mgt201 short lectures || mgt201 guess paper || mgt201 module 5
Summary
TLDRThis transcript offers an in-depth explanation of key financial analysis tools, focusing on liquidity, profitability, and solvency ratios. It covers essential topics such as benchmarking, debt-equity ratios, and market comparisons. The script highlights the significance of these financial metrics in evaluating a company's performance, stability, and growth potential. It also emphasizes the importance of analyzing financial statements to gain insights into a company’s operational efficiency, financial health, and its ability to meet short-term and long-term obligations. Practical examples of ratio calculations and their real-world applications are also discussed.
Takeaways
- 😀 Profitability ratios measure a company's ability to generate profit, with key metrics like gross, operating, and net profit.
- 😀 Liquidity ratios help assess a company's ability to meet short-term obligations, using metrics like current assets vs. current liabilities.
- 😀 Solvency ratios focus on a company’s long-term financial health, such as the debt-to-equity ratio, which indicates the company’s financial leverage.
- 😀 Common-size analysis compares financial statements in percentage terms, making it easier to analyze performance across time and companies.
- 😀 Benchmarking involves comparing a company's performance with industry standards or key competitors to assess its relative strength.
- 😀 Market analysis gauges a company’s position in the market and its financial health relative to market leaders, such as GlaxoSmithKline in the pharmaceutical sector.
- 😀 Working capital is an important metric that indicates a company's short-term financial health and operational efficiency.
- 😀 Credit and inventory turnover ratios are used to analyze how quickly a company converts its assets (like inventory and receivables) into cash.
- 😀 Risk analysis evaluates the likelihood of negative events (like adverse market conditions) impacting the company’s financial performance.
- 😀 Financial ratios, when analyzed correctly, can offer insights into a company's overall performance, liquidity, and solvency, helping stakeholders make informed decisions.
Q & A
What is the purpose of financial ratio analysis in business?
-Financial ratio analysis is used to evaluate various aspects of a company's financial performance. It helps reveal insights into profitability, liquidity, efficiency, and solvency, allowing businesses to compare their performance with competitors or industry standards.
What does the liquidity ratio measure?
-The liquidity ratio measures a company's ability to cover its short-term liabilities with its short-term assets. It provides an indication of the company's financial health in the short term.
How are profitability ratios calculated and what do they indicate?
-Profitability ratios, such as gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin, are calculated by dividing profit figures by revenue. They show how effectively a company is generating profit from its sales, operational efficiency, and overall financial health.
What is the significance of solvency ratios in financial analysis?
-Solvency ratios, like the debt-to-equity ratio, measure a company's ability to meet its long-term obligations. These ratios are crucial in assessing the financial stability and long-term viability of a business.
What is benchmarking in the context of financial analysis?
-Benchmarking involves comparing a company's financial performance to that of industry leaders, competitors, or established standards. It helps identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
What are common-size financial statements, and how are they useful?
-Common-size financial statements express each line item as a percentage of a base value, such as total revenue or total assets. This allows for easier comparison between companies of different sizes or for tracking performance over time.
How does the current ratio relate to liquidity?
-The current ratio is a key liquidity metric calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities. It indicates whether a company has enough short-term assets to cover its short-term obligations, with a standard ratio typically between 1.5 and 2.
What is the difference between gross profit, operating profit, and net profit?
-Gross profit represents the revenue left after subtracting the cost of goods sold. Operating profit accounts for operating expenses like rent and salaries. Net profit is the final profit after all expenses, taxes, and interest are deducted from total revenue.
What role does the debt-to-equity ratio play in assessing solvency?
-The debt-to-equity ratio compares a company's total debt to its shareholders' equity. It indicates the proportion of a company's financing that comes from debt versus equity, helping assess the company's financial leverage and risk.
Why is it important to understand the relationship between financial ratios and business strategy?
-Understanding financial ratios is critical for business strategy as they help managers, investors, and creditors assess the company's financial health, operational efficiency, and potential risks. These insights are vital for making informed decisions on investments, credit, and business direction.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Rasio Keuangan, PPT Rasio Keuangan

Ratio Analysis (Introduction) | A-Level, IB & BTEC Business
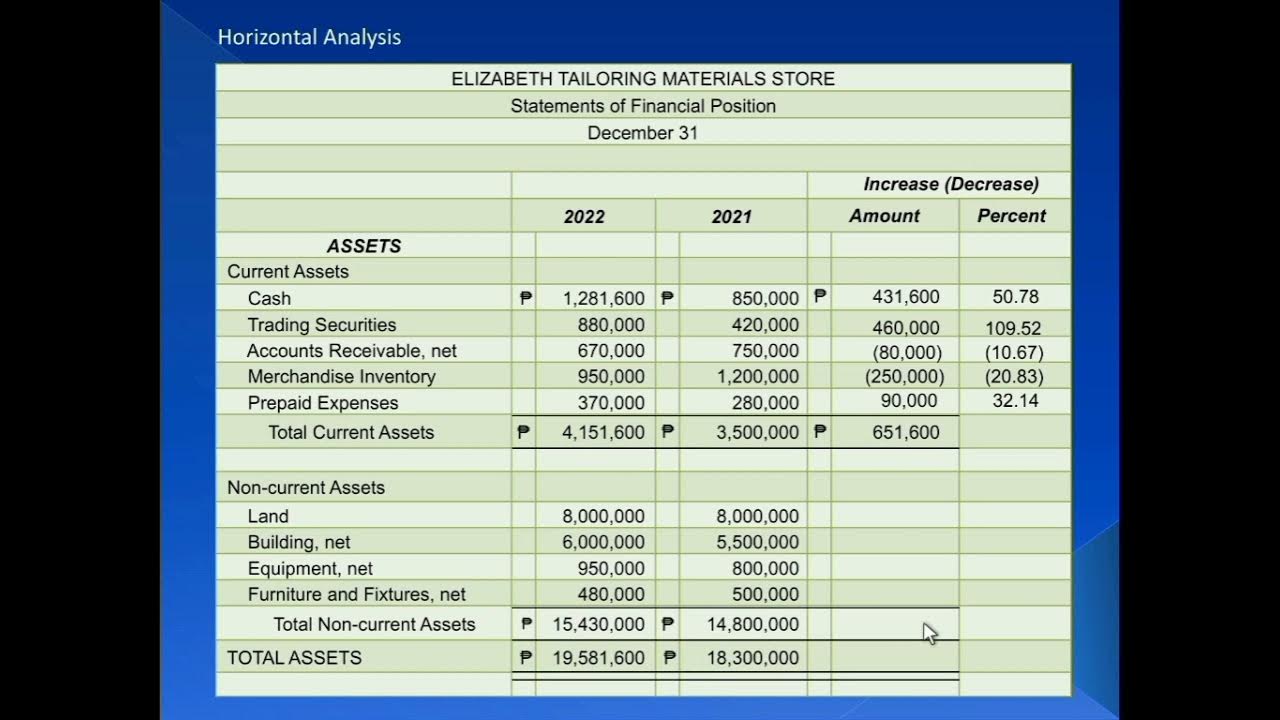
Part 1: Financial Statements Analysis (Intro, Horizontal Analysis and Vertical Analysis)

11 Financial Analyst Interview Questions - Concepts to Practical Implications | Conceptual Interview

How to Analyze Financial Statements For a Corporation. 4 Types of Financial Analyses

Rasio-rasio Penting dalam Laporan Keuangan | feat. Brenda Andrina
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)