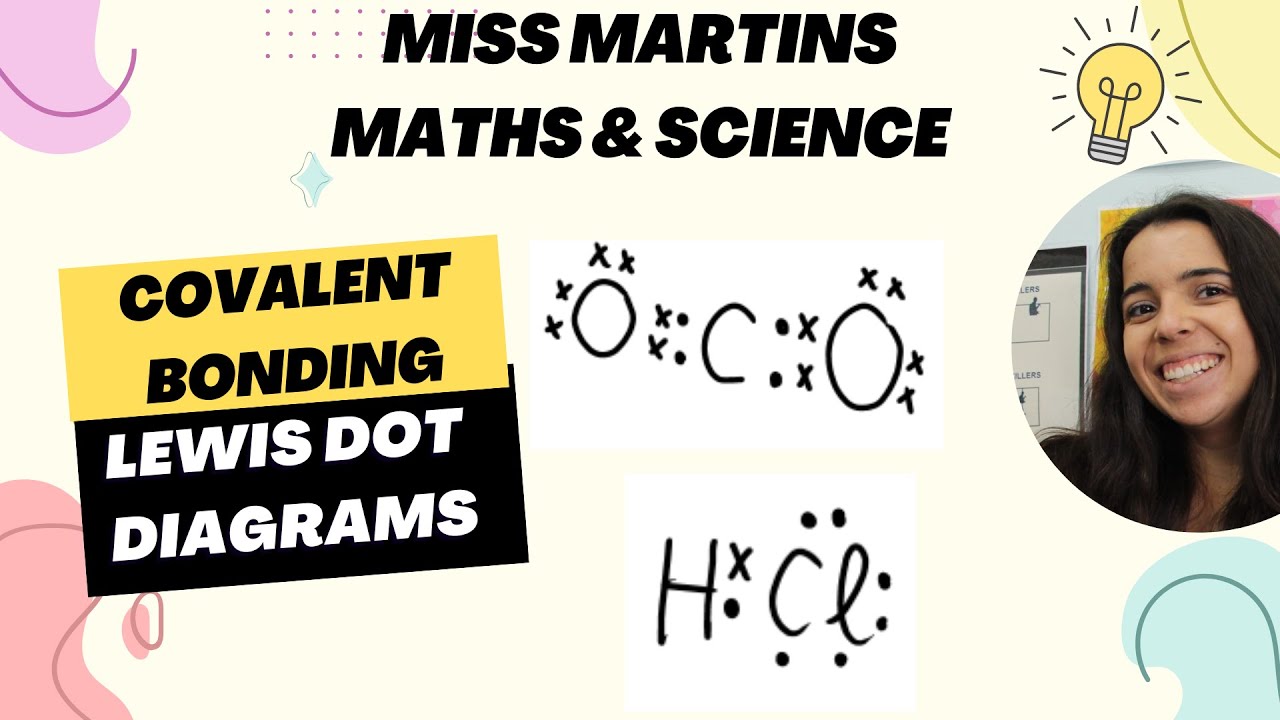5 Covalent Bonding Intro
Summary
TLDRThis introductory video on covalent bonding explains the essential concepts of how atoms form covalent bonds by sharing electrons. It contrasts covalent bonding with metallic and ionic bonding, highlighting that covalent bonds occur between non-metal elements. The video defines molecules and covalent bonds, emphasizing the shared attraction between nuclei and electron pairs. It also explores how to represent these bonds using electron dot diagrams, showing examples of single, double, and triple bonds. The video serves as a foundational guide, preparing viewers for more detailed studies on covalent bonding in later videos.
Takeaways
- 😀 Covalent bonding occurs between two non-metal elements that prefer to share electrons rather than give them away or gain them.
- 😀 Molecules are formed by two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds, which can be the same or different elements.
- 😀 A covalent bond is defined as the mutual attraction of two atomic nuclei for a shared pair of electrons.
- 😀 The elements involved in covalent bonding tend to have high electronegativity, meaning they strongly attract electrons.
- 😀 Common examples of covalent molecules include HCl (hydrochloric acid), ammonia (NH₃), and sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
- 😀 A covalent molecule can involve two or more atoms, and the elements in the molecule must be non-metals.
- 😀 The sharing of a pair of electrons in covalent bonding creates a bond, which can be represented by dots, crosses, or a line in diagrams.
- 😀 A single bond in covalent bonding involves one shared pair of electrons, while double and triple bonds involve two and three shared pairs of electrons, respectively.
- 😀 The electron dot diagram uses dots to represent electrons, while lines can also be used to represent shared electron pairs in bonds.
- 😀 Understanding the basic definitions of covalent bonding and its representation is essential for avoiding errors in further discussions of bonding.
Q & A
What is a covalent bond?
-A covalent bond is the mutual attraction between two atomic nuclei for a shared pair of electrons. This bond occurs between non-metal atoms, which share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
How do covalent bonds differ from ionic bonds?
-Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between non-metal atoms, while ionic bonds occur when electrons are transferred from a metal atom to a non-metal atom, resulting in oppositely charged ions attracting each other.
What kind of elements typically form covalent bonds?
-Covalent bonds typically form between two non-metal elements. These elements have high electronegativity and prefer to share electrons rather than lose or gain them.
Can a molecule be made of atoms from different elements in covalent bonding?
-Yes, a molecule can be made of atoms from different elements, as long as they are held together by covalent bonds. For example, H₂O (water) is a molecule made of hydrogen and oxygen atoms, which are covalently bonded.
What is the definition of a molecule in the context of covalent bonding?
-A molecule is defined as any two or more atoms that are held together by covalent bonds. This includes both simple molecules like O₂ and more complex compounds like glucose.
How can you visually represent a covalent bond in diagrams?
-Covalent bonds can be represented in diagrams using electron dot diagrams, where electrons are shown as dots or crosses, or with lines that represent shared pairs of electrons between atoms.
What does a line in a molecule diagram represent?
-A line in a molecule diagram represents a shared pair of electrons, which is the key characteristic of a covalent bond. One line indicates a single bond, while two or three lines indicate double or triple bonds, respectively.
What is meant by electronegativity in covalent bonding?
-Electronegativity refers to an atom's ability to attract electrons in a covalent bond. Atoms with high electronegativity, like non-metals, are more likely to share electrons with other atoms to fill their outer electron shells.
Why do non-metals prefer to form covalent bonds?
-Non-metals prefer to form covalent bonds because they have a strong desire to gain electrons to fill their outer shells. Rather than losing electrons, they share them with other atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration.
What is a shared pair of electrons in a covalent bond?
-A shared pair of electrons refers to two electrons that are shared between two atoms in a covalent bond, helping to hold the atoms together and allowing both atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)