Understanding Periodic Table
Summary
TLDRThe periodic table is a chart that organizes all 118 chemical elements based on their atomic structure and electron configuration. It illustrates the relationships between elements, from hydrogen, which dominates the universe, to the complex combinations that make up everything around us. By understanding how atoms interact and combine, the table reveals the properties of each element, predicting how they behave when combined. The periodic arrangement of elements in rows and columns reflects their similar properties and helps us understand the underlying structure of matter, from the smallest atoms to the largest molecules essential for life.
Takeaways
- 😀 The periodic table displays all 118 known chemical elements, which make up everything in the universe.
- 😀 Chemical symbols like C for carbon and O for oxygen represent elements, and their atomic numbers indicate the number of protons in an atom.
- 😀 Some elements have symbols derived from Latin, such as sodium (Na) from 'natrium' and gold (Au) from 'aurum'.
- 😀 94 of the 118 elements occur naturally, while the rest are synthesized in laboratories.
- 😀 Atoms, the smallest units of elements, are composed of a nucleus (protons and neutrons) surrounded by electrons.
- 😀 The outermost electrons of an atom determine how it interacts with other atoms to form compounds.
- 😀 The periodic table is organized by atomic number and electron configuration, which influence an element's chemical properties.
- 😀 Elements in the same column of the periodic table have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons in their outer layer.
- 😀 The table is 'periodic' because the properties of elements repeat at regular intervals as you move across rows and columns.
- 😀 The periodic table helps predict how elements will combine to form compounds, essential to everything around us.
- 😀 Understanding the periodic table is key to understanding the chemistry of materials like water, metal, sugar, and even our bodies.
Q & A
What is the periodic table?
-The periodic table is a chart that organizes all 118 known chemical elements based on their atomic number and electron configuration. It represents the building blocks of the universe and helps predict how elements interact and combine to form compounds.
How many elements are naturally occurring and how many were created in labs?
-Out of the 118 elements, 94 can be found in nature, while the remaining elements were synthesized in laboratories.
What is the significance of the numbers next to the element symbols in the periodic table?
-The numbers next to the element symbols typically represent the atomic number, which is the number of protons (and electrons) in the atom, defining its chemical properties.
Why is the periodic table not a square or rectangular shape?
-The periodic table's shape reflects the distribution of elements based on quantum chemistry rules and electron configurations, resulting in a unique structure that helps organize elements according to their chemical properties.
What are some examples of elements and their chemical symbols?
-Examples include carbon (C), oxygen (O), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), sodium (Na), and gold (Au). Some symbols come from Latin names, like Na for sodium from 'natrium' and Au for gold from 'aurum'.
How are atoms structured?
-An atom consists of a nucleus containing protons (positive charge) and neutrons (no charge), surrounded by a cloud of electrons (negative charge). The properties of an element are defined by its atom's nucleus and electron distribution.
What does the term 'periodic' refer to in the periodic table?
-The term 'periodic' refers to the repeating patterns of chemical properties observed in elements at regular intervals across the table. As you move across a row, the properties change systematically, and once the row ends, elements in the next row start again with similar properties.
How do elements in the same column of the periodic table behave?
-Elements in the same column of the periodic table share similar properties because they have the same number of electrons in their outermost electron shell, which influences their chemical behavior and reactions.
How does the periodic table help us understand chemical reactions?
-The periodic table helps predict how elements will combine and react with each other by organizing them based on their electron configuration. Elements with similar properties are grouped together, and their chemical behavior can be understood based on their position.
Why is hydrogen such a significant element in the universe?
-Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe, making up about 94% of all atoms in stars like the Sun. It is the simplest and lightest element, and its reactions are essential for the energy produced by stars.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

The (truly) Periodic Table

Periodic Law: The Origin of the Periodic Table

BAB 5 UNSUR SENYAWA DAN CAMPURAN - Bagian 1 (IPA Kelas 8 Kurikulum Merdeka)
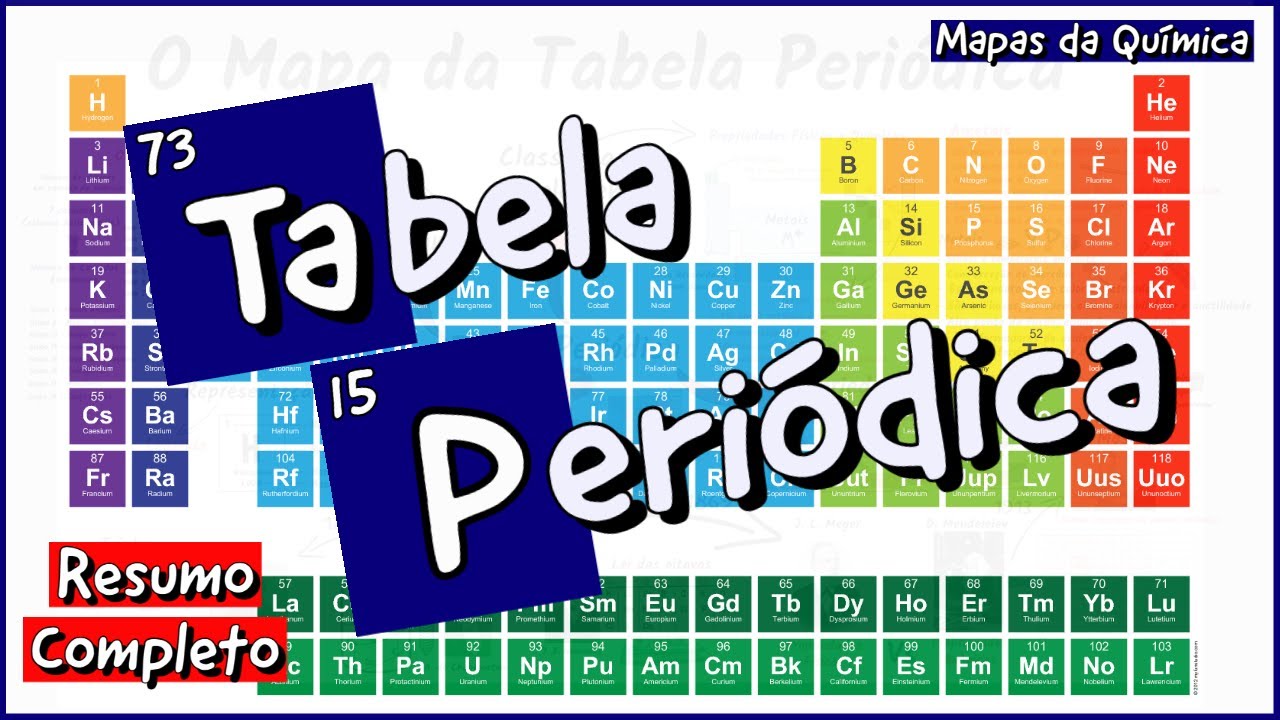
Tabela Periódica [Mapa Mental] [COMPLETO] - Mapas da Química

Why Does the Periodic Table Look the Way It Does?

Atomic Structure: Protons, Electrons & Neutrons
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)