What Is Scrum? (An Agile Cartoon)
Summary
TLDRThis video offers a comprehensive overview of Scrum, emphasizing its flexible framework for effective team collaboration on complex products. It breaks down Scrum's three pillars—Transparency, Inspection, and Adaptation—and explores its core components: roles (Product Owner, Scrum Master, Development Team), events (Sprints, Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, Sprint Retrospective), and artifacts (Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, Increment). The video highlights the iterative nature of Scrum and the importance of continuous improvement through feedback and collaboration. Ideal for those new to Scrum or looking to deepen their understanding of its practices.
Takeaways
- 😀 Scrum is a framework for effective team collaboration on complex products, not a methodology.
- 😀 Scrum is based on three key pillars: Transparency, Inspection, and Adaptation.
- 😀 The main Scrum roles are the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team, each with specific responsibilities.
- 😀 A Sprint is a time-boxed iteration, typically 2 to 4 weeks, where a team works towards a business goal.
- 😀 Sprint planning is a collaborative effort where the team defines the work and goal for the upcoming Sprint.
- 😀 The Daily Scrum is a 15-minute meeting for the team to synchronize and adapt their work towards achieving the Sprint goal.
- 😀 The term 'Scrum' comes from rugby, where a scrum is a way to restart play, metaphorically symbolizing the team's collective effort.
- 😀 The Sprint Review is a collaborative meeting to showcase the work done during the Sprint and gather feedback from stakeholders.
- 😀 The Sprint Retrospective is an opportunity for the team to reflect and adapt to improve future Sprints.
- 😀 Scrum artifacts include the Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment, which help manage the work and provide transparency.
- 😀 The Scrum process can be visualized as two loops: the outer loop being the Sprint cycle and the inner loop focused on daily adjustments during the Sprint.
Q & A
What is Scrum?
-Scrum is a flexible framework designed to help teams collaborate effectively on complex projects. It emphasizes transparency, inspection, and adaptation to continuously improve the process and outcomes.
What are the three pillars of Scrum?
-The three pillars of Scrum are Transparency, Inspection, and Adaptation. These pillars help guide the Scrum process by ensuring openness, regular evaluation, and adjustments to improve outcomes.
Why is Scrum not considered a methodology?
-Scrum is not a methodology because it is flexible and adaptable to different contexts. It is a framework that guides how teams work together, but it doesn't dictate rigid rules. However, some people may use the term methodology, which can cause confusion.
What are the roles in Scrum?
-Scrum defines three primary roles: the Product Owner, who is responsible for defining and prioritizing the work; the Scrum Master, who helps organize and remove obstacles; and the Development Team, which carries out the work.
What is a Sprint in Scrum?
-A Sprint is a time-boxed iteration, typically lasting between 2 to 4 weeks, in which the Scrum team works toward achieving a specific goal or business objective. The Sprint has a fixed duration and remains consistent from iteration to iteration.
What happens during Sprint Planning?
-During Sprint Planning, the Scrum team collaboratively defines the work to be done in the upcoming Sprint. They set clear goals and prioritize the tasks to be completed, ensuring that they can deliver value to the Product Owner within the Sprint’s timeframe.
What is the purpose of the Daily Scrum?
-The Daily Scrum is a brief 15-minute meeting where the team members synchronize their work by discussing what they did yesterday, what they plan to do today, and any obstacles they are facing. It helps ensure transparency and allows the team to adapt quickly to new information.
How does the term 'Scrum' relate to Rugby?
-The term 'Scrum' comes from Rugby, where a 'Scrummage' is a restart of play involving players forming a tight group to compete for possession of the ball. In Scrum, the team comes together to reset and collaborate effectively, though without the physical competition.
What is the Sprint Review, and why is it important?
-The Sprint Review is a meeting held at the end of the Sprint where the team presents their completed work to stakeholders for feedback. It is important because it provides transparency into the team's progress and allows for adjustments based on stakeholder input.
What happens during the Sprint Retrospective?
-The Sprint Retrospective is a meeting where the Scrum team reflects on their processes and identifies areas for improvement. The goal is to continually improve team effectiveness and adapt their practices for the next Sprint.
What are the main artifacts in Scrum?
-The main artifacts in Scrum are the Product Backlog, which is a list of all desired work items; the Sprint Backlog, which is the set of tasks selected for the current Sprint; and the Increment, which is the potentially shippable output produced by the team during the Sprint.
How does Scrum handle unfinished work at the end of a Sprint?
-If work remains unfinished at the end of a Sprint but is still valuable, it can be moved to the next Sprint. However, the team does not change the length of the Sprint to accommodate unfinished tasks, as the Sprint duration remains fixed.
How do the two loops in Scrum function?
-Scrum operates with two loops: the outer loop represents the two-week iteration cycle, including Sprint Planning, the Daily Scrums, Sprint Review, and Retrospective. The inner loop represents the daily touchpoint through the Daily Scrum, ensuring that the team adapts based on the progress of the current day.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Inside The Scrum Team - 15-Minute Introduction to Scrum - Free Scrum Course
Scrum Explained in Hindi l Software Engineering and Project Management Course
Scrum Methodology | Scrum Master Tutorial | Simplilearn

LEARN How to SCALE with Nexus in 9 mins (SIMPLE STEP BY STEP GUIDE)

Introduction to Scrum | What is Scrum? | Scrum Tutorial | Scrum Master Training by KnowledgeHut
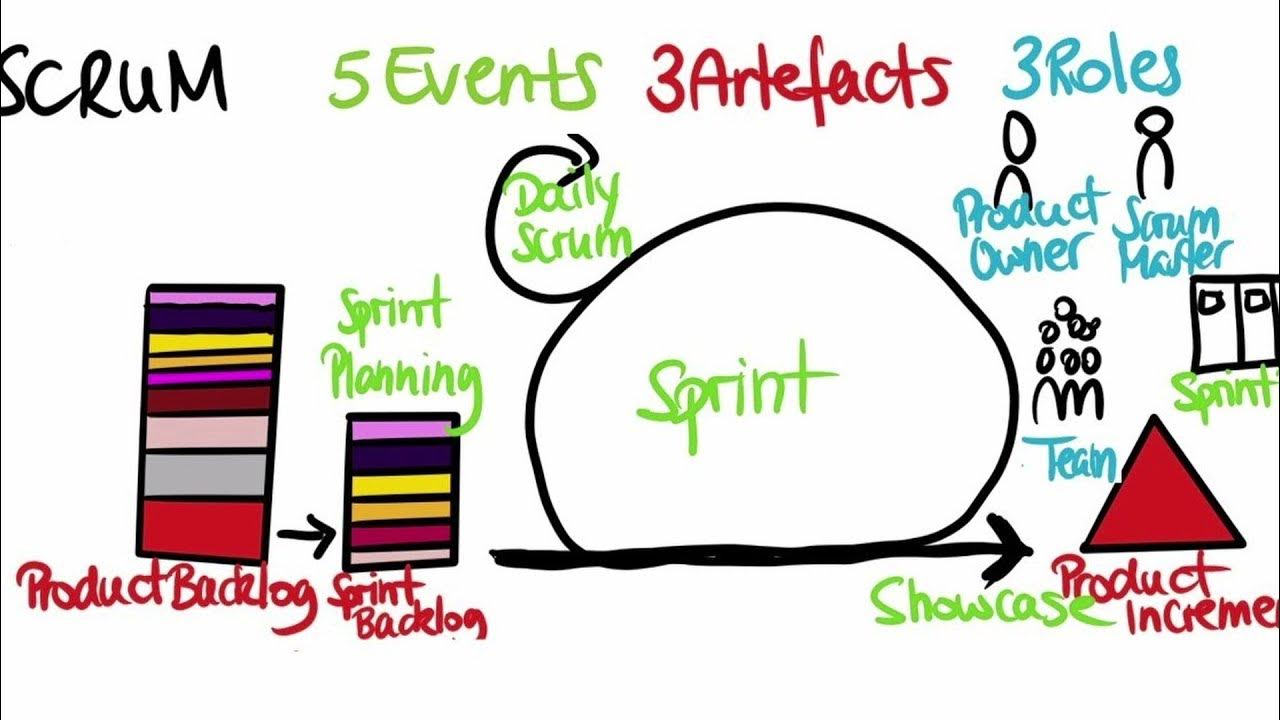
The Scrum Guide (In under 15 minutes!)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)