Lesson 1: Introduction to Electromagnetic Waves
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Marian Soriano introduces students to electromagnetic waves (EM waves), explaining how they differ from mechanical waves by not requiring a medium to transfer energy. The video covers the formation of EM waves, their characteristics like amplitude, wavelength, and frequency, and the wave equation. It also explores the electromagnetic spectrum, distinguishing between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, and concludes with an activity to reinforce learning.
Takeaways
- 📱 Electromagnetic waves (EM waves) are used in various technologies such as smartphones, radios, and microwave ovens.
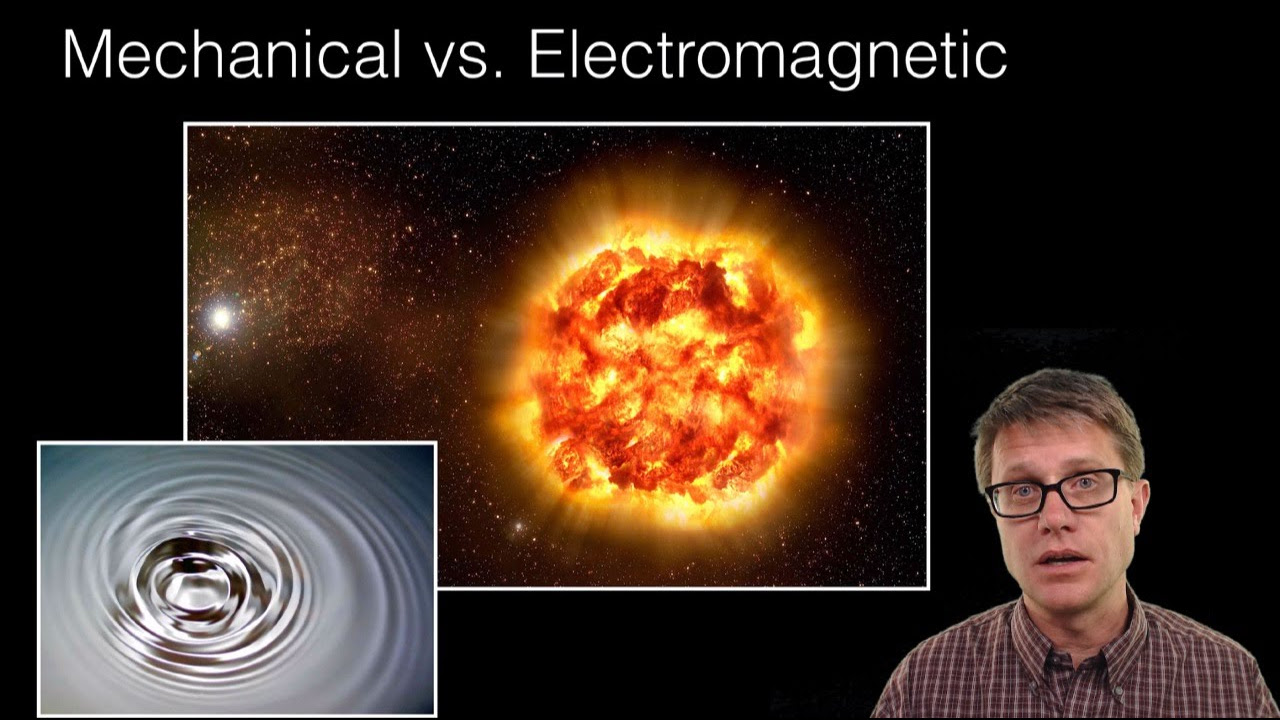
- 🌊 EM waves differ from mechanical waves as they do not require a medium to propagate and can travel through a vacuum.
- 🌀 EM waves are formed by the interaction of electric and magnetic fields, which are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of energy transfer.
- 🔢 The speed of EM waves in a vacuum is a constant, approximately 3 x 10^8 meters per second.
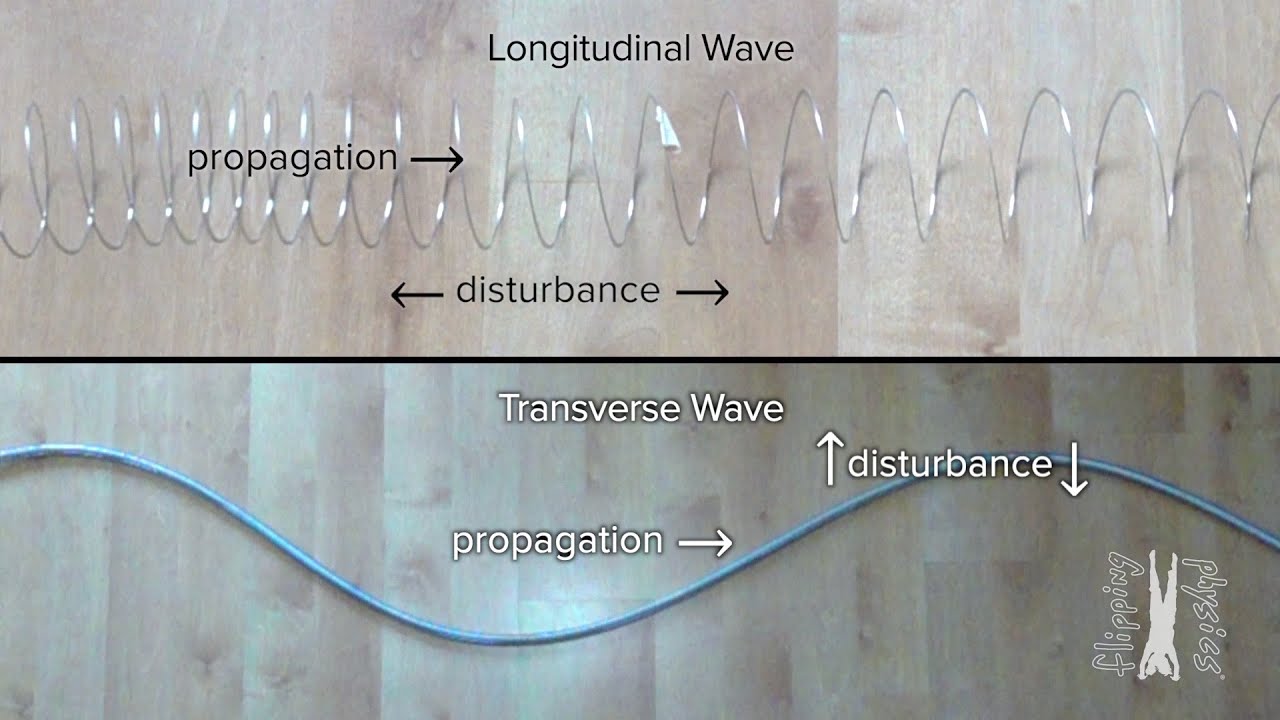
- 🌊 EM waves are transverse waves, with characteristics like amplitude, wavelength, and frequency.
- 📊 Wavelength and frequency are inversely related; as one increases, the other decreases.
- 🔗 The wave equation for EM waves is wave speed = frequency × wavelength.
- 🌈 The electromagnetic spectrum includes a range of EM waves from radio waves to gamma rays, each with different frequencies and wavelengths.
- ⚡ Non-ionizing EM waves like radio waves and visible light have lower energy, while ionizing waves like X-rays and gamma rays have higher energy and are more dangerous.
- 🎨 The energy of photons in EM waves increases with frequency, with gamma rays having the highest energy and shortest wavelength.
Q & A
What are electromagnetic waves?
-Electromagnetic waves, or EM waves, are temporary disturbances that transfer energy from one place to another without requiring a medium. They can travel through air, solid materials, and even a vacuum.
How do electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves?
-Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium to propagate, unlike mechanical waves which need a medium like solid, liquid, gas, or plasma to travel through.
What happens when an electric field comes in contact with a magnetic field?
-When an electric field comes in contact with a magnetic field, it forms electromagnetic waves. A changing magnetic field induces an electric field, and vice versa, creating these waves.
What is the constant speed at which electromagnetic waves travel in a vacuum?
-Electromagnetic waves travel at a constant speed of approximately 3 times 10 to the power of 8 meters per second in a vacuum.
What are the characteristics of electromagnetic waves?
-Characteristics of EM waves include amplitude, wavelength, and frequency. Amplitude is the height of a wave, wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs, and frequency is the number of waves passing a point in a certain time.
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency in electromagnetic waves?
-There is an inverse relationship between wavelength and frequency in electromagnetic waves. As one increases, the other decreases.
How can you calculate the frequency of an electromagnetic wave if you know its wavelength?
-You can calculate the frequency of an electromagnetic wave using the wave equation: frequency = speed of light / wavelength.
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
-The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuum that includes all types of electromagnetic waves arranged according to their frequency and wavelength, ranging from radio waves to gamma rays.
What is the difference between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation?
-Non-ionizing radiation, such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, and ultraviolet, does not have enough energy to cause ionization. Ionizing radiation, such as gamma rays and X-rays, has enough energy to ionize atoms and is more dangerous to humans.
How are different types of electromagnetic waves defined?
-Different types of electromagnetic waves are defined by the amount of energy found in their photons. The energy is directly proportional to the frequency of the wave.
What is the order of colors in the visible light spectrum from lowest to highest frequency?
-The order of colors in the visible light spectrum from lowest to highest frequency is red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)