The Scrum Guide (In under 15 minutes!)
Summary
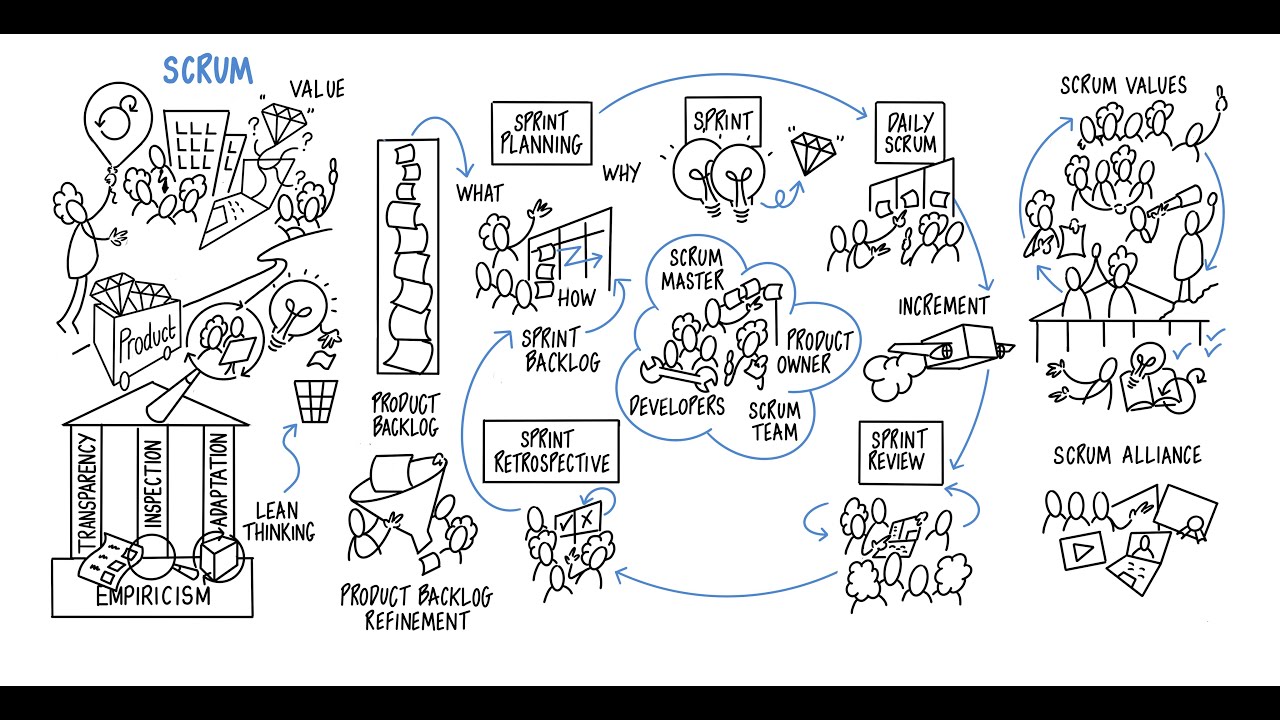
TLDRScrum is a lightweight framework designed to help teams solve complex problems and deliver value iteratively. Developed by Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland in the 1990s, Scrum emphasizes transparency, inspection, and adaptation. It defines three main roles—Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Development Team—and organizes work into time-boxed sprints. Through events like Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective, Scrum fosters collaboration and continuous improvement. With its simple yet powerful structure, Scrum enables teams to deliver valuable increments efficiently while adapting to changing needs.
Takeaways
- 😀 Scrum is a lightweight framework that helps teams solve complex problems and deliver value, developed in the early 1990s by Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland.
- 😀 Scrum is based on empiricism (learning from experience) and lean thinking (reducing waste and focusing on essentials).
- 😀 The framework defines three roles: Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Team Members, each with specific responsibilities.
- 😀 Scrum promotes transparency, inspection, and adaptation, which are the core pillars of its empirical process.
- 😀 Scrum values commitment, focus, openness, respect, and courage, which should be embodied by all team members.
- 😀 Scrum encourages self-management and cross-functionality within teams, empowering them to decide how to get work done.
- 😀 The Scrum team should be small enough to remain nimble but large enough to complete significant work within a sprint (usually 10 or fewer people).
- 😀 The five Scrum events include: Sprint, Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective, each serving a distinct purpose to inspect and adapt.
- 😀 The Product Backlog is an ordered list of work required to improve the product, which evolves over time. The Sprint Backlog is a subset of items for the current sprint.
- 😀 The Definition of Done ensures that the increment of work is complete and meets quality standards, creating transparency for the team and stakeholders.
- 😀 Scrum emphasizes the importance of regular reflection and adaptation to improve processes, with the Sprint Retrospective being a key event for continuous improvement.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of the Scrum framework?
-The main purpose of Scrum is to help teams generate value for complex problems by providing a lightweight framework that defines roles, events, artifacts, and rules, which bind them together.
Who were the creators of Scrum, and when was it developed?
-Scrum was developed by Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland in the early 1990s.
What are the five core values of Scrum?
-The five core values of Scrum are commitment, focus, openness, respect, and courage.
What is the significance of empiricism and lean thinking in Scrum?
-Empiricism in Scrum emphasizes learning through experience and decision-making based on observation, while lean thinking focuses on reducing waste and maximizing value by focusing on essential activities.
What is the Scrum team's role in maximizing value?
-The Scrum team, especially the Product Owner, is responsible for maximizing the value of the product by prioritizing work in the product backlog and ensuring that each increment delivers value.
How many roles exist in a Scrum team, and what are they?
-There are three roles in a Scrum team: the Product Owner, the Scrum Master, and the Team Members.
What is the purpose of the Sprint in Scrum?
-A Sprint is a fixed-length time-box that serves as a container for all Scrum events. It creates consistency and allows the team to focus on delivering an increment of value within that time period, usually lasting two weeks.
What are the key responsibilities of a Scrum Master?
-The Scrum Master is accountable for establishing and defending the Scrum process, helping the team understand Scrum theory, removing impediments, and ensuring that Scrum events are productive and timely.
What is a Sprint Backlog, and how is it created?
-The Sprint Backlog is a plan for the current Sprint, consisting of the Sprint Goal and the product backlog items selected for the Sprint, along with an actionable plan for delivering them. It is created collaboratively by the team during Sprint Planning.
What is the difference between the Product Backlog and the Sprint Backlog?
-The Product Backlog is an ordered list of everything needed to improve the product, while the Sprint Backlog is a plan for the current Sprint, which includes the product backlog items selected for that Sprint and how they will be completed.
Why is the Sprint Review considered a working session?
-The Sprint Review is a working session because it is designed to inspect the work completed during the Sprint and to collaborate on what actions to take next. It is not just a presentation, but a chance to adapt the product backlog based on stakeholder feedback.
What is the Definition of Done in Scrum?
-The Definition of Done is a formal description of the state of an increment when it meets the required quality measures. It provides transparency and ensures that everyone has a shared understanding of what work is considered complete.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Scrum Essentials in Under 10 Minutes

Inside The Scrum Team - 15-Minute Introduction to Scrum - Free Scrum Course
Scrum Explained in Hindi l Software Engineering and Project Management Course
SCRUM Model in Software Engineering | Agile Technology

What do Scrum Masters do all day? I How to be a Great Scrum Master

SAFe Explained in Five Minutes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)