Mengenal Perang Siber dari Jejak Mossad-CIA Lumpuhkan Sistem Nuklir Iran
Summary
TLDRIndonesia's government is considering creating a specialized 'cyber force' within the Indonesian National Armed Forces (TNI) to address growing cyber threats. However, concerns are raised about the lack of legal frameworks and thorough research before proceeding. Experts distinguish between 'cybersecurity' (protecting civilian systems) and 'cyber defense' (countering more severe national security threats like cyber terrorism and espionage). The video explores the evolving nature of cyber warfare, citing the Stuxnet attack on Iranian nuclear facilities as a notable example, and emphasizes the growing risks posed by interconnected global systems.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Indonesian government and military (TNI) are planning to establish a cyber force to address the increasing threat of cyberattacks on national security.
- 😀 Experts argue that there is no current legal framework to support the creation of a cyber defense branch, and further studies are needed to evaluate its necessity and effectiveness.
- 😀 There is a clear distinction between cybersecurity (focused on protecting civilian systems) and cyber defense (focused on military-grade operations such as cyber terrorism and espionage).
- 😀 Cybersecurity deals with incidents like data breaches, hacking, and other attacks on civilian infrastructure, whereas cyber defense handles more severe threats like cyber terrorism and espionage.
- 😀 The Indonesian military already has cyber defense capabilities across all branches (Army, Navy, Air Force), each with dedicated cyber centers to handle digital threats.
- 😀 The Indonesian Ministry of Defense defines cyber warfare as deliberate, coordinated actions to disrupt a nation's sovereignty, including cyberattacks, terrorism, and espionage.
- 😀 Stuxnet, a virus developed by the CIA and Mossad, is a key example of cyber warfare. It was used to sabotage Iran's nuclear program by crippling systems used in uranium enrichment.
- 😀 The Stuxnet attack, launched by the US and Israel, was one of the most significant cyberattacks in history, marking a shift in how nations can use cyber tactics in geopolitical conflicts.
- 😀 Cyber warfare is expected to evolve and expand, particularly as human life becomes increasingly dependent on interconnected digital systems and infrastructure.
- 😀 Nations with advanced technological infrastructure are at higher risk of cyberattacks, which could target critical infrastructure like power grids, communication systems, and transportation networks.
- 😀 As technology advances and digital interconnectivity grows, cyber warfare will likely become an increasingly important tool in international relations and conflict.
Q & A
What is the purpose of Indonesia's government and military planning to establish a cyber branch?
-The primary goal is to strengthen Indonesia's national security by addressing the growing threat of cyberattacks. This division would focus on cyber defense, distinguishing itself from general cybersecurity efforts.
What is the difference between cyber defense and cybersecurity?
-Cybersecurity focuses on protecting civilian digital infrastructure from smaller-scale threats such as hacking and data breaches. In contrast, cyber defense deals with larger, more dangerous threats, such as terrorism, espionage, and attacks on national infrastructure.
Why is the establishment of a cyber branch considered necessary by some, but not by all?
-Some experts, including Wahyudi Jafar, argue that forming a new cyber branch is premature, as there is no clear legal framework for such a division. They suggest that further research and assessment of the current level of cyber threats are needed before creating a separate military branch.
What is the role of Indonesia’s existing military branches in cyber defense?
-Each branch of Indonesia’s military (Army, Navy, and Air Force) already has its own cyber defense unit, and the Indonesian National Military (TNI) also has a central cyber defense unit at its headquarters, Mabes TNI.
How does the Ministry of Defense of Indonesia define cyber warfare?
-According to the Ministry of Defense, cyber warfare includes all coordinated, deliberate actions aimed at disrupting a nation’s sovereignty, which may involve cyberattacks, cyberterrorism, and cyber espionage that threaten national security.
What is the Stuxnet cyberattack, and why is it significant?
-Stuxnet was a sophisticated cyberattack in 2010 aimed at Iran’s nuclear facilities, specifically its uranium-enrichment program. It was developed by the US and Israel as part of Operation Olympic Games and is considered one of the most significant examples of cyber warfare, as it directly targeted critical infrastructure.
Why did the Stuxnet attack surprise many countries, including Iran?
-The attack was unexpected because the method of sabotage was novel, using a computer virus to damage critical industrial equipment. This type of cyberattack was previously unheard of, and its scale and precision stunned both Iran and other nations.
What are the potential consequences of increasing interconnectivity in the digital age?
-As nations and their infrastructures become more digitally connected, they face greater vulnerability to cyberattacks. Key sectors like energy, finance, and urban infrastructure could be targeted, leading to widespread disruptions and potentially devastating consequences.
How do cyberattacks differ from traditional warfare in terms of legal and political implications?
-Cyberattacks can complicate international relations as they lack the clear legal, political, and military frameworks that traditional warfare has. The boundaries between espionage, terrorism, and warfare become blurred, making it difficult to apply established international laws.
What role do advanced technologies and digital connectivity play in modern warfare?
-Advanced technologies and digital connectivity have transformed modern warfare by providing new means of sabotage, espionage, and influence. Cyber capabilities allow countries to target sensitive systems without the need for physical confrontation, creating new vulnerabilities in global security.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Sistem Pertahanan dan Keamanan Negara Indonesia (Sishankamrata) | Pancasila SMA

KASUS KASUS ANCAMAN DI BIDANG IPOLEKSOSBUDHANKAM

TAK SADAR, KITA SEDANG BERADA DI TENGAH WORLD CYBER WAR !! INI YANG SEDANG TERJADI - Mardigu Wowiek
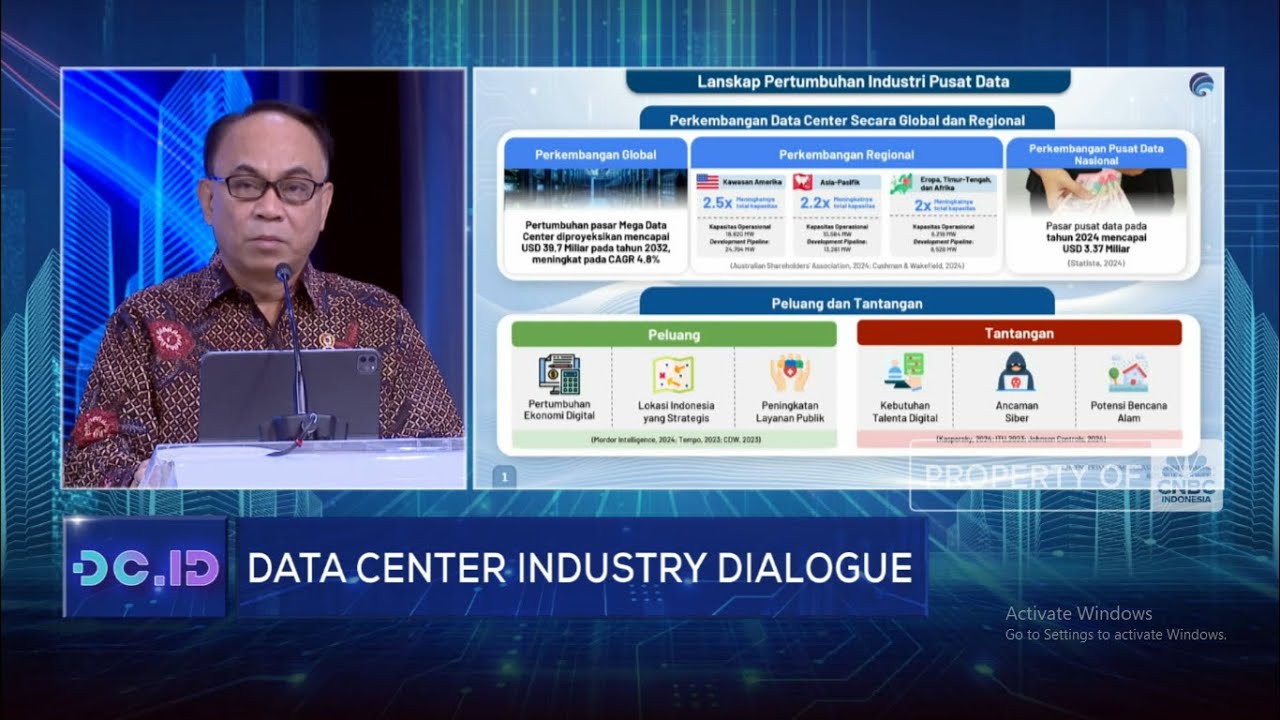
Menkominfo: Bisnis Data Center Beri RI Peluang Cuan USD 3,37 Miliar

Membangun Digital Trust Masyarakat Indonesia dengan IT Governance dan Artificial Intelligence!

Professor Richard Harknett describes the nature of cyber power
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)