TRIGONOMETRI ( PERBANDINGAN TRIGONOMETRI DLM SEGITIGA SIKU SIKU & SUDUT SUDUT ISTIMEWA )
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the presenter provides a comprehensive overview of trigonometric ratios in right triangles, including sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent. The tutorial explains each ratio with examples and practical applications, demonstrating how to find missing sides using the Pythagorean theorem. Special angles like 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90° are also explored, along with a simple method using hand positions to calculate trigonometric values. This video is ideal for students looking to master trigonometry through clear explanations and easy-to-understand examples.
Takeaways
- 😀 Trigonometric ratios relate the sides of a right-angled triangle to its angles, and they are fundamental for solving many geometric problems.
- 😀 In a right-angled triangle, the hypotenuse is opposite the right angle, the opposite side is opposite the angle of interest, and the adjacent side is next to the angle.
- 😀 The primary trigonometric ratios are: sine (sin), cosine (cos), and tangent (tan). Sin is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse, cos is the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse, and tan is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side.
- 😀 There are inverse functions for each of the primary ratios: cosecant (csc), secant (sec), and cotangent (cot), which are the reciprocals of sine, cosine, and tangent, respectively.
- 😀 Special angles like 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90° have well-known and easily memorized trigonometric values, which can be applied directly without a calculator or table.
- 😀 Using the Pythagorean theorem helps calculate missing sides in a right-angled triangle when two sides are known, which is useful for finding specific trigonometric ratios.
- 😀 A practical method for calculating trigonometric ratios for special angles involves using hand positions. Each finger corresponds to a specific angle, and counting fingers helps determine the trigonometric value.
- 😀 When solving trigonometric problems, it's essential to use the correct ratio based on the sides involved, and ensure the angle reference is clear in each case.
- 😀 Understanding how to apply trigonometric ratios in real-world problems, such as calculating unknown sides in a triangle, is a vital skill for geometry and physics.
- 😀 Practice and memorization of trigonometric ratios for key angles can simplify problem-solving and increase accuracy without needing extensive calculations.
Q & A
What is the definition of the hypotenuse in a right triangle?
-The hypotenuse is the side opposite the right angle, and it is the longest side in a right triangle.
How is the sine (sin) of an angle defined in a right triangle?
-The sine of an angle (sin α) is the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle (the 'opposite') to the length of the hypotenuse.
What is the formula for cosine (cos) in a right triangle?
-Cosine (cos α) is the ratio of the length of the adjacent side (the 'side next to' the angle) to the length of the hypotenuse.
What does tangent (tan) represent in a right triangle?
-Tangent (tan α) is the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side (tan α = opposite / adjacent).
What is the reciprocal of sine (cosecant)?
-The reciprocal of sine (cosecant) is defined as 1 divided by sine (csc α = 1 / sin α).
How is secant defined in terms of cosine?
-Secant (sec α) is the reciprocal of cosine (sec α = 1 / cos α).
What is the reciprocal of tangent, called cotangent?
-Cotangent (cot α) is the reciprocal of tangent (cot α = 1 / tan α), which is equivalent to the ratio of the adjacent side to the opposite side.
How can you calculate the length of the missing side of a right triangle when you know the other two sides?
-You can use the Pythagorean theorem, which states that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides (a² + b² = c²).
What is the value of sin 30°?
-The value of sin 30° is 1/2.
How do you calculate the cosine of a 60° angle using a simple method?
-You can use the 'hand method' by counting the number of fingers between the angle (e.g., 60°) and the cosine side. For 60°, this gives a value of 1/2.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Identitas Trigonometri: Identitas Kebalikan, Perbandingan dan Pythagoras - SMA Kelas 10

Trigonometri Matematika Kelas 10 • Part 4: Perbandingan Trigonometri Sudut Istimewa

Trigonometric Ratios (Tagalog Math)
¿Qué son las razones trigonométricas? @MatematicasprofeAlex

ENTENDIENDO realmente QUÉ son SEN, COS y TAN ▶ ¿De DONDE PROVIENEN las RAZONES TRIGONOMÉTRICAS? 📐📖
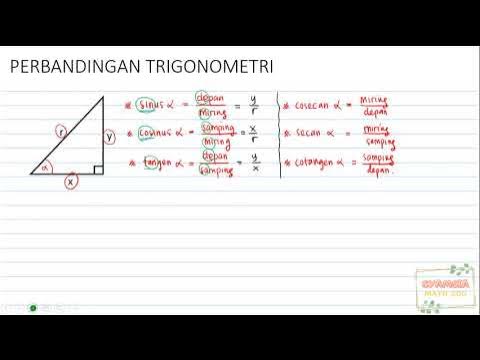
PERBANDINGAN TRIGONOMETRI (PART 1) SINUS, COSINUS, TANGEN, SECAN, COSECAN, COTANGEN
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)