Synchronizer Operation Explained
Summary
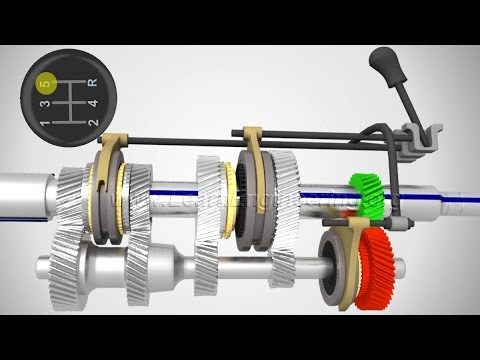
TLDRThis video explains the basic operation of a synchronizer in mechanical systems, highlighting its key tasks: synchronizing the rotational speed of two objects, locking them together, and preventing gear clash. It details the components such as the synchronizer hub, sleeve, speed gear, blocker ring, and synchronizer key. The video demonstrates how the synchronizer sleeve and clutching teeth engage to lock the gear to the shaft, ensuring smooth operation. The blocker ring’s role in synchronization and preventing gear grinding is also covered, showcasing the complex yet essential mechanisms behind smooth gear shifting in transmissions.
Takeaways
- 😀 The synchronizer performs three key tasks: synchronizing rotational speed, mechanically locking two rotating objects, and preventing gear clash when synchronization fails.
- 😀 The synchronizer hub fits onto the shaft via splines, ensuring the hub rotates with the shaft at all times.
- 😀 The synchronizer sleeve slides onto the synchronizer hub through splines and is designed to engage with the speed gear using clutching teeth.
- 😀 The synchronizer sleeve has special features, including a cutout for the synchronizer key and unique teeth designed to prevent gear separation.
- 😀 The free-spinning speed gear has angle-cut teeth (helical cut) for smooth operation and load-carrying ability, while clutching teeth engage the synchronizer sleeve.
- 😀 When the synchronizer sleeve moves toward the speed gear, clutching teeth lock the sleeve to the gear, fixing it to the shaft.
- 😀 The synchronizer blocker ring uses a reverse conical surface to align with the conical face of the speed gear, helping synchronize rotational speed.
- 😀 The blocker ring features a friction surface (e.g., sintered metal or fiber material) that prevents gear grinding when synchronization is not achieved.
- 😀 Synchronizer keys fit into the hub and blocker ring, allowing the synchronizer system to function properly and preventing improper engagement.
- 😀 The animation demonstrates how the synchronizer sleeve, blocker ring, and speed gear work together to synchronize speeds and prevent gear clash.
- 😀 Proper alignment and engagement of the clutching teeth are crucial to ensure the gear does not jump out of place or engage improperly.
Q & A
What are the three basic tasks performed by a synchronizer?
-The three basic tasks of a synchronizer are: (1) to synchronize the rotational speed of two rotating objects, (2) to mechanically lock the two rotating objects together, and (3) to block or prevent the mechanical locking mechanism if synchronization is not possible to avoid gear grinding (also known as gear clash).
How does the synchronizer hub connect to the shaft?
-The synchronizer hub connects to the shaft through splines. The splines in the center of the hub fit into corresponding splines on the shaft, ensuring that the hub rotates with the shaft at all times.
What is the significance of the recessed and raised areas on the synchronizer hub?
-The recessed and raised areas on the synchronizer hub ensure that the hub fits onto the shaft in only one specific orientation. This design helps in aligning the hub properly for correct functionality, preventing it from functioning improperly if mounted the wrong way.
What role does the synchronizer sleeve play in the system?
-The synchronizer sleeve slides onto the synchronizer hub and interacts with the clutching teeth to engage the speed gear. It helps lock the gear to the shaft when properly aligned and prevents gear separation when the clutching teeth are engaged.
How do the clutching teeth on the synchronizer sleeve engage with the speed gear?
-When the synchronizer sleeve moves towards the speed gear, the clutching teeth on both the sleeve and the gear interlock, which locks the sleeve to the gear, thereby locking the gear to the shaft.
What happens when the clutching teeth on the synchronizer sleeve are not properly engaged?
-If the clutching teeth are not properly engaged, the sleeve will not lock correctly with the speed gear. This can lead to jumping out of gear or improper engagement, potentially causing mechanical issues.
What is the function of the synchronizer blocker ring?
-The synchronizer blocker ring works in conjunction with the sleeve and synchronizer keys to synchronize the speed of two rotating objects. If synchronization is not possible, the blocker ring prevents the sleeve from engaging, which helps to avoid gear grinding.
How does the blocker ring synchronize the speed of the rotating objects?
-The blocker ring has a reverse conical surface that fits against the conical surface of the speed gear. This allows the blocker ring to gradually synchronize the speed of the two objects by using friction and clutching teeth before locking the sleeve to the gear.
What is the role of the synchronizer key in the system?
-The synchronizer key fits into the synchronizer hub and helps coordinate the interaction between the synchronizer sleeve, blocker ring, and speed gear. The key ensures proper alignment and function of the system by engaging with specific cutouts in both the sleeve and the blocker ring.
What happens during the synchronization process when the sleeve moves over the speed gear?
-As the sleeve moves over the speed gear, the blocker ring begins to synchronize with the speed gear. Once the speeds of both objects align, the sleeve locks them together, ensuring a smooth and effective engagement without gear clash.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)