A level Business Revision - Porter's 5 Forces
Summary
TLDRThis video explains Michael Porter's Five Forces framework, a tool for assessing competition in an industry. The Five Forces are: Supplier Power, Buyer Power, the Threat of New Entrants, Rivalry Among Existing Competitors, and the Threat of Substitutes. The video discusses how businesses can use this framework to evaluate market dynamics, develop strategies to improve their position, and determine whether to enter a new market. Key strategies include leveraging economies of scale, differentiating products, creating barriers to entry, and managing competitive pressures to maximize profits and minimize risks.
Takeaways
- 😀 Porter’s Five Forces model helps businesses assess the competitive forces within an industry, guiding decisions on market entry or positioning.
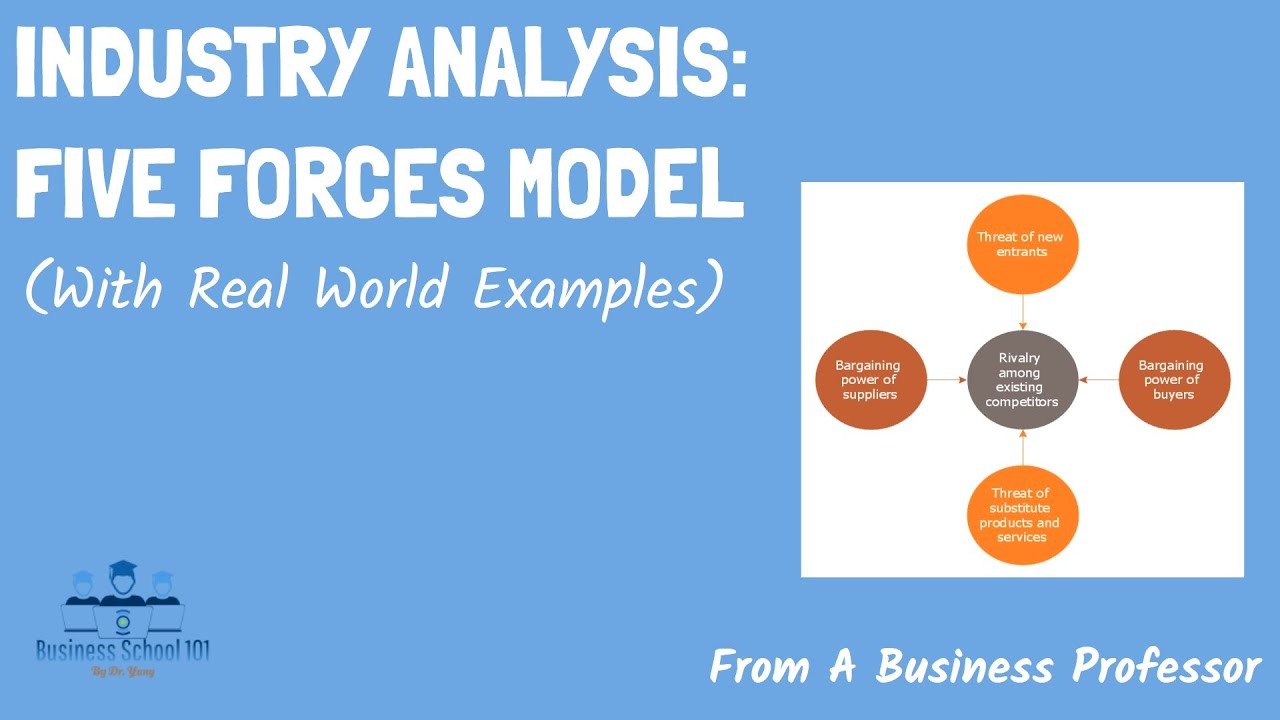
- 😀 The five key forces in Porter's model are supplier power, buyer power, the threat of new entrants, rivalry among existing competitors, and the threat of substitutes.
- 😀 Supplier power refers to the influence suppliers have over a firm’s costs and terms. A few suppliers or unique products give suppliers more power.
- 😀 To reduce supplier power, businesses can form joint ventures, seek new suppliers, or leverage economies of scale to become a more attractive customer.
- 😀 Buyer power refers to how much influence customers have over a business. When customers can easily switch or place large orders, they gain power.
- 😀 To manage buyer power, firms can diversify their customer base, differentiate their products, or drive competitors out of the market.
- 😀 The threat of new entrants highlights the risk that new businesses may enter the market and take market share from established firms.
- 😀 Barriers to entry, such as patents, strong brand loyalty, and economies of scale, can help firms prevent new competitors from entering the market.
- 😀 Rivalry among existing competitors can lead to price wars and increased marketing costs, especially when firms are of similar size or power.
- 😀 Firms can reduce rivalry by focusing on low-cost production or product differentiation to attract customers and stand out in the market.
- 😀 The threat of substitutes occurs when customers can replace a product with alternatives from different industries. Strong branding and low-cost strategies can help mitigate this threat.
Q & A
What is Porter's Five Forces theory?
-Porter's Five Forces is a framework used to analyze the competitive forces in an industry or market. It helps businesses understand where power lies in key relationships and how to use that knowledge to develop strategies for competitive advantage.
How can businesses use Porter's Five Forces when entering a new market?
-When entering a new market, businesses can use Porter's Five Forces to assess the power dynamics in that industry. By understanding who holds power—whether suppliers, customers, competitors, or new entrants—a company can decide whether it’s beneficial to enter the market or if it might face insurmountable challenges.
What are the five forces identified by Porter?
-The five forces identified by Porter are: 1) Supplier power, 2) Buyer power, 3) The threat of new entrants, 4) Rivalry among existing competitors, and 5) The threat of substitutes.
How does supplier power affect a business?
-Supplier power refers to the influence suppliers have over a business. If there are few suppliers or they provide unique products, they hold more power. Businesses can reduce supplier power by diversifying suppliers, maximizing economies of scale, or forming joint ventures with suppliers.
What is buyer power and how can businesses manage it?
-Buyer power is the influence that customers have over a business. It increases when customers have many choices or can easily switch to competitors. Businesses can reduce buyer power by expanding their customer base, differentiating their products, and engaging in promotional strategies to build customer loyalty.
What strategies can firms use to counter the threat of new entrants?
-To counter the threat of new entrants, firms can create barriers to entry, such as obtaining patents, building brand loyalty, achieving economies of scale, and establishing strong customer relationships. These actions make it more difficult for new firms to enter the market and compete effectively.
Why is rivalry among existing competitors a significant force?
-Rivalry among competitors is a major force because intense competition can lead to price wars, increased marketing costs, and pressure on profits. Firms need to differentiate their offerings, focus on cost leadership, and use strategic tactics to minimize the impact of rivals on their market position.
What does the 'threat of substitutes' mean in Porter's model?
-The 'threat of substitutes' refers to competition from products or services in different industries that could replace what a business is selling. For example, a cinema faces competition not only from other cinemas but also from other forms of leisure activities. Businesses can protect against substitutes by building strong brands, offering loyalty programs, and pursuing cost leadership.
How can businesses handle high supplier power?
-Businesses can manage high supplier power by seeking alternative suppliers, increasing the volume of their orders to become more attractive to suppliers, or forming joint ventures or partnerships with suppliers to create mutually beneficial relationships.
What role does product differentiation play in reducing buyer power?
-Product differentiation reduces buyer power by making a company's offerings unique or more attractive than competitors' products. This uniqueness increases customer loyalty and reduces the likelihood of customers switching to other suppliers, giving the business more leverage in the market.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Porter's 5 Forces EXPLAINED | B2U | Business To You

Porter's Five Forces Explained | Supermarket Industry Examples

Porter's five forces model
Industry Analysis: Porter's Five Forces Model | Strategic Management | From A Business Professor

The Explainer: The 5 Forces That Make Companies Successful

The Five Forces Analysis explained
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)