Teori Humanistik
Summary
TLDRThis video explores humanistic learning theory, emphasizing the importance of fulfilling students' basic needs as outlined in Maslow's hierarchy. The theory suggests that education should focus on motivating students and nurturing their full potential. It highlights five levels of needs: physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization. In the classroom, teachers can apply this theory by rewarding achievements, reducing pressure, providing opportunities for skill development, and offering supportive learning resources. The goal is to create a conducive environment where students can thrive emotionally and academically.
Takeaways
- 😀 Humanistic learning theory emphasizes the process of 'humanizing' individuals, helping them develop their full potential in a supportive environment.
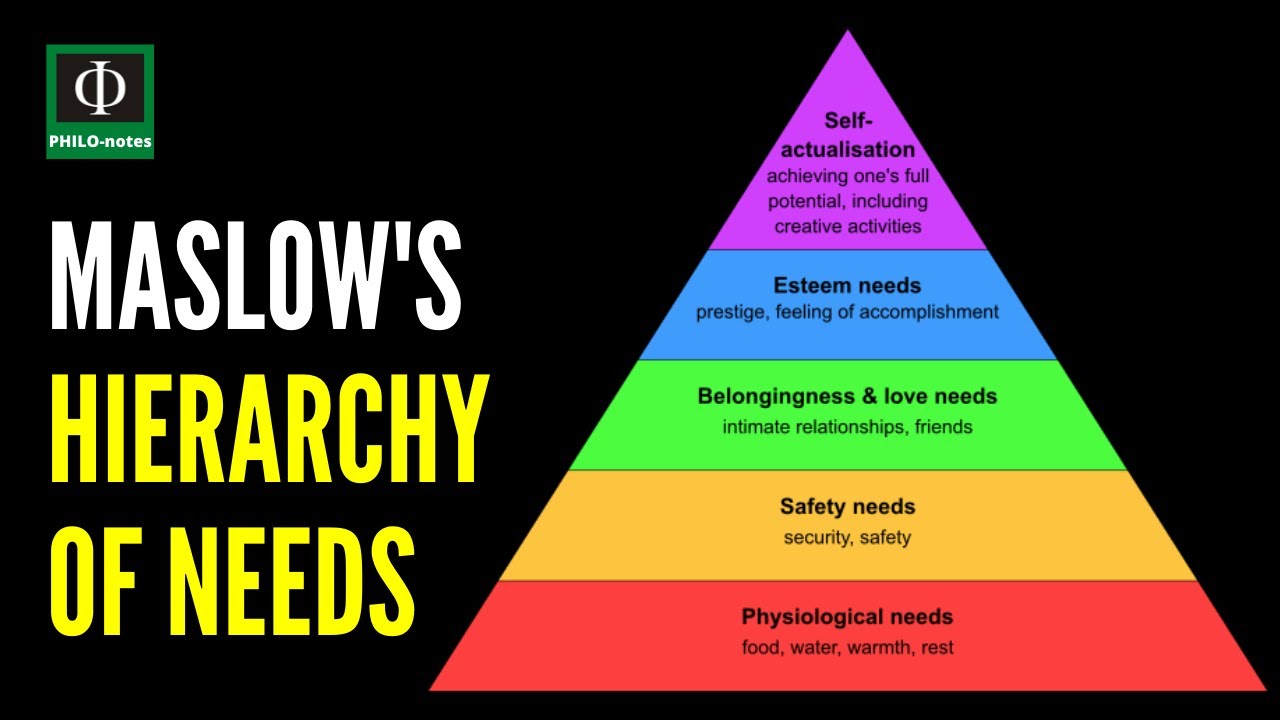
- 😀 Maslow's hierarchy of needs is central to humanistic learning theory, proposing that basic needs must be met before higher needs can motivate behavior.
- 😀 The five levels of Maslow's hierarchy are physiological needs, safety needs, social needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization.
- 😀 Physiological needs are the most basic and must be fulfilled first; if unmet, individuals cannot focus on higher needs.
- 😀 Safety needs, which include both physical and emotional security, must be met for individuals to feel comfortable enough to engage in learning.
- 😀 Social needs emphasize the importance of relationships, such as love, affection, and belonging, for effective learning.
- 😀 Esteem needs involve seeking respect, reputation, and acknowledgment for achievements, which motivate individuals to continue learning.
- 😀 Self-actualization is the highest need, involving the realization of one’s full potential, personal growth, and alignment with one's interests and talents.
- 😀 According to Rogers, the learning environment must be supportive and facilitate self-actualization by allowing individuals to explore their potential.
- 😀 Teachers can apply humanistic principles in the classroom by rewarding students, reducing stress, offering opportunities for growth, and providing diverse learning resources.
Q & A
What is humanistic learning theory?
-Humanistic learning theory focuses on 'humanizing' individuals, helping them realize and develop their potential. It emphasizes motivation and personal growth, with the aim of achieving self-actualization.
How does Maslow's hierarchy of needs relate to humanistic learning theory?
-Maslow's hierarchy of needs provides a framework for understanding how individuals prioritize their needs. According to the theory, lower-level needs like physiological and safety needs must be met before individuals can focus on higher-level needs such as self-esteem and self-actualization, which are central to humanistic learning.
What are the five levels of needs in Maslow's hierarchy?
-The five levels in Maslow's hierarchy are: 1) Physiological needs (basic survival), 2) Safety needs (security), 3) Social needs (belonging and affection), 4) Esteem needs (respect and accomplishment), and 5) Self-actualization (personal growth and fulfillment).
Why is it important for basic physiological needs to be met in humanistic learning?
-Basic physiological needs must be met first because they are fundamental for survival. If these needs are unmet, individuals cannot focus on higher needs like safety, social belonging, or personal growth.
How can teachers apply humanistic learning theory in the classroom?
-Teachers can apply humanistic learning theory by rewarding students for their achievements, creating a safe and supportive learning environment, allowing students to explore and develop their potential, and acting as facilitators of learning.
What role does motivation play in humanistic learning theory?
-Motivation is a key element in humanistic learning theory. It encourages students to reach their full potential by satisfying their intrinsic needs, such as the need for self-esteem and self-actualization, which ultimately fosters a love for learning.
How does the environment affect the learning process in humanistic theory?
-In humanistic theory, the learning environment is crucial. A supportive, safe, and nurturing environment helps students feel secure and confident, which facilitates personal growth and learning.
What is the teacher's role in a humanistic classroom?
-In a humanistic classroom, the teacher acts as a facilitator. The teacher creates an environment where students feel safe, valued, and motivated to explore their potential, rather than just providing information.
What are the benefits of providing rewards in the classroom according to humanistic theory?
-Providing rewards can enhance students' motivation and encourage positive behavior, helping them feel recognized for their efforts and success. This, in turn, boosts their engagement and willingness to learn.
What is the importance of self-actualization in humanistic learning theory?
-Self-actualization is the highest level of Maslow's hierarchy, representing the desire to realize one's full potential. In humanistic learning, it encourages students to develop their talents, creativity, and abilities to the fullest, fostering a sense of accomplishment and personal growth.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)