PDE 2 | Three fundamental examples
Summary
TLDRThis video explores three key partial differential equations: the Wave, Laplace, and Heat equations, each representing different physical phenomena. The Wave equation models behaviors like water waves and vibrating strings, while the Laplace equation addresses mechanical and thermal equilibrium, such as stretching an elastic membrane or temperature distribution in a metal plate. The Heat equation, introduced by Fourier, describes the diffusion of heat in a metal rod over time. Through animations and examples, the video showcases how these equations model real-world dynamics in physics and engineering.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script covers three fundamental partial differential equations: the Wave equation, the Laplace equation, and the Heat equation.
- 😀 The Wave equation is a prototypical example of 'hyperbolic' equations and describes phenomena like vibrations and water waves.
- 😀 The mathematical form of the Wave equation is 'u_tt = u_xx', where 't' represents time and 'x' represents spatial position.
- 😀 Water waves and vibrating strings are examples used to illustrate solutions to the Wave equation, showing how waves can interact and propagate.
- 😀 The Laplace equation is prototypical for 'elliptic' equations, and it describes steady-state physical phenomena such as gravitational potential.
- 😀 The mathematical form of the Laplace equation is 'u_xx + u_yy = 0', which applies to systems in mechanical equilibrium or thermal equilibrium.
- 😀 A practical example of the Laplace equation involves stretching a rubber sheet over a wireframe, where the shape of the membrane is determined by the equation.
- 😀 Laplace's equation is also used to model thermal equilibrium in a metal plate with a parabolic temperature distribution, showing how the interior temperature is distributed.
- 😀 The Heat equation is a prototypical example of 'parabolic' equations and describes heat conduction over time, where 'u_t = u_xx'.
- 😀 The Heat equation can be visualized with examples like a metal rod heated at one point, showing how the temperature diffuses over time until equilibrium is reached.
- 😀 More complex examples of the Heat equation include periodic boundary conditions, where a metal rod experiences periodic heating and cooling.
Q & A
What are the three fundamental examples of partial differential equations discussed in the video?
-The three fundamental examples discussed are the Wave equation, the Laplace equation, and the Heat equation.
What types of physical phenomena do the three equations describe?
-The Wave equation describes wave phenomena, the Laplace equation describes static equilibrium (mechanical and thermal), and the Heat equation describes heat conduction over time.
What kind of equations are each of the three examples prototypical for?
-The Wave equation is prototypical for hyperbolic equations, the Laplace equation is prototypical for elliptic equations, and the Heat equation is prototypical for parabolic equations.
Who first wrote down the Wave equation, and what physical scenario was it meant to describe?
-The Wave equation was first written down by the mathematician d'Alembert in the 1740s to describe the vibrations of strings.
What are the key observations made when visualizing water waves as solutions to the Wave equation?
-When visualizing water waves, we observe that the waves interact (grow and shrink) when they meet, and that one wave moves to the left at twice the speed of the wave moving to the right.
How does the animation of a vibrating string demonstrate the Wave equation?
-The animation of a vibrating string, such as a guitar string being plucked, shows the displacement of the string over time and illustrates how overtones and higher-frequency vibrations are superimposed over the fundamental vibration.
What is the physical interpretation of the Laplace equation, and who studied it?
-The Laplace equation, studied by Laplace in the 1780s, describes static equilibrium such as gravitational potential, and it can be applied to systems in mechanical equilibrium or thermal equilibrium.
How is the Laplace equation applied to the scenario of a stretched elastic membrane?
-In the case of a stretched elastic membrane, the Laplace equation is used to find the shape of the membrane as it conforms to the boundary conditions set by a wire frame, such as a parabolic shape.
What does the Heat equation model, and what real-world example does it use for illustration?
-The Heat equation models heat conduction, and a real-world example used in the video is a metal rod heated at one point and then allowed to cool, illustrating how heat diffuses over time.
How does the Heat equation apply to a periodic boundary condition in the metal rod scenario?
-In the periodic boundary condition scenario, the right end of the metal rod is heated periodically with a blowtorch, and the temperature change is observed to diffuse through the rod over time according to the Heat equation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Fisika Komputasi - Metode Finite Difference 05 Sifat Diferensial dan Persamaan Diferensial

Persamaan Diferensial Parsial (Pengertian, Definisi, dan Klasifikasi)
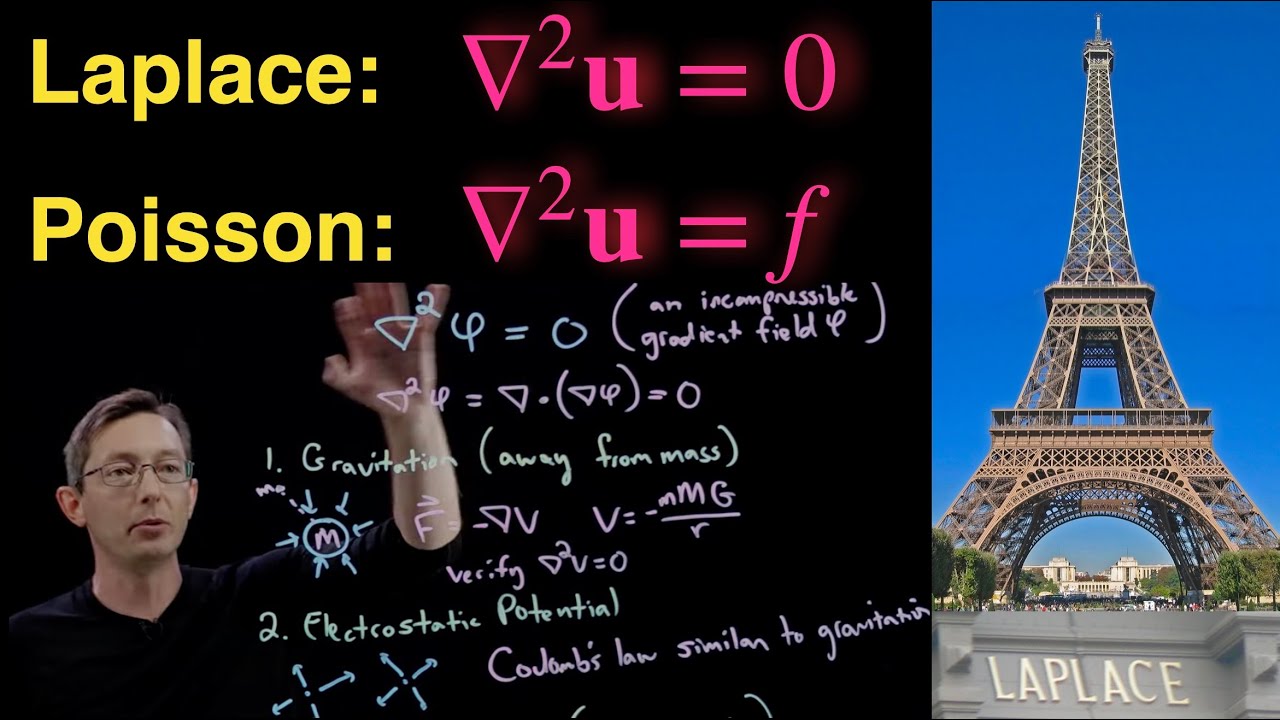
Laplace's Equation and Poisson's Equation

Transform Calculus and its applications in Differential Equations

PENYELESAIAN PDP DENGAN PEMISAHAN VARIABEL BAG 3

Introduction to Differential Equations (Differential Equations 2)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)