Menghitung Nilai TPC (SNI 2897:2008)
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the host explains how to calculate the CPC (Colony Per Cubic) value using different dilution cases. The process is based on the 2008 SNI 2897 standards and involves calculating average colony counts across varying dilution levels. The host walks through eight distinct cases, detailing how to handle situations such as colony counts within, below, or above the acceptable range. The video emphasizes proper rounding, calculations with dilution factors, and provides tips for accurate reporting, ensuring the audience gains a clear understanding of CPC calculation in microbiological studies.
Takeaways
- 😀 CPC value calculation depends on the range of colony counts, which should be between 25 and 250.
- 😀 For the first case, the average colony count from valid dilutions is calculated and multiplied by the dilution factor to determine the CPC value.
- 😀 When colony counts fall outside the 25 to 250 range, they are excluded from the calculation (e.g., counts below 25).
- 😀 In cases with multiple dilutions, the average of valid colony counts from all appropriate dilutions is used to calculate the CPC.
- 😀 If all colony counts are below 25, the lowest dilution is used, and the result is marked with a star to indicate it's out of range.
- 😀 For cases with all colony counts above 250, the highest colony counts are averaged, and the result is marked with a star to indicate it is out of range.
- 😀 If some dilutions produce valid results within the range while others don’t, only the valid data is considered for averaging.
- 😀 When all colony counts are zero, the last dilution is used, and the CPC value is noted as less than 100.
- 😀 In case of inconsistent data, such as only one valid dilution, the average is taken from the valid counts and adjusted accordingly.
- 😀 If none of the data falls within the valid range, a specific dilution factor is applied, and the result is reported with a star indicating the out-of-range issue.
Q & A
What is CPC, and why is it important in microbiological testing?
-CPC stands for Colony-Forming Units per mL, which is a measure used in microbiological testing to estimate the number of viable microorganisms in a sample. It helps in assessing the microbial load in liquids and is essential for quality control in various industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and water treatment.
What does SNI 2897:2008 refer to in the context of the script?
-SNI 2897:2008 is the Indonesian National Standard that provides guidelines for microbiological testing, particularly focusing on the calculation of CPC using dilution series and colony counts.
What is the acceptable range for the number of colonies when calculating CPC?
-The acceptable range for the number of colonies is between 25 and 250 colonies, as this is the range within which accurate calculations for CPC can be made.
In Case 1, how is the CPC calculated when the colony counts are within the acceptable range?
-In Case 1, the colony counts from dilutions within the range of 25 to 250 are averaged, and then the CPC is calculated by multiplying the average by the dilution factor. The result is rounded to two significant figures.
What happens if the colony counts fall outside the 25-250 range, as seen in Case 3?
-In Case 3, when the colony counts are below 25, the lowest dilution factor is used, and the CPC is calculated based on that. The result is marked with a star (*) to indicate that it is outside the acceptable range.
How is the CPC adjusted in Case 4 when the colony counts exceed 250?
-In Case 4, when the colony counts exceed 250, the average colony count is taken, and then the CPC is calculated using the dilution factor. The result is also marked with a star (*) to show that it falls outside the acceptable range.
What should be done when no colonies are detected, as shown in Case 6?
-In Case 6, when no colonies are detected, the CPC is calculated by using the lowest dilution factor, and the result is reported as less than 100, with a star (*) to indicate that the result is outside the expected range.
In Case 7, why is the colony count of 278 disregarded when calculating the CPC?
-In Case 7, the colony count of 278 is disregarded because it falls outside the acceptable range. Only the colony counts that fall within the correct range (e.g., 245) are used in the calculation.
What is the significance of the star (*) in the reported CPC values?
-The star (*) indicates that the result is outside the acceptable range for colony counts (either below 25 or above 250), which means that the calculation may not be as reliable or representative of typical microbial concentration.
How is the final CPC value presented when the result is rounded or in scientific notation, as seen in Case 8?
-In Case 8, the final CPC value is rounded to two significant digits, and if necessary, it is expressed in scientific notation (e.g., 2.7 × 10^5). This ensures the result is concise and standardized for reporting.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Acara 3 Perhitungan Standard Plate Count (SPC)

How Adsense CPC works

IGCSE Physics [Syllabus 1.4] Density
5 - Class 12 - Chemistry - Solid State - Calculation of number of atoms per unit cell
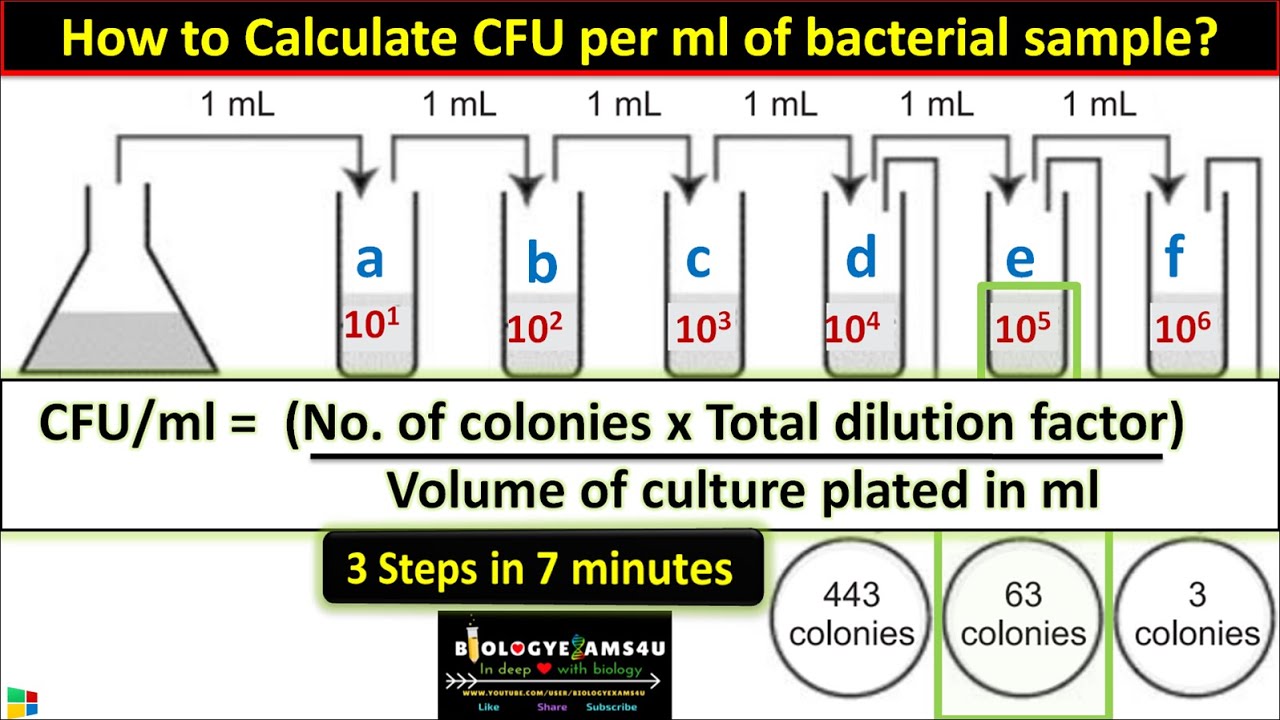
How to Calculate CFU per ml of Bacterial Sample? in 3 Steps || cfu/ml in Microbiology

Advanced Process Control - Minimum flow control for centrifugal pumps
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)