[1.5] Interference of waves
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the phenomenon of wave interference, focusing on how two coherent waves interact when they meet. It introduces concepts such as constructive and destructive interference, demonstrating how waves can reinforce or cancel each other. Through the principle of superposition, the resultant displacement is the sum of the individual wave displacements. The video also covers how to study wave interference in a ripple tank experiment, explaining terms like coherent sources, antinodes, and nodal lines. The role of wavelength and distance between sources in the interference pattern is also highlighted.
Takeaways
- 😀 Interference occurs when two or more waves meet and interact with each other, either reinforcing or canceling each other.
- 😀 Coherent sources of waves maintain the same frequency and a constant phase difference.
- 😀 In a ripple tank experiment, when water waves from two coherent sources meet, they overlap to create a uniform pattern of ripples.
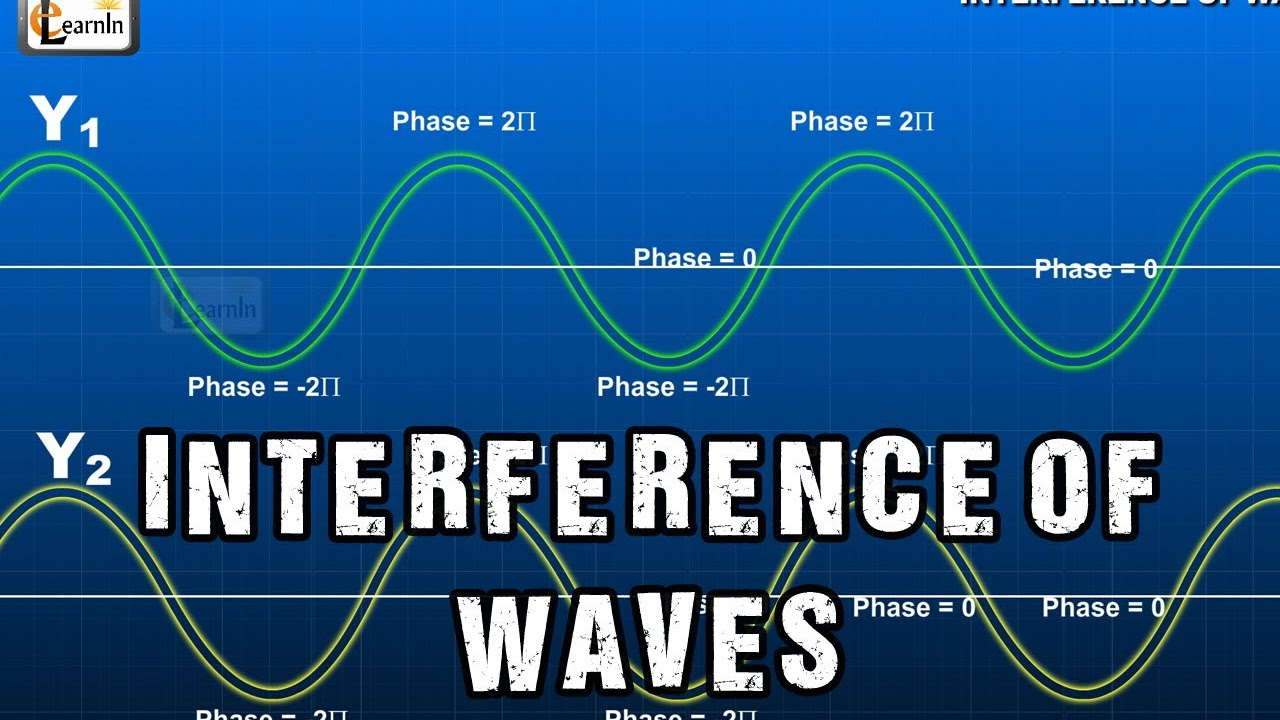
- 😀 The phenomenon of interference occurs due to the principle of superposition, which states that the resultant displacement is the sum of individual displacements of the waves.
- 😀 Wave interference can occur when two waves traveling in opposite directions meet and interact with each other.
- 😀 There are two types of interference: constructive interference (waves amplify each other) and destructive interference (waves cancel each other out).
- 😀 Constructive interference happens when the crests of one wave overlap with the crests of another wave, resulting in a wave with a greater amplitude.
- 😀 Destructive interference occurs when the crest of one wave overlaps the trough of another, canceling out the waves to produce zero amplitude.
- 😀 The interference pattern in a ripple tank can be studied through nodal and antinodal lines, representing points of destructive and constructive interference, respectively.
- 😀 The distance between two successive antinodal or nodal lines depends on the wavelength and the separation between the two coherent sources.
Q & A
What is interference in the context of wave behavior?
-Interference is the phenomenon where two or more waves meet and interact with each other. The waves can reinforce or cancel each other, depending on their relative phases and amplitudes.
What are coherent sources of waves?
-Coherent sources are waves that have the same frequency and a constant phase difference. This consistency is important for producing stable interference patterns.
How does the interference pattern appear in a ripple tank experiment?
-In a ripple tank, coherent sources produce uniform patterns of ripples that can be observed when the waves meet and overlap. The resulting pattern shows alternating regions of constructive and destructive interference.
What is superposition in wave theory?
-The principle of superposition states that the resultant displacement at any point where two waves cross is the sum of the displacements of the individual waves.
What are the two types of interference, and how do they differ?
-The two types of interference are constructive and destructive. Constructive interference occurs when the crests of two waves overlap, resulting in a larger wave. Destructive interference occurs when the crest of one wave overlaps the trough of another, leading to cancellation and a wave with zero amplitude.
What happens during constructive interference?
-In constructive interference, the crests (highest points) of one wave align with the crests of another wave, resulting in a wave with a greater amplitude.
What happens during destructive interference?
-In destructive interference, the crests of one wave align with the troughs (lowest points) of another wave, leading to cancellation and a wave with zero amplitude.
What role do Spill Dippers play in the Ripple Tank experiment?
-Spill Dippers are used to generate coherent sources of waves in the Ripple Tank experiment. They create waves that produce interference patterns when they meet and overlap.
What are antinodal and nodal lines in the context of interference patterns?
-Antinodal lines consist of points where maximum displacement occurs (maximum crest or trough), while nodal lines consist of points where there is zero displacement (destructive interference).
How is the distance between successive antinodal or nodal lines determined?
-The distance between successive antinodal or nodal lines depends on the wavelength of the waves, the separation between the two coherent sources, and the perpendicular distance from the sources to the measurement position.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Intro to wave superposition

Ripple Tank, showing superposition, constructive and destructive interference.

Il fenomeno dell'interferenza

Wave Interference | Arbor Scientific

Fenômenos ondulatórios - reflexão, refração, difração, interferência e ressonância
Interference of Waves | Superposition and Interference in light and water waves | Physics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)