Physiology of Lipoproteins Cholesterol
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the role of lipoproteins in the body, focusing on the four main types: chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL, and HDL. It details how each type of lipoprotein functions in transporting fats and cholesterol, with an emphasis on their respective compositions and health implications. Chylomicrons deliver dietary fats, VLDL transports triglycerides, LDL carries cholesterol to tissues (often linked to heart disease when elevated), and HDL removes excess cholesterol, earning its 'good' reputation. The video also covers the use of statins to lower cholesterol and balance lipoproteins for better cardiovascular health.
Takeaways
- 😀 Lipoproteins are molecules that transport fats (lipids) and proteins in the body, playing a vital role in cholesterol metabolism.
- 😀 There are four main types of lipoproteins: Chylomicrons, VLDL (Very Low-Density Lipoproteins), LDL (Low-Density Lipoproteins), and HDL (High-Density Lipoproteins).
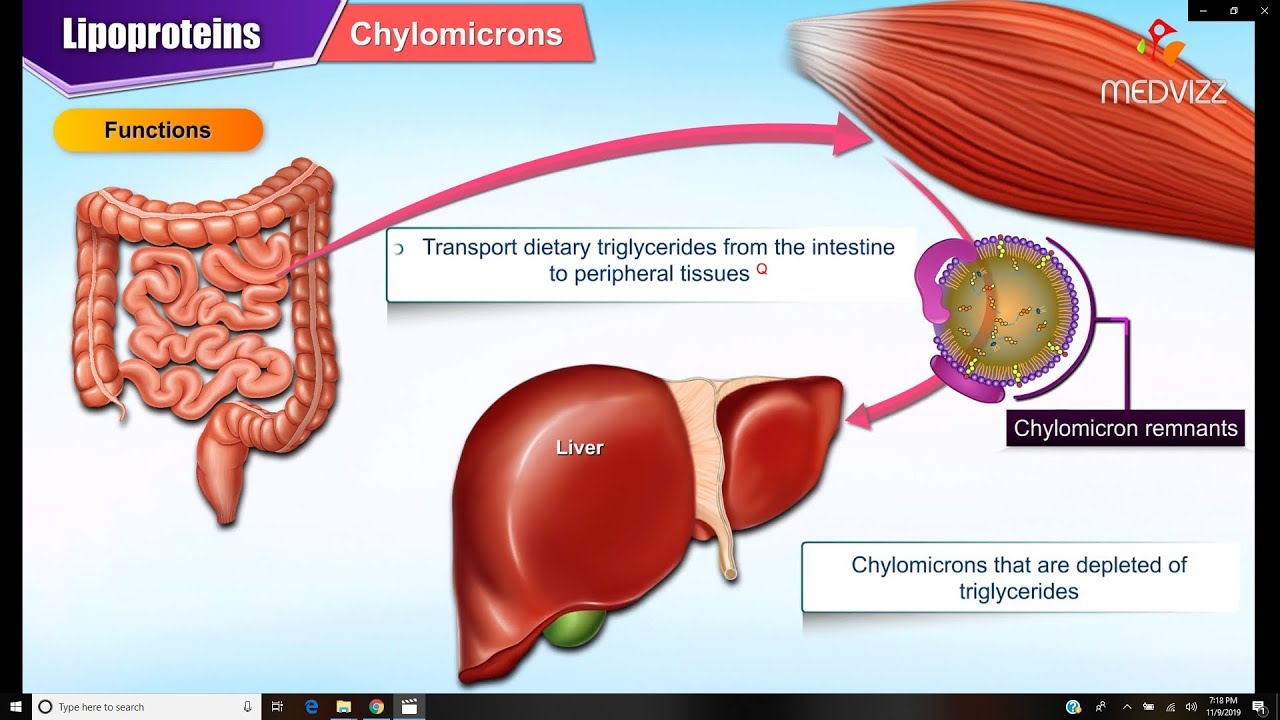
- 😀 Chylomicrons are the largest lipoproteins, primarily made of lipids and responsible for transporting dietary fats from the small intestine to body tissues.
- 😀 VLDL is produced by the liver and transports triglycerides to tissues that need them for energy or storage.
- 😀 LDL is often called 'bad cholesterol' because it carries cholesterol to tissues, and high levels can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing cardiovascular risk.
- 😀 HDL is known as 'good cholesterol' because it helps remove excess cholesterol from tissues and returns it to the liver for excretion or recycling.
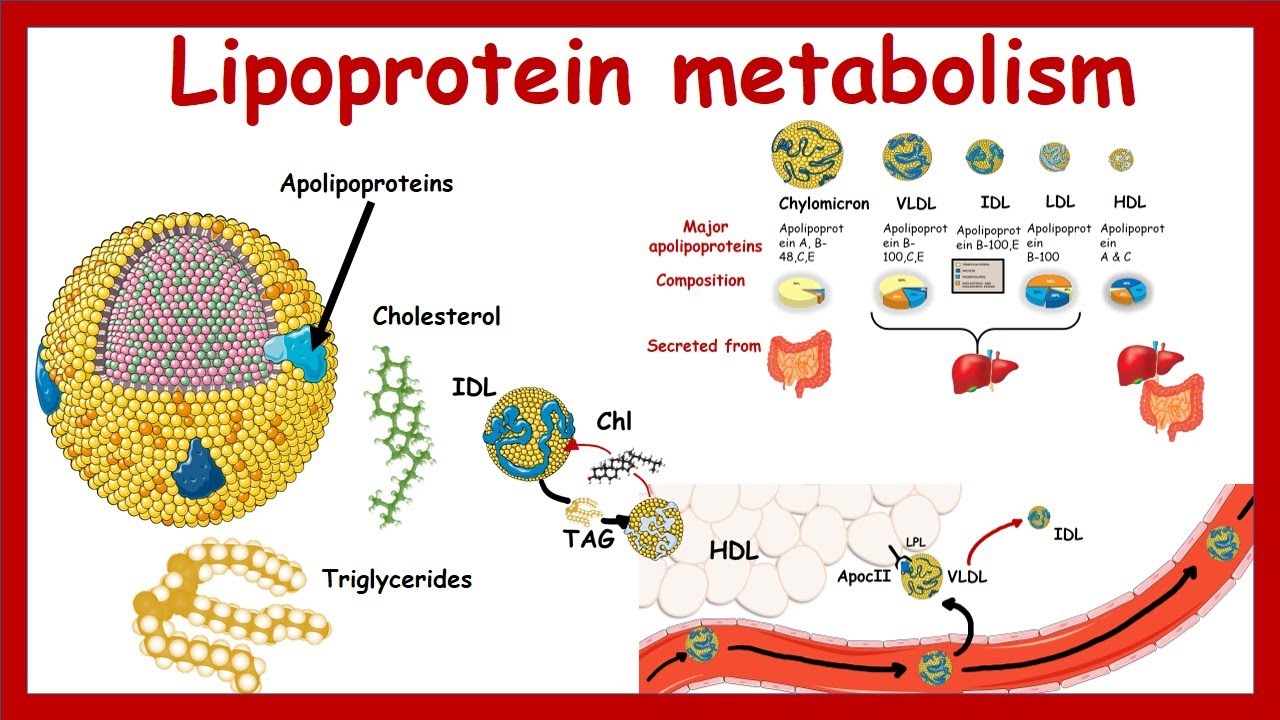
- 😀 Lipoproteins differ in their protein-to-lipid ratio: Chylomicrons are mostly lipids, VLDL and LDL have varying lipid content, and HDL has an equal ratio of proteins to lipids.
- 😀 Cholesterol is synthesized in the liver from glucose, with HMG-CoA reductase playing a key role in its production. This enzyme is the target of cholesterol-lowering drugs like statins.
- 😀 Maintaining a balance between lipoproteins is crucial for heart health—while LDL delivers cholesterol to cells, excess levels contribute to heart disease risk, whereas HDL protects by removing cholesterol.
- 😀 Statins, which inhibit HMG-CoA reductase, help lower cholesterol production in the liver, contributing to improved cardiovascular health by reducing cholesterol levels.
Q & A
What are lipoproteins and what role do they play in the body?
-Lipoproteins are complexes made of fats (lipids) and proteins. They are essential for transporting lipids, such as cholesterol and triglycerides, through the bloodstream to various tissues in the body, where they are either used for energy, stored, or processed further.
What are the four main types of lipoproteins mentioned in the video?
-The four main types of lipoproteins are chylomicrons, VLDL (Very Low-Density Lipoproteins), LDL (Low-Density Lipoproteins), and HDL (High-Density Lipoproteins).
What is the composition of chylomicrons and how are they formed?
-Chylomicrons are composed mostly of lipids (fats) with very little protein. They are formed in the intestinal cells after dietary fats (lipid droplets) are absorbed and processed. These fats are then packaged with proteins, forming chylomicrons, which are absorbed into the lymphatic system before entering the bloodstream.
What is the primary function of chylomicrons?
-Chylomicrons primarily transport dietary fats, specifically triglycerides, from the small intestine to the body’s tissues for energy or storage.
How are VLDL lipoproteins different from chylomicrons?
-VLDL lipoproteins are produced by the liver and mainly transport triglycerides to tissues for energy or storage. They contain more triglycerides and less protein compared to chylomicrons, which primarily transport dietary fats absorbed by the intestine.
What happens to VLDL in circulation?
-In circulation, VLDL is broken down by lipases, which release fatty acids to tissues. This process transforms VLDL into intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL), which can further convert into LDL.
What is the role of LDL in the body, and why is it considered 'bad cholesterol'?
-LDL's main role is to deliver cholesterol to body tissues, which use it to build cell membranes and produce hormones. It is considered 'bad cholesterol' because high levels of LDL can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, contributing to heart disease.
How does the body process excess cholesterol from LDL?
-Excess cholesterol from LDL is taken back to the liver by binding to LDL receptors on liver cells. Once in the liver, it can be recycled to create more lipoproteins or excreted through bile.
What is the function of HDL and why is it considered 'good cholesterol'?
-HDL is responsible for removing excess cholesterol from tissues and returning it to the liver for processing or excretion. It is considered 'good cholesterol' because it helps prevent cholesterol buildup in the arteries, reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
What is the difference between HDL and LDL in terms of their lipid content?
-HDL has a higher protein content and lower lipid content compared to LDL, which is rich in cholesterol and carries more lipids. HDL helps to remove cholesterol from tissues, whereas LDL transports cholesterol to tissues.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Konsep Dasar Lipid(Lemak) : Kolesterol, Trigliserida, Fosfolipid

Tiga Jalur Metabolisme Lipid dalam Tubuh

Kimia Klinik: Analisis Lipid dan Lipoprotein
Lipoproteins and Apolipoproteins - Structure , function and metabolism : Medical Biochemistry
Lipoprotein metabolism and transport | Chylomicron, VLDL,IDL, LDL,HDL | Metabolism | Biochemistry

LIPOPROTEÍNAS - QUILOMÍCRONS, VLDL, LDL E HDL
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)