Zero Crossing Detector | Non Linear Applications of Operational Amplifier | EXTC Engineering
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the concept of an inverting zero crossing detector is explained. The circuit detects when an input signal crosses zero volts, converting sinusoidal signals into square waves. The op-amp configuration switches the output between positive and negative voltage whenever the input crosses zero. This type of detector is useful for square wave generation, synchronization in AC circuits, and triggering in microcontroller applications. While the circuit has practical uses, it’s sensitive to noise, which can cause false transitions in the output.
Takeaways
- 😀 The inverting zero crossing detector detects when an input signal crosses zero.
- 😀 In this configuration, the input signal is applied to the inverting terminal of an op-amp, and the reference voltage is grounded.
- 😀 The non-inverting terminal is also connected to ground, setting the reference voltage to zero.
- 😀 The differential input voltage (VD) is the difference between the signals at the inverting and non-inverting terminals of the op-amp.
- 😀 The op-amp's high input impedance ensures that the current through the input terminals is negligible (approximately zero).
- 😀 When the input signal becomes positive after crossing zero, the op-amp output switches to negative saturation (V_sat).
- 😀 When the input signal becomes negative after crossing zero, the output switches to positive saturation (V_sat).
- 😀 The circuit converts a sinusoidal input waveform into a square waveform by switching the output between positive and negative saturation voltages.
- 😀 The circuit can be used as a square wave generator, making it useful in signal processing applications.
- 😀 The zero crossing detector is useful for synchronization in AC main circuits and as a trigger circuit in microcontroller-based applications.
- 😀 A disadvantage of the circuit is that noise at the input can cause false transitions, leading to incorrect output switching even without an actual zero crossing.
Q & A
What is the purpose of a zero crossing detector?
-A zero crossing detector is used to detect when an input signal crosses zero, meaning it can identify the point where the signal changes polarity from positive to negative or vice versa.
What is the key difference between the inverting and non-inverting zero crossing detectors?
-In an inverting zero crossing detector, the input signal is applied to the inverting terminal of the op-amp, and the reference voltage is set to zero (ground). In a non-inverting zero crossing detector, the input signal is applied to the non-inverting terminal, and the reference voltage may differ.
How does the output of an inverting zero crossing detector behave?
-The output of an inverting zero crossing detector switches between positive and negative saturation voltages (V_satur) every time the input signal crosses zero. If the input signal becomes positive, the output goes negative, and if the input becomes negative, the output goes positive.
What is the role of the reference voltage in the inverting zero crossing detector?
-The reference voltage is connected to ground (zero volts) in the inverting zero crossing detector, which helps establish the point of zero crossing for the input signal.
What is the significance of the differential input voltage in the operation of the zero crossing detector?
-The differential input voltage (V_D) is the difference between the voltages applied to the inverting and non-inverting terminals of the op-amp. In the case of an inverting zero crossing detector, V_D is the difference between the reference voltage (V_reference) and the input signal (V_in).
How does the input signal's polarity affect the operation of the inverting zero crossing detector?
-When the input signal is positive (crossing zero from negative), the inverting input terminal has a higher potential than the non-inverting terminal, and the output goes negative. When the input signal becomes negative (crossing zero from positive), the inverting terminal has a lower potential, and the output goes positive.
What is a potential disadvantage of the zero crossing detector circuit?
-A potential disadvantage is that noise at the input can cause false transitions. This means the noise could trigger a change in the output, even when there is no actual zero crossing in the input signal.
What type of waveform is produced by an inverting zero crossing detector?
-An inverting zero crossing detector converts a sine waveform into a square waveform, where the output switches between high and low voltage levels every time the input signal crosses zero.
What are some applications of the inverting zero crossing detector?
-Applications of the inverting zero crossing detector include generating square wave signals, synchronizing AC mains circuits, and serving as a trigger circuit in microcontroller or microprocessor-based applications.
What happens when noise is present at the input of a zero crossing detector?
-When noise is present at the input, it can cause false transitions in the output, even if no actual crossing of zero occurs. This can lead to erroneous behavior in the circuit.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

05 0 Openloop Comparator with 2Signals

Comparator Explained (Inverting Comparator, Non-Inverting Comparator and Window Comparator)
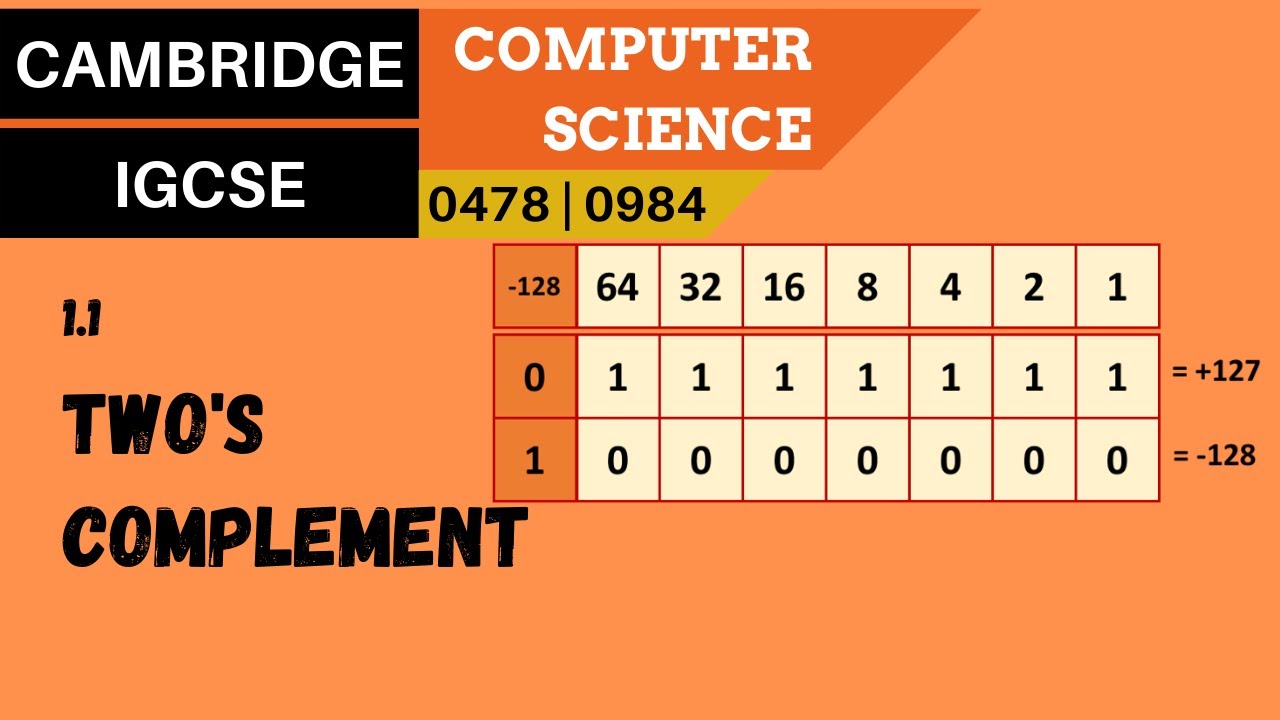
8. CAMBRIDGE IGCSE (0478-0984) 1.1 Signed integers using two's complement

Theatre Arts - Terms & Concepts
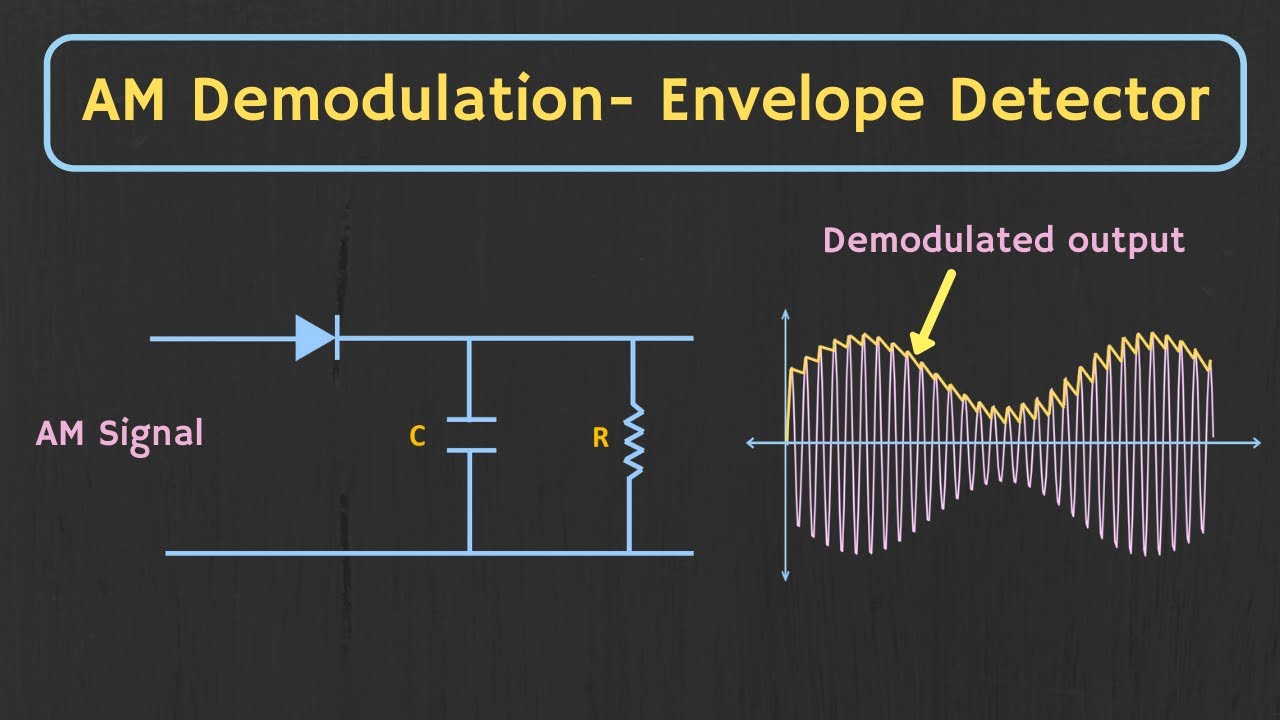
AM Demodulation - Envelope Detector Explained (with Simulation)
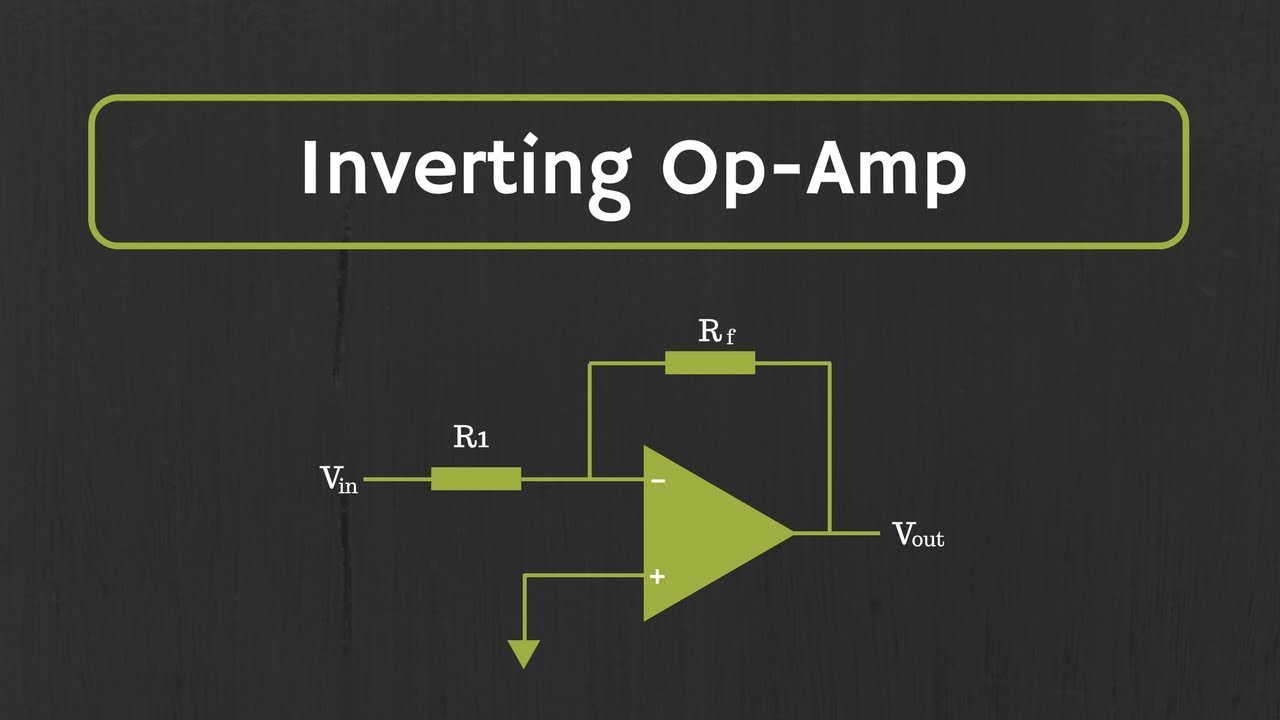
Operational Amplifier: Inverting Op Amp and The Concept of Virtual Ground in Op Amp
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)