Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
Summary
TLDRThis transcript explains the Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) and its differences from the Critical Path Method (CPM) in project management. PERT addresses uncertainties by modeling activity durations as random variables with optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely estimates. The script covers how to calculate expected durations, variances, and standard deviations, and emphasizes the use of normal distribution to predict the likelihood of a project finishing within a specific time. It provides a step-by-step guide for solving related problems, focusing on calculating critical paths, variances, and probabilities for project completion.
Takeaways
- 😀 PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) is used to model uncertain project durations, unlike CPM (Critical Path Method) which assumes fixed durations for activities.
- 😀 In PERT, each activity has three time estimates: Optimistic (A), Most Likely (M), and Pessimistic (B). These estimates help model uncertainty in project scheduling.
- 😀 The expected duration of an activity in PERT is calculated as: E = (A + 4M + B) / 6, with A being the optimistic time, M the most likely time, and B the pessimistic time.
- 😀 Variance in PERT is calculated using the formula: Variance = (B - A)^2 / 36, which helps quantify the uncertainty in the activity durations.
- 😀 CPM is useful for projects where the durations are deterministic, but it may not be realistic for projects with uncertain timelines, which is why PERT is introduced.
- 😀 The critical path in a project, calculated using CPM, can be analyzed in PERT for probabilistic duration and variability, using the expected duration and variance of each activity.
- 😀 In PERT, the durations of activities on the critical path are treated as random variables and the overall duration follows a normal distribution, making it possible to calculate the probability of completing the project within a specific timeframe.
- 😀 The standard deviation (σ) of the project duration is the square root of the total variance of the critical path. This is used to calculate the probability that the project will finish within a certain period.
- 😀 Z-scores are used to calculate probabilities in PERT. The Z-score formula is: Z = (X - μ) / σ, where X is the target time, μ is the mean (expected duration), and σ is the standard deviation.
- 😀 An example calculation showed how to determine the probability of completing a project in 35 days using the normal distribution, with a calculated Z-score of -1.12 corresponding to a 13.14% chance of finishing the project within that timeframe.
Q & A
What is the primary difference between PERT and CPM in project management?
-The primary difference is that PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) models activity durations as random variables and accounts for uncertainty, whereas CPM (Critical Path Method) assumes that the duration of each activity is known with certainty.
What does the acronym PERT stand for?
-PERT stands for Program Evaluation and Review Technique.
In the PERT model, what are the three categories of duration estimates for an activity?
-The three categories are: Optimistic (a), Pessimistic (b), and Most Likely (m).
How is the expected duration of an activity in PERT calculated?
-The expected duration is calculated using the formula: (a + 4m + b) / 6, where 'a' is the optimistic duration, 'b' is the pessimistic duration, and 'm' is the most likely duration.
What is the purpose of using random variables in the PERT model?
-Using random variables allows PERT to model the uncertainty in the duration of activities, acknowledging that actual project durations may vary due to unforeseen factors.
What distribution does PERT assume for modeling activity durations?
-PERT assumes that the duration of each activity follows a Beta distribution.
How is variance in PERT calculated?
-Variance is calculated using the formula: ((b - a)^2) / 36, where 'b' is the pessimistic duration and 'a' is the optimistic duration.
What role does the Central Limit Theorem play in PERT?
-The Central Limit Theorem allows PERT to assume that the total duration of the critical path (CP) follows a normal distribution, even if individual activities' durations are modeled using a Beta distribution.
What is the purpose of calculating the Z-score in PERT analysis?
-The Z-score is used to standardize the total duration of the critical path to a normal distribution, allowing the calculation of probabilities, such as the likelihood of finishing the project within a specific timeframe.
How is the probability of completing a project within a given time determined using PERT?
-The probability is determined by calculating the Z-score for the critical path duration and then using standard normal distribution tables to find the corresponding cumulative probability.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Network Charts: What's the Difference between PERT and CPM?

KULIAH ONLINE PROJECT MANAGEMENT PERT CPM

Teknik PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) dalam Manajemen Proyek

Tools and Techniques of Project Management
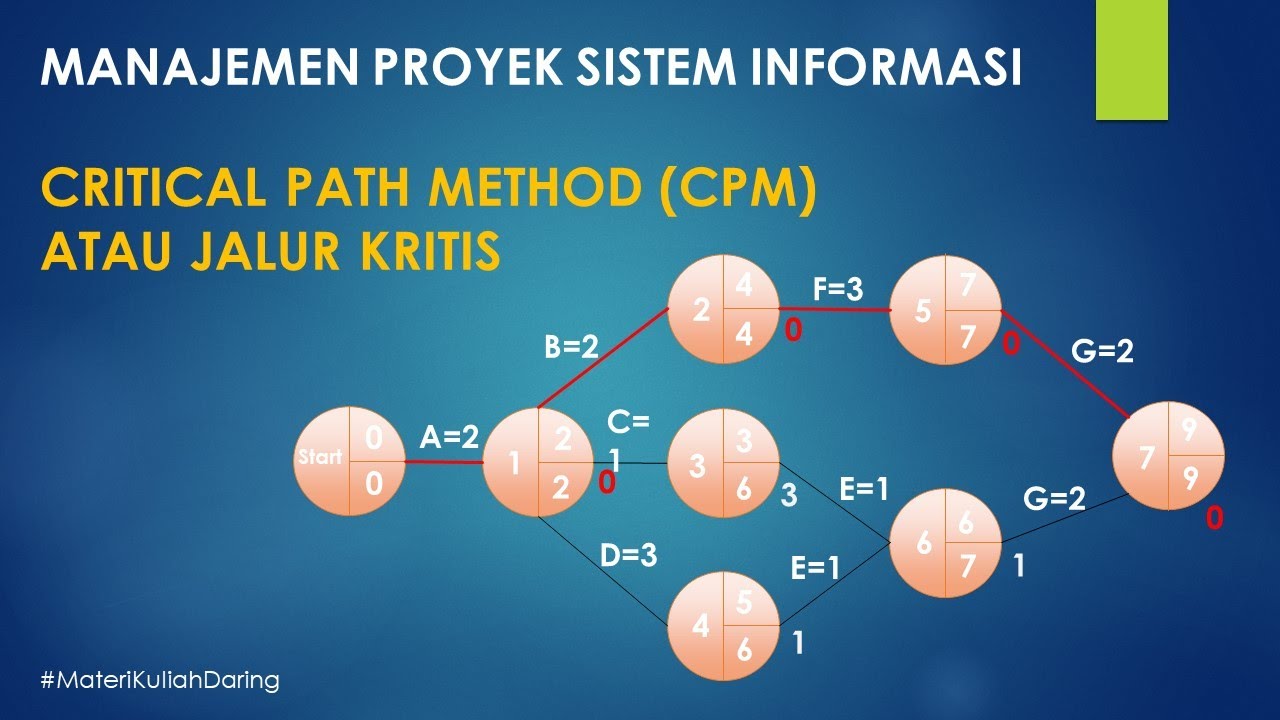
Critical Path Method (CPM) Atau Jalur Kritis Dalam Manajemen Proyek | Manajemen Proyek SI | GIS

Akbar Adhi Utama: Project Management (Part 2)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)