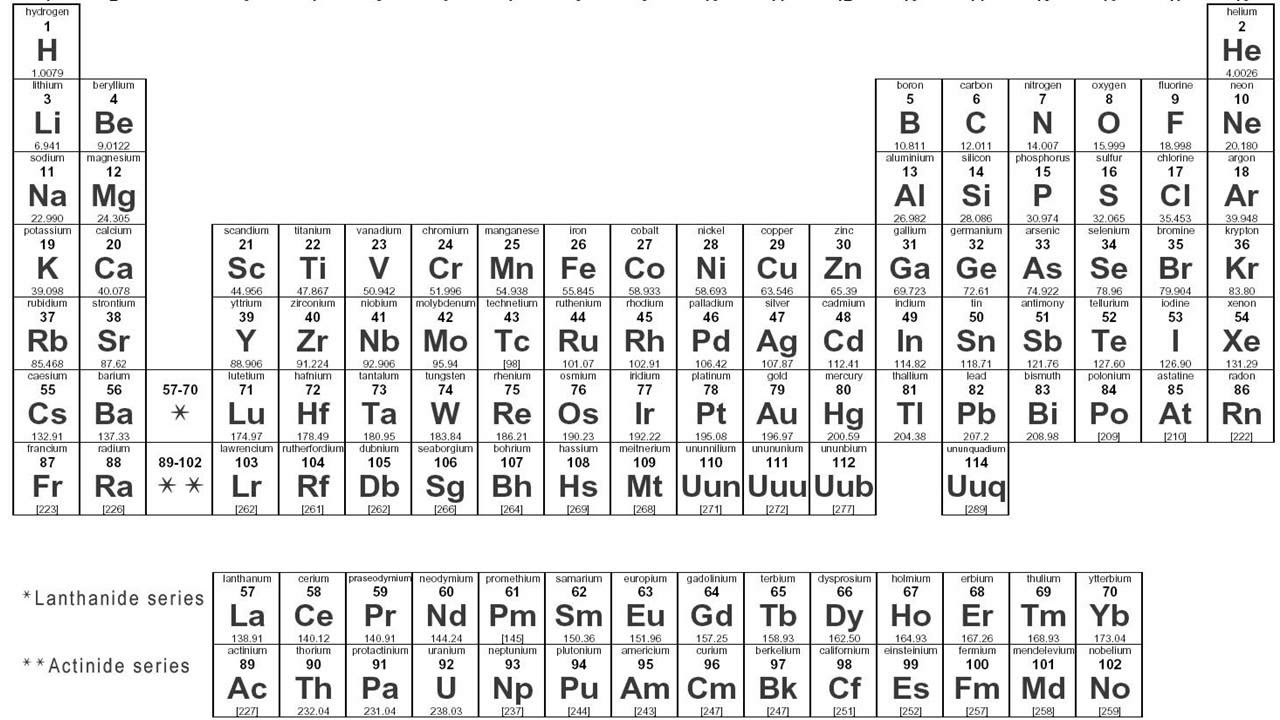
- 😀 The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic number (number of protons), electron configuration, and periodic properties.
- 😀 Elements in the same group of the periodic table share similar properties because they have the same number of electrons in their outermost shell.
- 😀 Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons, leading to different atomic masses, such as Carbon-12 and Carbon-14.
- 😀 The concept of atomic mass focuses on the mass of protons and neutrons, as electrons contribute a negligible amount.
- 😀 The electron configuration in an atom follows specific rules about energy levels and orbitals, with electrons filling shells in order of increasing energy.
- 😀 Key periodic properties such as atomic radius and electronegativity vary predictably across the periodic table, with smaller atoms having higher electronegativity.
Q & A
What is chemistry the study of?
-Chemistry is the science that studies matter, its transformations, and the interactions between atoms and molecules.
What defines the physical state of a substance?
-The physical state of a substance is determined by temperature, pressure, and the types of interactions between its particles or molecules, known as intermolecular forces.
How does the interaction between particles affect the physical state of matter?
-The stronger the attraction between molecules, the more tightly they are bound, leading to a solid state. As the attraction decreases, the substance transitions to a liquid or gas.
What is an atom composed of?
-An atom consists of a nucleus, which contains protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral), and an electron cloud or electrosphere where electrons (negatively charged) reside.
How did scientists first conceptualize the atom?
-The concept of the atom dates back to Democritus, who theorized that matter could not be divided infinitely and eventually reached a fundamental, indivisible unit called the 'atom'.
What are isotopes?
-Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons, resulting in different atomic masses. For example, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon.
What is the role of the atomic number?
-The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in an atom's nucleus and defines the element. It also determines the element's position on the periodic table.
Why is the mass of electrons considered negligible?
-The mass of electrons is so small compared to protons and neutrons that it is considered negligible when calculating atomic mass. The mass of a proton or neutron is about 1836 times greater than that of an electron.
What is the significance of the periodic table?
-The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic number and properties. It helps predict the behavior of elements, including their reactivity and bonding patterns.
How are elements organized in the periodic table?
-Elements are organized into periods (horizontal rows) based on the number of electron shells, and groups (vertical columns) based on the number of electrons in their outermost shell. This organization helps explain patterns in chemical properties.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)