Espectro Eletromagnético | ciências 9º ano
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the teacher introduces electromagnetic waves, explaining how they transfer energy through vibrations. Using relatable examples like sound and sunlight, the teacher highlights the concept of wave frequency and wavelength. The video explains the electromagnetic spectrum, covering various types of waves such as gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet, visible light, infrared, microwaves, and radio waves. The teacher emphasizes the relationship between wave length and frequency, showing how these waves are applied in everyday technologies like X-rays, microwaves, and Wi-Fi. The session aims to simplify complex concepts for students, encouraging practice and engagement.
Takeaways
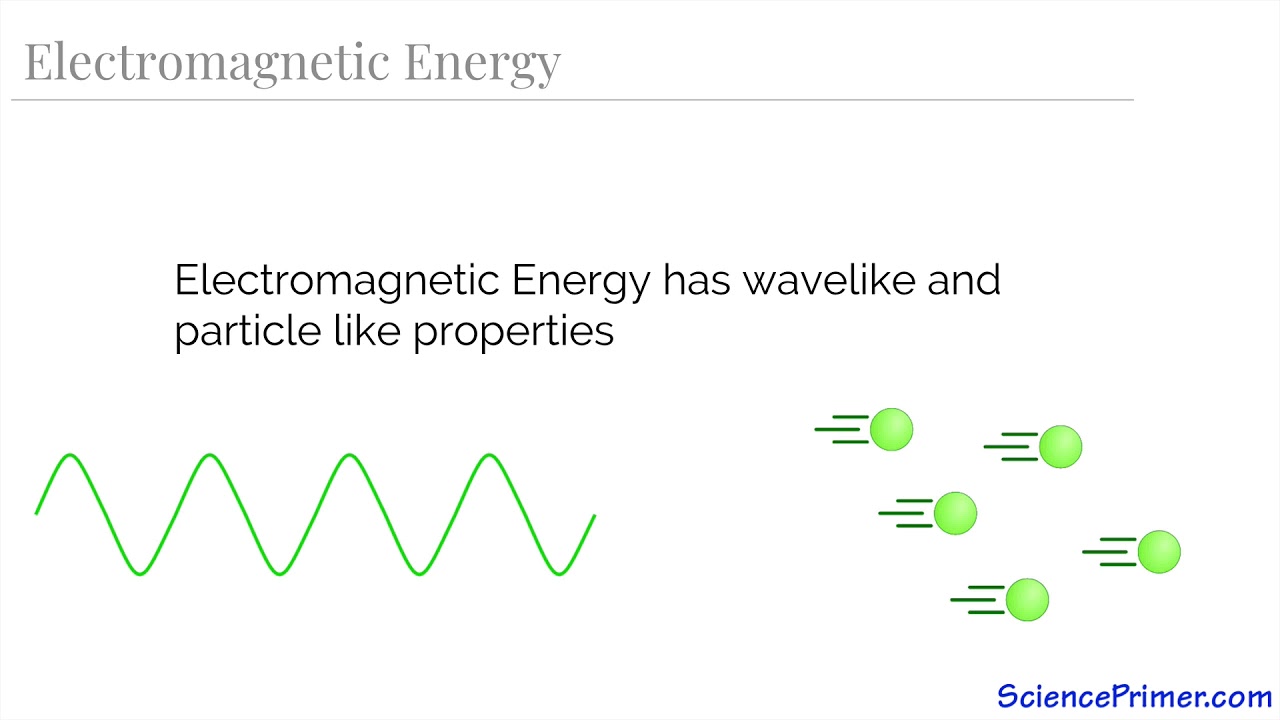
- 😀 A wave is a vibration that transfers energy as it propagates. It can carry energy without the need for matter to move along with it.
- 😀 Sound is an example of a wave. While we can't see sound, it carries energy from the source to our ears, where it's interpreted by the brain as sound.
- 😀 Sunlight is another example of a wave. The light from the sun carries energy, which we perceive as heat.
- 😀 Waves can be classified based on their wavelength (λ) and frequency. Wavelength is the distance between repeating parts of a wave, and frequency is how often the wave repeats in a given time.
- 😀 Longer wavelength waves have lower frequencies, while shorter wavelength waves have higher frequencies.
- 😀 The electromagnetic spectrum includes all types of electromagnetic waves, ranging from high-frequency gamma rays to low-frequency radio waves.
- 😀 Gamma rays have the smallest wavelengths and the highest frequencies, while radio waves have the largest wavelengths and the lowest frequencies.
- 😀 X-rays are useful in medical imaging because they can pass through soft tissues but are absorbed by bones.
- 😀 Ultraviolet (UV) rays are responsible for tanning and sunburns, but they're not visible to the human eye.
- 😀 Infrared (IR) waves are associated with heat. They are detected by thermal cameras and are also used in technologies like remote controls.
- 😀 Microwaves are used in communications, including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, and also for heating food in microwave ovens.
- 😀 Radio waves are used for transmitting signals in radio and television broadcasts.
Q & A
What is an electromagnetic wave?
-An electromagnetic wave is a vibration that transfers energy as it propagates through space.
How is sound related to waves?
-Sound is a type of wave that carries energy from its source to your ear. It cannot be seen, but it is captured by your ear and interpreted by your brain as sound.
How does sunlight relate to electromagnetic waves?
-Sunlight is an electromagnetic wave that propagates through space from the Sun to the Earth, carrying energy that we perceive as heat.
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency?
-Wavelength and frequency are inversely related. A longer wavelength corresponds to a lower frequency, and a shorter wavelength corresponds to a higher frequency.
What are the characteristics of a wave with a shorter wavelength?
-A wave with a shorter wavelength has a higher frequency and vibrates more times per second.
What does the electromagnetic spectrum represent?
-The electromagnetic spectrum represents the range of all possible electromagnetic waves, classified by their wavelength and frequency.
What types of waves are found at the beginning of the electromagnetic spectrum?
-At the beginning of the electromagnetic spectrum are gamma rays, which have the shortest wavelengths and the highest frequencies.
How are X-rays and ultraviolet rays used in daily life?
-X-rays are used in medical imaging, such as detecting bone fractures, while ultraviolet rays are involved in processes like sterilization and are part of the sunlight we receive.
Why do different electromagnetic waves have different applications?
-Different electromagnetic waves have different wavelengths and frequencies, which allow them to interact with matter in various ways, making them suitable for specific applications like medical imaging or communication (e.g., microwaves for cell phones and Wi-Fi).
How can the concept of wavelength and frequency help us understand the electromagnetic spectrum?
-By understanding wavelength and frequency, we can categorize electromagnetic waves and understand how their energy levels and applications differ across the spectrum. Longer wavelengths have less energy, while shorter wavelengths have more energy.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

getaran dan gelombang

SCIENCE 10 (Quarter 2-Module 1): DIFFERENT FORMS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES

THE NATURE OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES TAGALOG | GRADE 10 SCIENCE QUARTER 2 MODULE 1 LESSON 1

Lesson 1: Introduction to Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic Energy

Gelombang Fisika Kelas 11 • Part 1: Definisi, Jenis dan Sifat-Sifat Dasar Gelombang
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)