Conjunto R de los Números Reales. Teoría de Conjuntos
Summary
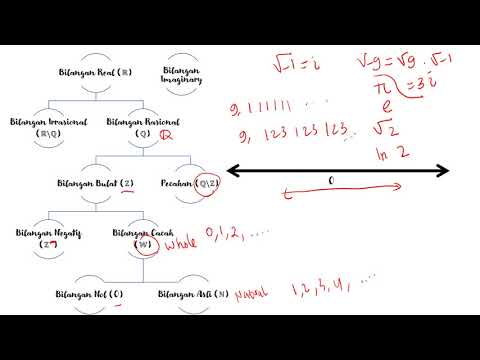
TLDRIn this video, the math teacher explains the concept of real numbers by breaking down its subsets. The lesson begins with natural numbers (N), which are whole numbers greater than zero. It then covers integers (Z), which include both positive and negative whole numbers, and zero. The teacher introduces rational numbers (Q), which can be expressed as fractions of integers, and explains that they include natural and integer numbers. The video concludes with irrational numbers, like pi and the square root of 2, which have non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansions. Finally, it connects rational and irrational numbers to form the set of real numbers.
Q & A
What are natural numbers?
-Natural numbers are numbers that do not have a decimal part and are greater than 0. They are the basic counting numbers.
What is the difference between natural numbers and integers?
-Integers include not only natural numbers but also negative numbers and zero. Natural numbers are a subset of integers.
What does the symbol 'Z' represent?
-'Z' represents the set of integers, which includes positive numbers, negative numbers, and zero.
What are rational numbers?
-Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as the ratio of two integers, where the denominator is not zero.
What is the symbol used to denote rational numbers?
-The set of rational numbers is denoted by the letter 'Q'.
Are natural numbers a subset of rational numbers?
-Yes, natural numbers are a subset of rational numbers because they can be expressed as the ratio of themselves to 1.
What are irrational numbers?
-Irrational numbers cannot be expressed as fractions. They have infinite, non-repeating decimal expansions.
What is the difference between rational and irrational numbers based on their decimal representation?
-Rational numbers have either finite or repeating decimal expansions, while irrational numbers have non-repeating, infinite decimal expansions.
Can you give examples of irrational numbers?
-Some examples of irrational numbers include the square root of 2, pi, and the golden ratio.
What does the set of real numbers consist of?
-The set of real numbers consists of both rational and irrational numbers. It includes all numbers that can be represented on the number line.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

EQUAÇÃO DO 1º GRAU COM DISTRIBUTIVA \Prof. Gis/

NÚMEROS QUADRADOS PERFEITOS |COMO SABER SE UM NÚMERO É PERFEITO| Matemática - 6º ano \Prof. Gis/

CONJUNTOS DOS NÚMEROS REAIS | APRENDA RÁPIDO!

Operasi Hitung Bilangan Cacah | MTK Fase C Level 6 | Kurikulum Merdeka
3.1 Bilangan Real (Pendahuluan)

🔴 HABILIDADE 1. SOMA e SUBTRAÇÃO entre inteiros
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)