L-4.1 I/O Interface | Input Output Interface | I/O Commands | Computer Architecture | COA | CSA
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of the Input-Output Interface, also referred to as I/O interface, in computer systems. It covers the importance of peripheral devices that facilitate communication between the computer's central system and external devices. Key topics discussed include the operation of various input and output devices such as keyboards, monitors, and printers, as well as the significance of data transfer between internal and external storage. The video also delves into the working of communication links and interface registers, emphasizing the technicalities of data transfer and synchronization mechanisms between the CPU and peripheral devices.
Takeaways
- 😀 In the video, the concept of an input-output interface (I/O interface) is explained, focusing on how it facilitates communication between the central processing unit (CPU) and peripheral devices.
- 😀 Peripheral devices, such as printers and monitors, are essential for input and output operations, allowing interaction with the computer system.
- 😀 An I/O interface helps manage the communication between a computer's internal and external storage, and its role in transferring information efficiently is emphasized.
- 😀 Different types of peripherals have distinct methods of transferring data, such as keyboards and monitors, which depend on the type of device and the data being handled.
- 😀 The video highlights the importance of synchronization mechanisms between devices to prevent data transfer errors due to speed mismatches between the CPU and peripherals.
- 😀 A key aspect discussed is how peripheral devices interact with memory registers and buffers to temporarily store data before it is processed or transferred.
- 😀 The concept of communication links between different devices is crucial, as these links enable the devices to exchange data without direct connection to the CPU.
- 😀 The I/O interface ensures that data is sent and received correctly between devices, with specific addresses and control lines being used to route data accurately.
- 😀 A brief mention is made of the difference between electromechanical devices and electronic devices, explaining how each type operates differently depending on its design.
- 😀 The video concludes by stressing the role of input-output systems in controlling data transfer, with special focus on how I/O commands are executed and how data is managed by the system.
Q & A
What is the primary role of input devices in a computer system?
-The primary role of input devices is to provide a sufficient mode of communication between the central system (CPU) and the outside environment, enabling users to input data into the system.
What is the importance of peripheral devices in a computer system?
-Peripheral devices are important as they attach to the computer to extend its functionality, allowing for input and output processes like printing, typing, and display.
What are the main differences between electromechanical and electronic devices?
-Electromechanical devices operate using a combination of mechanical components and electrical signals, while electronic devices rely purely on electronic components for operation, leading to different functioning mechanisms.
How does data transfer speed affect the synchronization between the CPU and peripheral devices?
-The data transfer speed mismatch between the CPU and peripheral devices can cause synchronization issues. To resolve this, specialized synchronization mechanisms are required to ensure smooth communication and data transfer.
What is the role of control lines in peripheral communication?
-Control lines are responsible for managing and directing communication between the CPU and peripheral devices. They help in determining which device is active and handle the flow of data, ensuring accurate transfer between components.
What is the purpose of the 'address bus' in a computer system?
-The address bus is used to select the specific peripheral device or memory location that the CPU wants to interact with, ensuring the correct device is activated during communication.
How do registers function in the data transfer process?
-Registers temporarily store data during processing. In the context of peripheral devices, registers help manage data transfer by storing incoming or outgoing information before it is processed or sent to its destination.
What are input and output commands in the context of peripheral devices?
-Input commands are sent to peripheral devices to receive data, while output commands direct peripheral devices to send data back to the CPU. These commands control the flow of information between the CPU and peripherals.
Why is it important to have a communication link between the CPU and peripherals?
-A communication link is essential for data exchange between the CPU and peripheral devices. It enables the system to process input from external devices and deliver output to them, maintaining system functionality.
What is the role of an interface unit in data transfer?
-An interface unit facilitates communication between the CPU and peripheral devices. It helps manage data transfer, ensuring that the correct data is sent or received based on the instructions and status of the connected devices.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

What is OS - Animation

SAD - Chapter 8 : User Interface Design
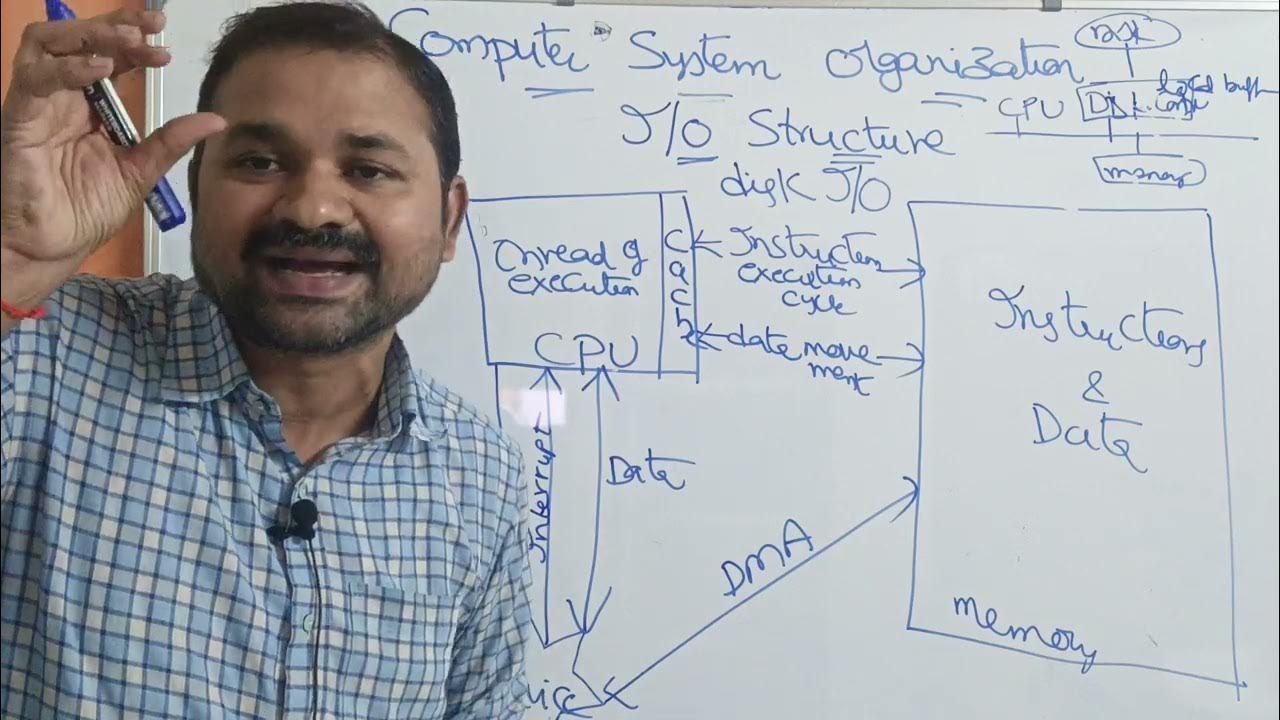
I/O Structure in Operating system || Computer System Organization || Operating System

HCI 2.1 Input Output Channel in Human Computer Interaction with Examples
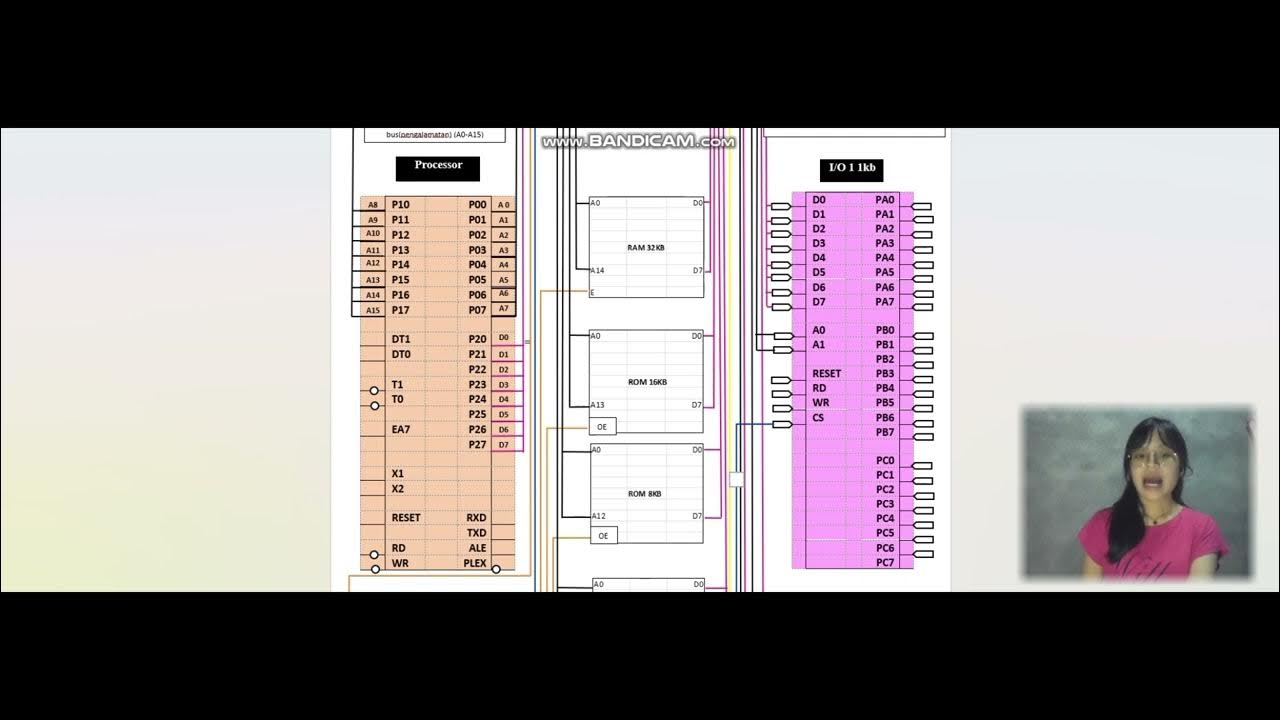
Organisasi dan Arsitektur Komputer

What is an Operating System? Goals & Functions of Operating System | Concept Simplified by Animation
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)