Teknik PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) dalam Manajemen Proyek
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the application of the Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) in project management, focusing on calculating project timelines and determining critical paths. The PERT method involves three key time estimates—optimistic, pessimistic, and realistic—used to calculate expected project durations and variances. Viewers learn to construct network diagrams, perform forward and backward passes, and identify critical paths with zero slack. Practical examples are provided to help viewers apply PERT in real-world project scenarios, emphasizing time management and scheduling efficiency.
Takeaways
- 😀 PERT (Project Evaluation and Review Technique) uses three time estimates for each activity: optimistic (A), pessimistic (B), and realistic (M).
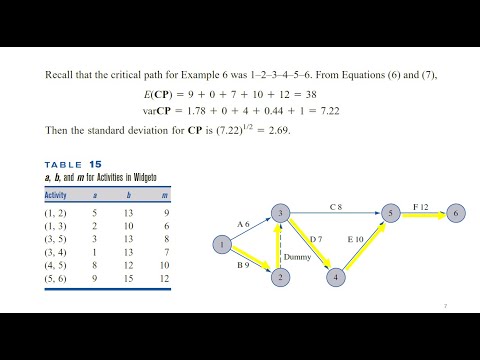
- 😀 The expected time for each activity is calculated using the formula: E = (A + 4M + B) / 6.
- 😀 Variance for each activity is calculated using the formula: V = ((B - A) / 6)^2.
- 😀 Forward Pass helps determine the earliest start and finish times for each activity in the project.
- 😀 Backward Pass is used to calculate the latest start and finish times for activities, helping in identifying slack time.
- 😀 The critical path in the project is the longest path in the network, determining the project's minimum completion time.
- 😀 Slack time refers to the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the overall project.
- 😀 Project network diagrams are crucial in visualizing activity dependencies and scheduling for project management.
- 😀 To find the critical path, activities with zero slack time are identified as crucial for timely project completion.
- 😀 Proper project scheduling requires inputting the calculated expected times and variances into a network diagram to track progress.
- 😀 Project completion time is determined by the latest finish time along the critical path, with no delays allowed in critical activities.
Q & A
What are the three types of time estimates used in the Three-Point Estimation technique?
-The three types of time estimates used in the Three-Point Estimation technique are Optimistic Time (O), Pessimistic Time (P), and Realistic Time (M).
How is the expected time (TE) for an activity calculated?
-The expected time (TE) for an activity is calculated using the formula: TE = (O + 4M + P) / 6, where O is the Optimistic Time, M is the Realistic Time, and P is the Pessimistic Time.
What does variance (V) represent in the context of project management, and how is it calculated?
-Variance (V) represents the uncertainty or variability in the duration of an activity. It is calculated using the formula: V = (P - O)² / 36, where P is the Pessimistic Time and O is the Optimistic Time.
What is the Critical Path in project management?
-The Critical Path is the longest sequence of dependent activities in a project. It determines the minimum project duration, and any delay in the activities on the Critical Path will delay the entire project.
What is the purpose of a network diagram in project management?
-A network diagram is used to visually represent the activities of a project and their dependencies. It helps identify the sequence of tasks, the Critical Path, and allows for better project scheduling and management.
What is the difference between Forward Pass and Backward Pass in scheduling?
-In the Forward Pass, you calculate the earliest start and finish times for each activity by moving from the start of the project towards the end. In the Backward Pass, you calculate the latest start and finish times by moving from the end of the project backwards.
What does Slack Time indicate in project management?
-Slack Time indicates the amount of time an activity can be delayed without affecting the overall project deadline. Activities on the Critical Path have zero slack time, meaning any delay will impact the project's duration.
Why is it important to identify the Critical Path in a project?
-Identifying the Critical Path is important because it allows project managers to focus on tasks that directly impact the project’s duration. Delays in these tasks must be avoided to ensure the project is completed on time.
How can slack time affect project scheduling?
-Slack time allows for some flexibility in scheduling non-critical activities. These activities can be delayed within the available slack time without delaying the overall project, which can help in resource allocation and task prioritization.
What steps should be taken after calculating the expected time and variance for activities?
-After calculating the expected time and variance for each activity, you should construct a network diagram to represent the project tasks and dependencies, identify the Critical Path, calculate the total project duration, and determine slack time for non-critical tasks.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)