Probability vs non probability
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the concept of sampling in research is explored, focusing on two main types: probability and nonprobability sampling. Probability sampling ensures every individual in the target population has an equal chance of being selected, making it more representative and less biased. In contrast, nonprobability sampling lacks a defined sampling frame and doesn't give all individuals an equal chance, often used in behavioral research. The video explains the strengths and challenges of each method and outlines different sampling strategies, including random, systematic, and cluster sampling, with a follow-up on specific techniques like stratified and quota sampling.
Takeaways
- 😀 Probability sampling ensures that every individual in the target population has an equal chance of being selected as a respondent.
- 😀 A sampling frame is necessary for probability sampling, which is a list of all members of the population being studied.
- 😀 The key characteristic of probability sampling is random selection, which reduces bias and provides more representative samples.
- 😀 Non-probability sampling does not give all individuals in the population an equal chance of being selected, which can introduce bias.
- 😀 Non-probability sampling is often used when the researcher does not know the size or structure of the population.
- 😀 Probability sampling is considered more reliable because it results in samples that are more representative of the population.
- 😀 A major challenge with probability sampling is the need for detailed knowledge about the population and its characteristics.
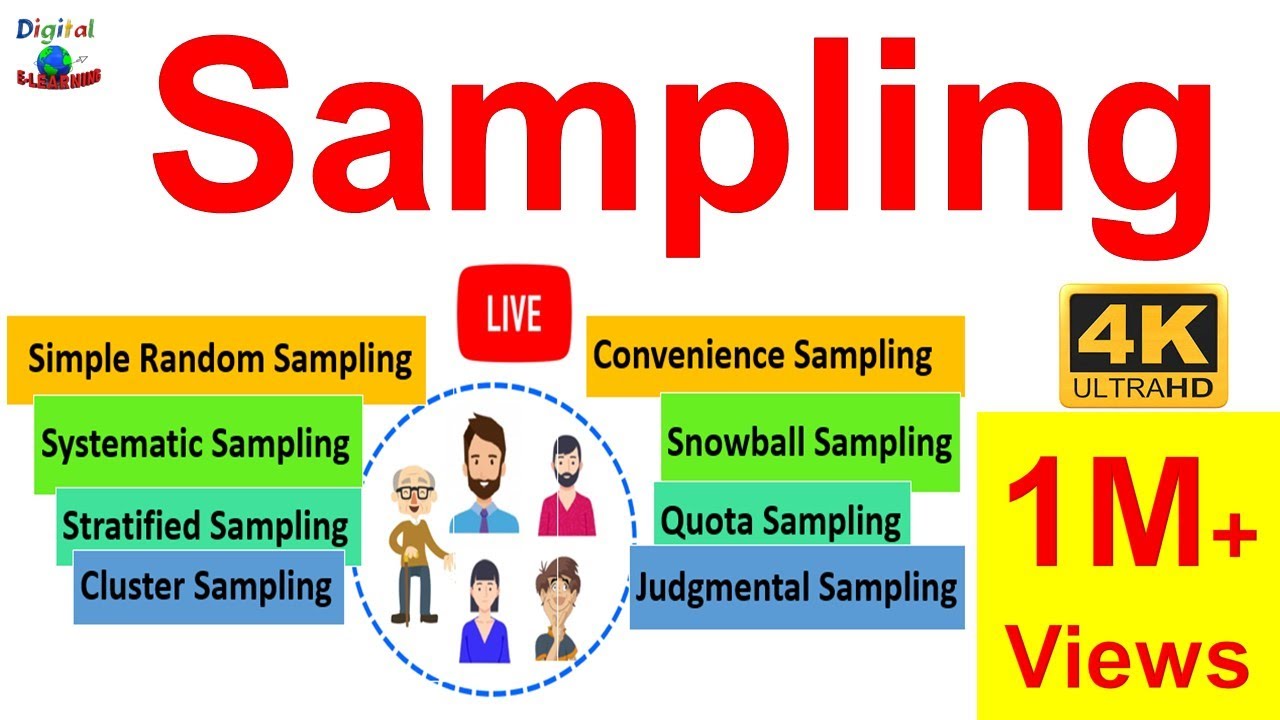
- 😀 Types of probability sampling include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified random sampling, and cluster sampling.
- 😀 Non-probability sampling methods include convenience sampling, quota sampling, and purposive sampling, which are more flexible but less representative.
- 😀 The video will later dive into specific types of sampling methods, comparing their strengths and weaknesses in detail.
Q & A
What is the definition of sampling in research?
-Sampling is the process of selecting participants from a larger population for research purposes. It involves choosing individuals who represent the population in the study.
What are the two main categories of sampling methods?
-The two main categories of sampling methods are probability sampling and non-probability sampling.
How does probability sampling differ from non-probability sampling?
-In probability sampling, every individual has an equal chance of being selected, ensuring a representative sample. In non-probability sampling, some individuals may not have a chance to be selected, making it less reliable for representing the population.
What is a sampling frame in probability sampling?
-A sampling frame is a complete list of all potential participants in the population. Researchers need it to ensure that every individual has an equal chance of being selected.
Why is probability sampling considered more reliable than non-probability sampling?
-Probability sampling is more reliable because it ensures that the sample is representative of the population, reducing bias and improving the accuracy of research findings.
What are the main challenges when using probability sampling?
-The main challenges of probability sampling include the need for a detailed knowledge of the population, including the size, members, and groups within it. Without this, it can be difficult to create an accurate sampling frame.
What are some examples of probability sampling methods?
-Examples of probability sampling methods include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified random sampling.
What is non-probability sampling and when is it typically used?
-Non-probability sampling is when not all individuals have an equal chance of being selected, usually because the researcher lacks detailed information about the population. It is often used in studies where such information is unavailable.
What are some examples of non-probability sampling methods?
-Examples of non-probability sampling methods include convenience sampling and quota sampling.
What are the advantages of using probability sampling in research?
-The advantages of probability sampling include its ability to provide a more representative sample, reduce bias, and increase the generalizability of the research results to the entire population.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Sampling: Sampling & its Types | Simple Random, Convenience, Systematic, Cluster, Stratified

Populasi dan Sampel serta Teknik Pengambilan Sampel

Sampling Techniques: A Comprehensive Guide

Kuliah Statistika Industri | Teknik Sampling

Sampling Techniques
Probability & Non-Probability Sampling Techniques - Statistics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)