Reaksi Oksidasi dan Reduksi - Redoks- kimia kelas 10
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth exploration of oxidation and reduction reactions, focusing on their development and key concepts. It explains how oxidation initially referred to oxygen addition, while reduction was seen as oxygen removal. The concept later expanded to include electron transfer and changes in oxidation numbers. Through examples like rusting iron, burning carbohydrates, and reduction of iron ore, viewers learn the mechanics of these reactions. The video also covers the rules for determining oxidation numbers and highlights how oxidation and reduction occur together in redox reactions, offering a clear understanding of these foundational chemical processes.
Takeaways
- 😀 Oxidation involves a reaction with oxygen, such as when iron rusts (Fe + O₂ → Fe₂O₃).
- 😀 Reduction is the opposite of oxidation, where oxygen is removed, like in the reduction of iron ore with carbon monoxide (Fe₂O₃ + CO → Fe + CO₂).
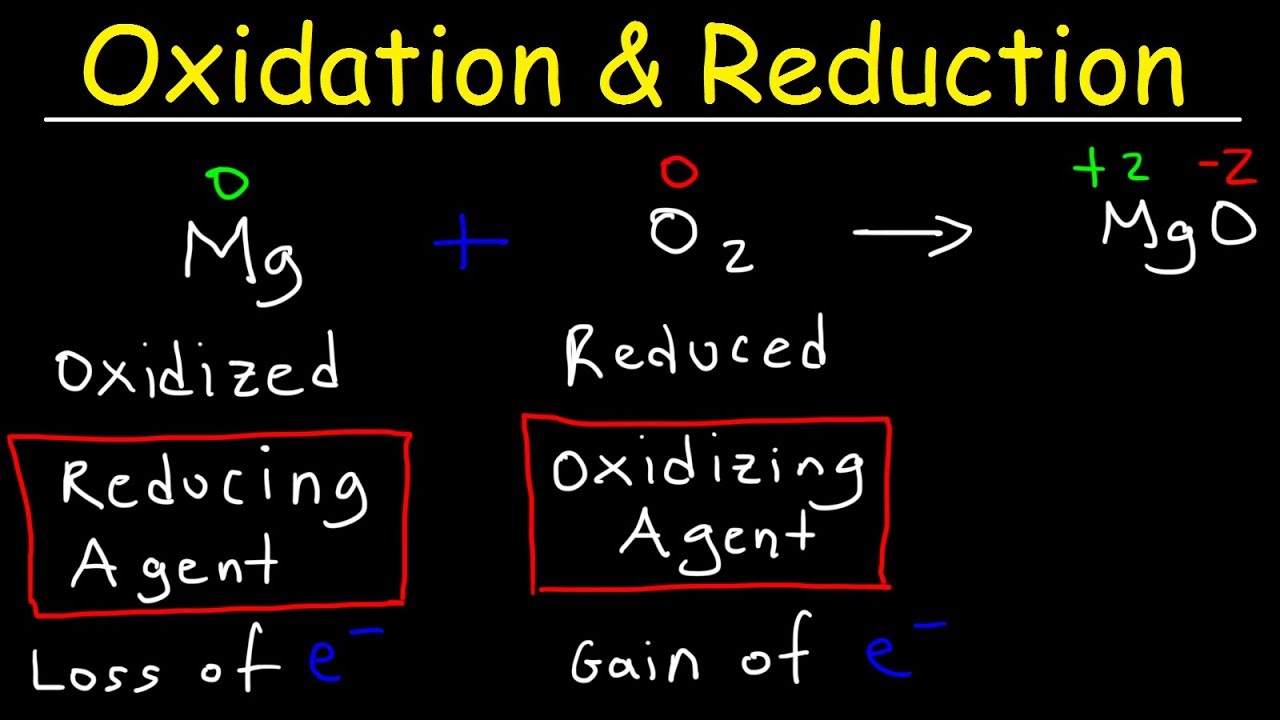
- 😀 Oxidation can be defined as the loss of electrons, while reduction is the gain of electrons.
- 😀 A redox reaction occurs when one substance undergoes oxidation (loses electrons) and another undergoes reduction (gains electrons).
- 😀 Oxidation states (bilangan oksidasi) help track electron transfer in redox reactions and indicate the electron count in a compound.
- 😀 Free elements (e.g., O₂, Na) always have an oxidation state of zero.
- 😀 In compounds, metals typically have positive oxidation states, such as Na in NaCl having a +1 state.
- 😀 Hydrogen has a +1 oxidation state, except when bonded with metals (hydrides), where it is -1.
- 😀 Fluorine always has an oxidation state of -1 in compounds, regardless of its bonding.
- 😀 Oxygen usually has an oxidation state of -2, except in peroxides and superoxides, where it can vary.
- 😀 To find oxidation states in complex compounds, sum the oxidation states of all elements, ensuring they match the overall charge of the compound or ion.
Q & A
What is the concept of oxidation as explained in the script?
-Oxidation is described as a reaction in which oxygen is added to a substance, such as when iron rusts due to its interaction with oxygen.
Can you provide another example of oxidation from the video?
-Another example of oxidation is the browning of an apple when exposed to air. The apple's flesh darkens as it interacts with oxygen, undergoing oxidation.
What is reduction according to the first concept mentioned?
-Reduction refers to a reaction in which oxygen is removed from a substance. For example, when iron ore (Fe2O3) is reduced by carbon monoxide, oxygen is released.
What does the second concept of oxidation and reduction focus on?
-The second concept focuses on the transfer of electrons. Oxidation is the release of electrons, while reduction involves the acceptance of electrons.
Give an example of oxidation from the second concept involving electron transfer.
-An example of oxidation is the reaction where calcium (Ca) loses two electrons to become Ca2+, as it releases electrons.
What is an example of reduction from the second concept?
-An example of reduction is when sulfur (S) accepts two electrons to become S2-, as it gains electrons.
What does the third concept of oxidation and reduction focus on?
-The third concept looks at the change in oxidation states (bilangan oksidasi). Oxidation is seen as an increase in the oxidation number, while reduction is a decrease.
What is oxidation number (bilangan oksidasi), and why is it important?
-Oxidation number is a value assigned to an element in a compound that reflects its electron participation in bonding. It's important for determining the extent of oxidation or reduction in reactions.
What are the general rules for assigning oxidation numbers in compounds?
-Some key rules include: (1) Uncombined elements have an oxidation number of zero, (2) Alkali metals always have an oxidation number of +1, (3) Hydrogen typically has an oxidation number of +1, (4) Oxygen generally has an oxidation number of -2, and (5) Fluorine always has an oxidation number of -1.
Can you explain how the oxidation number is determined in a compound like NaCl?
-In NaCl, sodium (Na) has an oxidation number of +1 because it's an alkali metal, and chlorine (Cl) has an oxidation number of -1. The sum of the oxidation numbers must be zero for the compound to be neutral.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)