12 Organ Systems | Roles & functions | Easy science lesson
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an overview of the 12 major systems in the human body and their functions. It covers the integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, circulatory, respiratory, digestive, excretory, urinary, reproductive, endocrine, and immune systems. Each system plays a crucial role, from protecting the body and supporting movement to regulating hormones and fighting infections. Understanding these systems helps to comprehend how the body works together to maintain health and function.
Takeaways
- 😀 The human body has 12 major systems that work together to form an organism.
- 😀 Similar cells form tissues, tissues form organs, organs form systems, and systems work together to maintain life.
- 😀 The integumentary system includes skin, hair, nails, and glands, and serves as a barrier to protect the body.
- 😀 The skeletal system consists of bones that support the body, protect internal organs, and produce blood cells in the bone marrow.
- 😀 The muscular system, made up of skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles, facilitates body movement and helps circulate blood.
- 😀 The nervous system includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, enabling electrical impulses to control body functions.
- 😀 The circulatory system, with the heart and blood vessels, transports blood and waste products throughout the body.
- 😀 The respiratory system provides oxygen to the bloodstream and removes carbon dioxide via automatic processes.
- 😀 The digestive system processes food for energy, involving organs such as the mouth, stomach, pancreas, and intestines.
- 😀 The excretory or urinary system filters blood and removes waste through the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
- 😀 The reproductive system facilitates fertilization, differing between males and females.
- 😀 The endocrine system regulates body processes by distributing hormones through various glands.
- 😀 The immune system, or lymphatic system, detects and fights infections using white blood cells.
Q & A
What are the 12 systems in the human body?
-The 12 systems in the human body are: integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, circulatory, respiratory, digestive, excretory (urinary), reproductive, endocrine, and immune systems.
How do similar cells contribute to the formation of tissues?
-Similar cells group together to form tissues, which are the basic building blocks of organs. Different tissues combine to form organs, and multiple organs work together to form systems in the body.
What is the role of the integumentary system?
-The integumentary system, made up of the skin, hair, nails, and glands, serves as the body's outer protective layer. It regulates the passage of substances in and out of the body and helps maintain homeostasis.
What is the function of the skeletal system?
-The skeletal system provides support and structure to the body, protects vital organs, stores minerals, and produces blood cells in the bone marrow.
What are the three types of muscles in the muscular system?
-The three types of muscles in the body are skeletal muscles, cardiac muscles, and smooth muscles. Each type has a unique role in movement and body functions.
How does the nervous system communicate throughout the body?
-The nervous system communicates through electrical impulses that are sent by the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system) to the rest of the body via nerves (peripheral nervous system), enabling movement and reactions.
What are the main components of the circulatory system?
-The circulatory system consists of the heart and blood vessels, which work together to transport blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients and removing waste products.
How does the respiratory system help in gas exchange?
-The respiratory system facilitates gas exchange by bringing oxygen into the bloodstream during inhalation and releasing carbon dioxide when we exhale. This process is automatic and part of the autonomic nervous system.
What happens to food in the digestive system?
-In the digestive system, food is broken down into smaller substances so the body can absorb nutrients and use them for energy. The food passes through various organs such as the mouth, stomach, pancreas, liver, and intestines.
What is the function of the urinary (renal) system?
-The urinary system filters blood to remove waste and excess fluids, producing urine. This process is carried out by the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Human Organ Systems Anatomy | 10 Systems in Human Body 3D Animation Video
Anatomical Organization of the Human Body From atoms and molecules to the entire organism as a whole

Cells and tissues: types and characteristics - Human histology | Kenhub
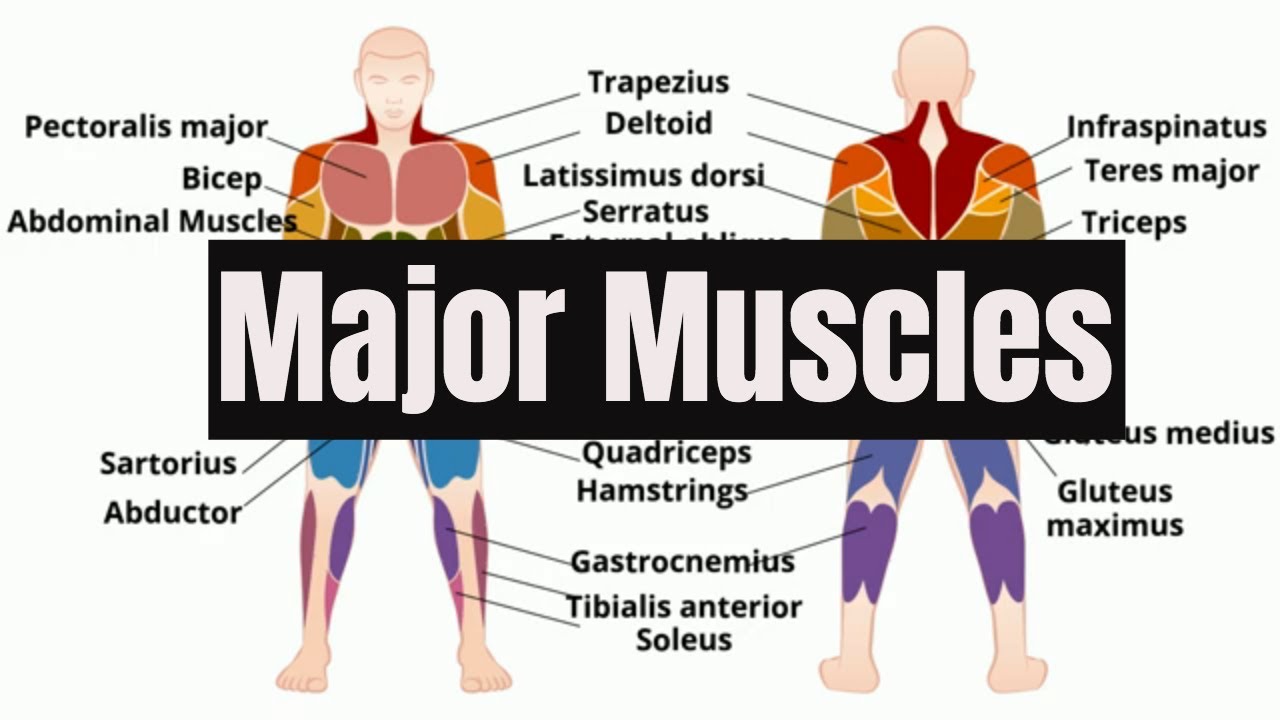
Major Muscles of the Human Body

Human Body Systems Overview (Updated 2024)

Komponen Darah | Sistem Peredaran Darah Pada Manusia
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)