Marine Diesel Two Stroke Engine - How it Works!
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth explanation of a large marine two-stroke diesel engine, focusing on key components like the exhaust gas valve, scavenging process, and fuel injection system. It details how the exhaust gases are expelled, the role of hydraulic systems in valve operation, and the rotation of the exhaust gas valve for even wear. Additionally, the video touches on fuel injectors and their integration in modern diesel engines. Viewers are encouraged to explore more engineering tutorials on Savree.com for deeper learning about diesel engines and related technologies.
Takeaways
- 😀 Diesel engines operate through compression ignition, meaning they don't require spark plugs for combustion.
- 😀 The exhaust gas valve is essential in controlling the release of exhaust gases and plays a role in the scavenging process.
- 😀 Uniflow scavenging ensures that exhaust gases are effectively removed from the cylinder by opening the exhaust gas valve.
- 😀 The exhaust gas valve rotates during operation, ensuring even wear and enhancing the lifespan of the valve and its seating area.
- 😀 The hydraulic system operates the exhaust gas valve by feeding oil into different chambers to open and close the valve.
- 😀 Fuel is injected into the combustion chamber through high-pressure fuel injectors, which are fed by a fuel pump.
- 😀 Marine two-stroke diesel engines typically feature exhaust gas valves that operate in a unique, controlled manner to optimize engine performance.
- 😀 The scavenging process helps to replace exhaust gases with fresh air, which is crucial for efficient combustion in the engine.
- 😀 Hydraulic oil is precisely managed to control the opening and closing of the exhaust gas valve, which is vital for engine performance.
- 😀 Modern engines often utilize common rail fuel injection systems, offering improved fuel delivery compared to older designs.
- 😀 The video encourages users to explore more educational content on Savree.com, with over 25 hours of video tutorials on various engineering topics.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the Uniflow scavenging system in the two-stroke diesel engine?
-The Uniflow scavenging system is designed to flush out the exhaust gases from the cylinder by using fresh air. As the air inlet ports open, the incoming air pushes the exhaust gases out, ensuring the cylinder is cleared before the exhaust gas valve closes for compression and combustion.
How does the exhaust gas valve work in this engine?
-The exhaust gas valve is hydraulically operated. Hydraulic oil is fed into the top and bottom of the valve to control its movement. When oil is fed to the top, the valve opens, and when oil is fed to the bottom, the valve closes and seals the cylinder.
Why does the exhaust gas valve rotate in this engine?
-The exhaust gas valve rotates to ensure even wear on both the valve itself and its seating area. This is achieved through veins on the valve stem, which cause rotation as exhaust gases pass over them.
What is the role of the veins on the exhaust gas valve stem?
-The veins on the exhaust gas valve stem cause the valve to rotate when exhaust gases pass through. This rotation promotes even wear and tear on both the valve and its seating area, extending the valve's lifespan.
How is the exhaust gas valve controlled in this engine?
-The exhaust gas valve is controlled hydraulically. Hydraulic oil is fed into chambers above and below the valve. Oil fed to the top opens the valve, and oil fed to the bottom reseats the valve when it needs to close.
What is the significance of hydraulic oil in the valve system?
-Hydraulic oil plays a crucial role in controlling the movement of the exhaust gas valve. It allows for precise and efficient operation of the valve, ensuring that it opens and closes at the right times during the engine cycle.
What happens during the compression stroke of the engine?
-During the compression stroke, the exhaust gas valve is closed, and the piston moves upwards, compressing the air in the cylinder. This compression raises the temperature of the air, preparing it for combustion, which happens when the fuel is injected.
What happens after the exhaust gas valve opens during the scavenging process?
-Once the exhaust gas valve opens, the exhaust gases are flushed out of the cylinder as fresh air enters through the inlet ports. The valve rotates to ensure even wear, and the exhaust gases then flow out toward the turbocharger turbine.
How is fuel injected into the combustion space?
-Fuel is injected into the combustion space through fuel injectors. High-pressure fuel is fed into the injectors via fuel lines, with the system often using a common rail fuel injection method in modern engines.
What is the purpose of the turbocharger in the engine?
-The turbocharger uses exhaust gases to increase the engine's intake air pressure, improving the engine's efficiency and power output by forcing more air into the combustion chamber.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

How a Ship Engine Works - 2-Stroke Marine Diesel Engine

El ciclo diésel (cuatro tiempos)
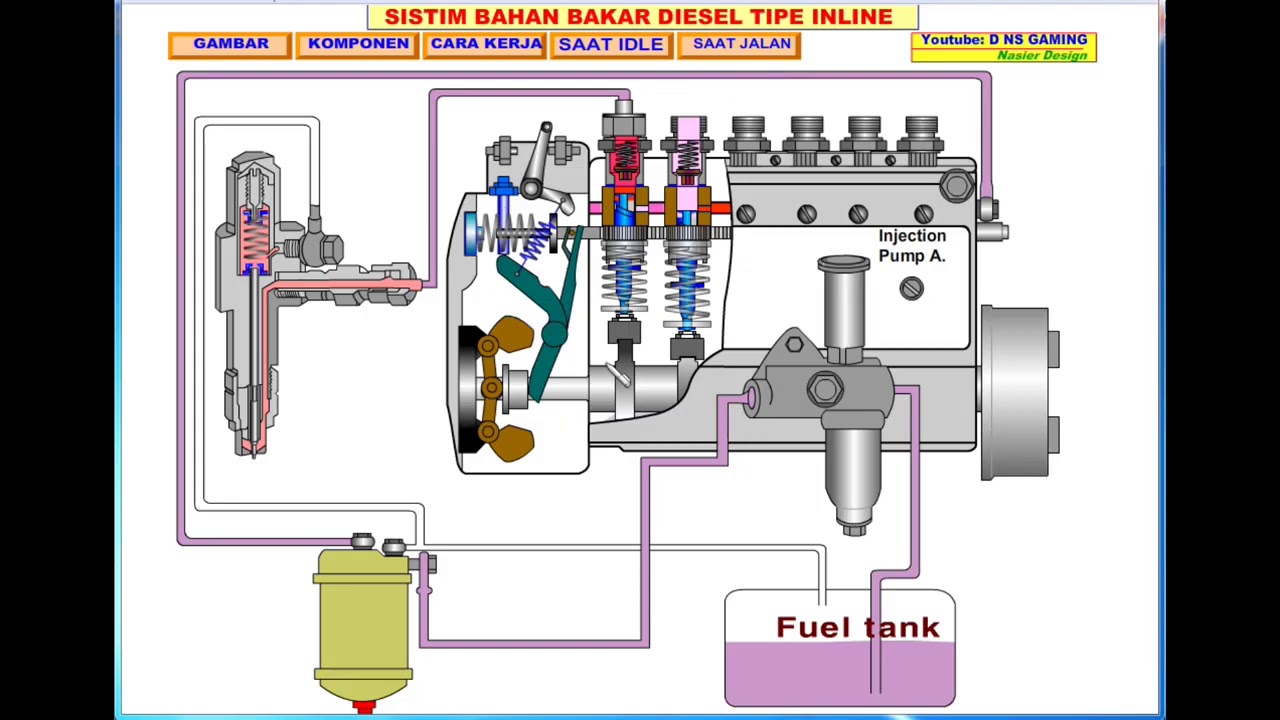
cara kerja bahan bakar diesel (Tipe Inline)

CARA KERJA SISTEM BAHAN BAKAR MESIN DIESEL

How car engine works? / 4 stroke internal combustion engine (3D animation)

Ship engine components and functions #mainengine #2strokeengine
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)