BIOREAKTOR DAN JENIS-JENIS BIOREAKTOR
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a detailed overview of bioreactors, their design, function, and various types used in biological and chemical processes. It explains how bioreactors enable microorganisms to grow and produce metabolites under controlled conditions, essential for applications such as enzyme production, fermentation, and wastewater treatment. Key types like airlift bioreactors, fermentor towers, fluidized bed reactors, and packed bed reactors are explored, highlighting their advantages and limitations. The video emphasizes the importance of selecting the right bioreactor based on the specific process requirements and scale.
Takeaways
- 😀 A bioreactor is a closed vessel used for synthesizing chemical signals and biological processes to produce biomass and waste from cultivated microorganisms.
- 😀 Bioreactors must include systems for aeration, agitation, temperature control, and pH control to ensure optimal microbial growth and product formation.
- 😀 The main processes in a bioreactor include regulation of parameters (temperature, pH, pressure), agitation for mixing, aeration for oxygen supply, and sterilization to maintain system cleanliness.
- 😀 The design and method of bioreactors are tailored to create ideal conditions for organisms to produce the desired products with high productivity and quality.
- 😀 Bioreactors should be made from materials that are non-corrosive, non-toxic, able to withstand sterilization procedures, and can endure high pressure and pH variations.
- 😀 Key components of a bioreactor include the fermentation vessel, heating and cooling systems, aeration devices, agitation mechanisms, and foam control systems.
- 😀 Types of bioreactors include airlift bioreactors, tower fermenters, fluidized bed reactors (FBR), and packed bed bioreactors, each with distinct advantages and disadvantages depending on the application.
- 😀 Airlift bioreactors are energy-efficient, provide adequate mixing, and are ideal for aerobic cultures but not suitable for anaerobic processes.
- 😀 Tower fermenters are simple in design with no moving parts and are energy-efficient but require high air pressure and are less efficient for high-pressure reactions.
- 😀 Fluidized bed reactors (FBR) facilitate high reaction rates by suspending particles, but they may suffer from unwanted temperature gradients and cleaning difficulties.
- 😀 Packed bed bioreactors provide high conversion rates for catalysts and are suitable for high-temperature and high-pressure operations, but they may suffer from poor temperature control and cleaning challenges.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a bioreactor?
-The primary function of a bioreactor is to provide a controlled environment for microorganisms or cells to grow and produce desired biochemical products through biological processes like fermentation or biotransformation.
What are the key components that make up a bioreactor?
-A bioreactor typically includes a fermentation vessel, heating and cooling systems, aeration systems, agitation systems, and sensors/control devices to monitor temperature, pH, oxygen levels, and nutrient concentrations.
Why is aeration important in bioreactors?
-Aeration is crucial in bioreactors, especially for aerobic fermentation, as it provides oxygen to the microorganisms, which is essential for their metabolism and growth.
What is the role of agitation in a bioreactor?
-Agitation in a bioreactor ensures proper mixing of the culture medium, nutrients, and microorganisms, improving the contact between them and helping to maintain uniform conditions throughout the reactor.
What types of bioreactors are commonly used in industry?
-Common types of bioreactors used in industry include airlift bioreactors, fermentor towers, fluidized bed reactors, packed bed reactors, and photo-bioreactors. Each has its specific use depending on the nature of the biological process.
What are the advantages of using an airlift bioreactor?
-Airlift bioreactors are energy-efficient, provide effective mixing and aeration, and are suitable for both free and immobilized cell cultures. They are particularly well-suited for aerobic cultures.
What are the limitations of an airlift bioreactor?
-Airlift bioreactors are not efficient for gas-phase reactions or high-pressure processes. They also may struggle with breaking down gas bubbles effectively, which can reduce overall process efficiency.
How does a fermentor tower differ from other bioreactor types?
-A fermentor tower, or packed bed bioreactor, uses unidirectional gas flow from bottom to top, with no mechanical agitation. It is simple in design, energy-efficient, and requires less maintenance, but requires high airflow pressure.
What are the key features of a fluidized bed bioreactor?
-A fluidized bed bioreactor allows particles to be suspended in a fluid, enhancing the contact between microorganisms and the medium. It is suited for continuous processes, but it can face issues with erosion and internal component wear.
What makes packed bed reactors suitable for high-pressure reactions?
-Packed bed reactors can operate at high pressure and temperature, making them ideal for processes requiring biocatalysts under extreme conditions. The flow of fluid through the packed bed helps provide nutrients to the biocatalysts.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of fluidized bed bioreactors?
-Fluidized bed bioreactors offer uniform particle mixing, consistent heat distribution, and are ideal for continuous operations. However, they suffer from issues like erosion of internal components, complex temperature control, and high-pressure losses.
How does a photo-bioreactor differ from other bioreactors?
-A photo-bioreactor uses light to facilitate photosynthesis, typically in algae cultivation for biofuel production. Unlike other bioreactors, it focuses on light-dependent processes rather than microbial or enzymatic reactions alone.
What factors must be considered when selecting a bioreactor type for an industrial process?
-The selection of a bioreactor depends on factors like the type of biological process, the desired product, scale of production, and environmental conditions. These factors help determine the most efficient and cost-effective bioreactor for the task.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
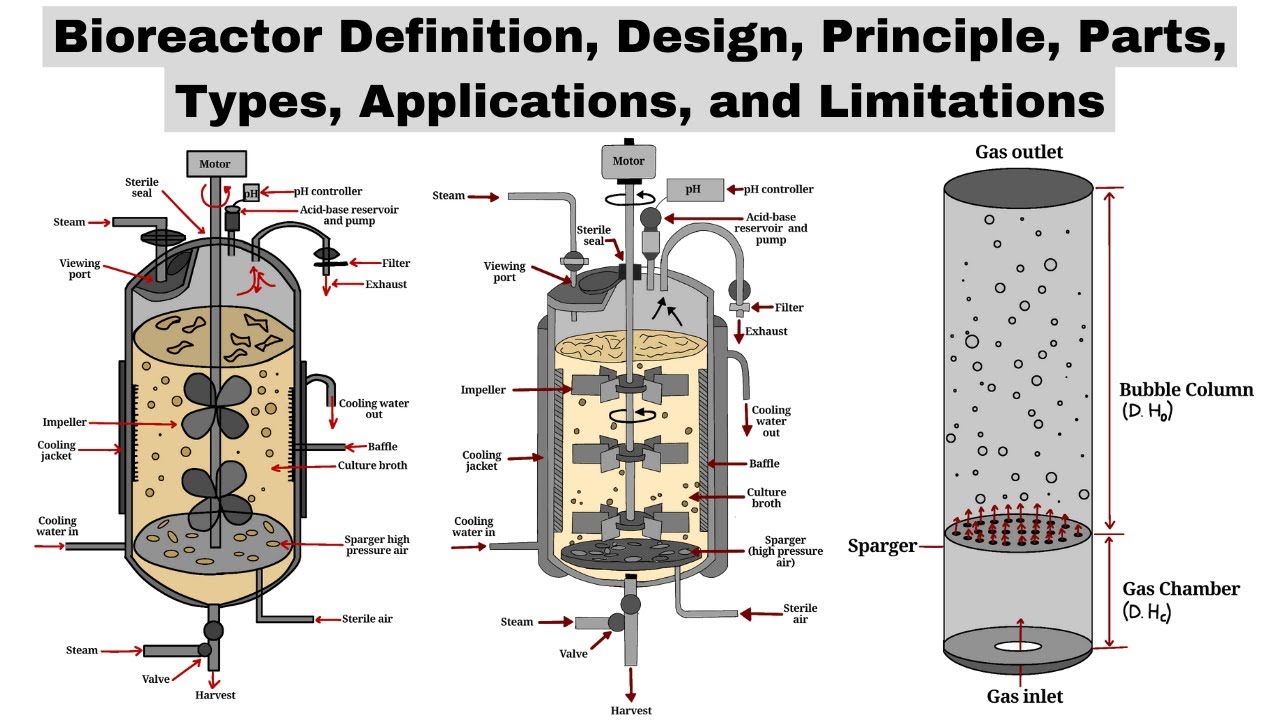
Bioreactors | Design, Principle, Parts, Types, Applications, & Limitations | Biotechnology Courses

Dairy Membrane Classifications

Enzim Mikroba

Controlling the Operation of Ships | Function and uses Winches, Windlasses, Capstans
Construction of Three Phase Induction Motor - Three Phase Induction Motor - Electrical Machines 3
Bio-processing overview (Upstream and downstream process)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)