Introduction to Fourier Transform CTFT/FT (Continuous Time Fourier Transform)
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the concept of the Fourier Transform for continuous, non-periodic signals, explaining its analysis and synthesis equations. It highlights the process of converting a time-domain signal into its corresponding frequency-domain representation. Key concepts such as linearity, time-shift, scaling, and frequency-domain properties like differentiation, convolution, and modulation are explored. The video also touches on the conditions for the existence of the Fourier Transform and special theorems such as duality and passive theorems. Overall, the content provides a foundational understanding of Fourier Transforms and their applications in signal analysis.
Please replace the link and try again.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of this video?
-The video focuses on explaining the Fourier Transform, specifically how it is applied to continuous-time, non-periodic signals, and how it relates to the frequency domain.
What is the difference between continuous-time and discrete-time signals in the context of Fourier Transform?
-Continuous-time signals are defined for all values of time (T), whereas discrete-time signals are defined only at discrete intervals (n). The Fourier Transform discussed in the video applies to continuous-time, non-periodic signals.
What is the role of the Fourier Transform in signal analysis?
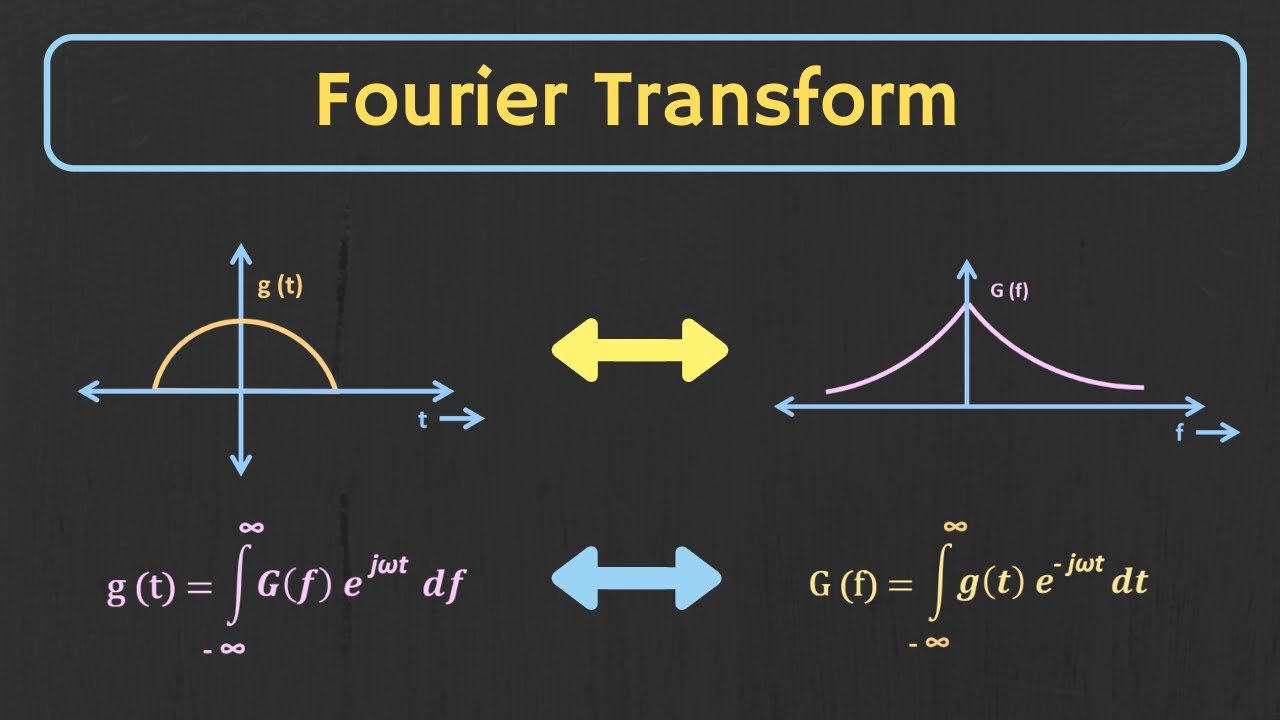
-The Fourier Transform converts a time-domain signal (X(t)) into its corresponding frequency-domain representation (X(jω)), allowing us to analyze the signal in terms of its frequency components.
What are the two key equations mentioned in the video for Fourier Transform?
-The two key equations are: 1) the analysis equation, which converts a time-domain signal to its frequency-domain counterpart using a complex exponential, and 2) the synthesis equation, which reconstructs the time-domain signal from its frequency-domain representation.
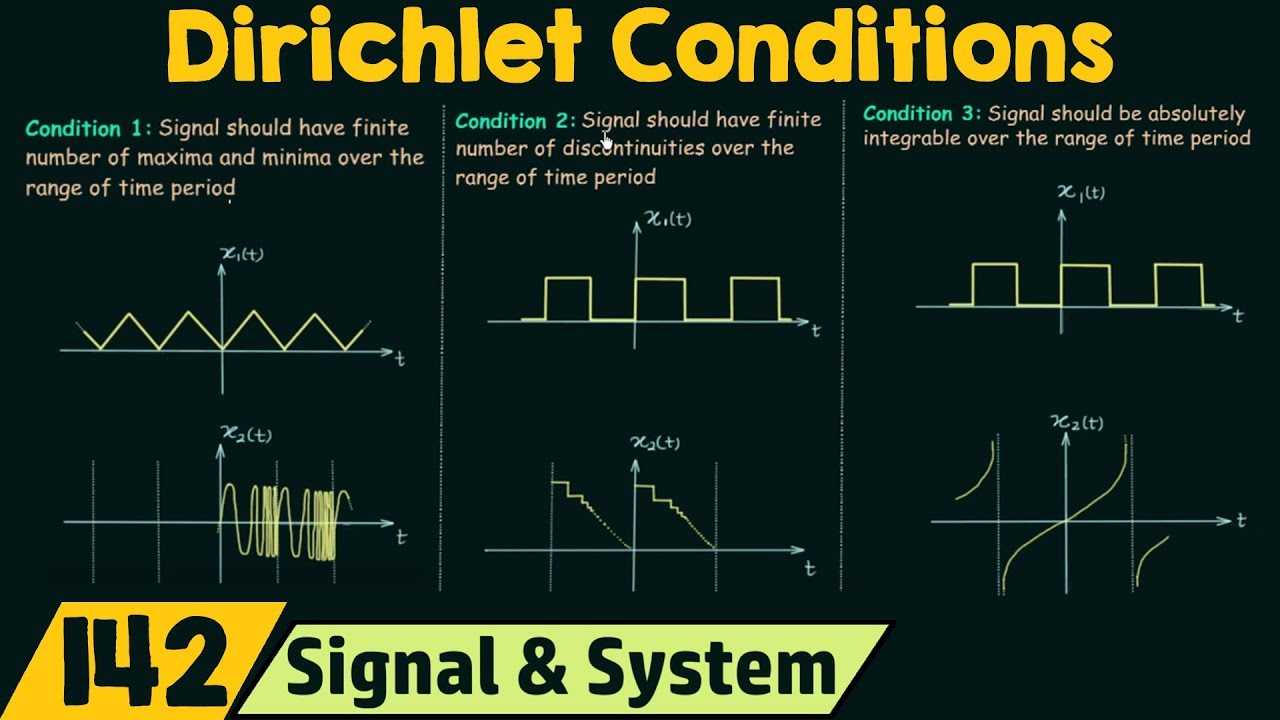
What is the significance of the 'Direct Criteria' for the existence of the Fourier Transform?
-The 'Direct Criteria' states that for the Fourier Transform of a continuous-time signal to exist, the integral of the absolute value of the signal over all time must be finite, ensuring that the signal is absolutely integrable.
What does the modulus of the Fourier Transform represent?
-The modulus of the Fourier Transform represents the magnitude of the frequency-domain signal, providing information about the strength of various frequency components in the original time-domain signal.
How does the time-shifting property of the Fourier Transform work?
-The time-shifting property states that if a time-domain signal is shifted by a certain amount, the resulting frequency-domain signal will be multiplied by a complex exponential. This shift affects the phase but not the magnitude of the frequency components.
What is the convolution theorem and how does it relate to the Fourier Transform?
-The convolution theorem states that convolution in the time domain corresponds to multiplication in the frequency domain. This makes it easier to analyze complex signals by working in the frequency domain, where multiplication is simpler than convolution.
What is the modulation property of the Fourier Transform?
-The modulation property states that multiplying a time-domain signal by a complex exponential results in convolution in the frequency domain. This is the inverse of the convolution theorem.
What is the Duality property in the context of Fourier Transforms?
-The Duality property is a special theorem that applies to continuous-time Fourier Transforms, and it states that many results in Fourier analysis have a dual or mirrored counterpart, making it a useful tool in solving problems.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)