Garis Singgung Lingkaran | Matematika SMA Kelas XI
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial covers essential concepts of circles and tangents in geometry for high school students. It explains the definition of a tangent line, its properties, and its relationship with the radius of a circle. The tutor provides clear examples, including solving problems involving tangent lines, calculating tangent lengths, and applying the Pythagorean theorem. Additionally, the video explores the concept of internal and external common tangents between two circles, demonstrating the use of mathematical formulas. The session wraps up with the Pitot theorem and practical problems to reinforce the understanding of these geometric principles.
Takeaways
- 😀 A tangent line to a circle touches the circle at exactly one point, called the point of tangency.
- 😀 The tangent line is always perpendicular to the radius of the circle at the point of tangency.
- 😀 In a problem with tangents, the sum of specific angles and distances can help solve for unknowns using geometry.
- 😀 To calculate the length of a tangent line from a point outside the circle, the Pythagorean Theorem is used.
- 😀 If two tangent lines are drawn from the same external point, their lengths will be the same.
- 😀 Pitot's Theorem states that for a tangential quadrilateral, the sum of the lengths of opposite sides is equal.
- 😀 The formula for the length of a tangent from a point outside the circle is √(AP² - r²), where AP is the distance from the point to the center, and r is the radius of the circle.
- 😀 The Pythagorean Theorem can be applied to solve for lengths in geometric shapes involving tangents, such as triangles formed by a radius and tangent.
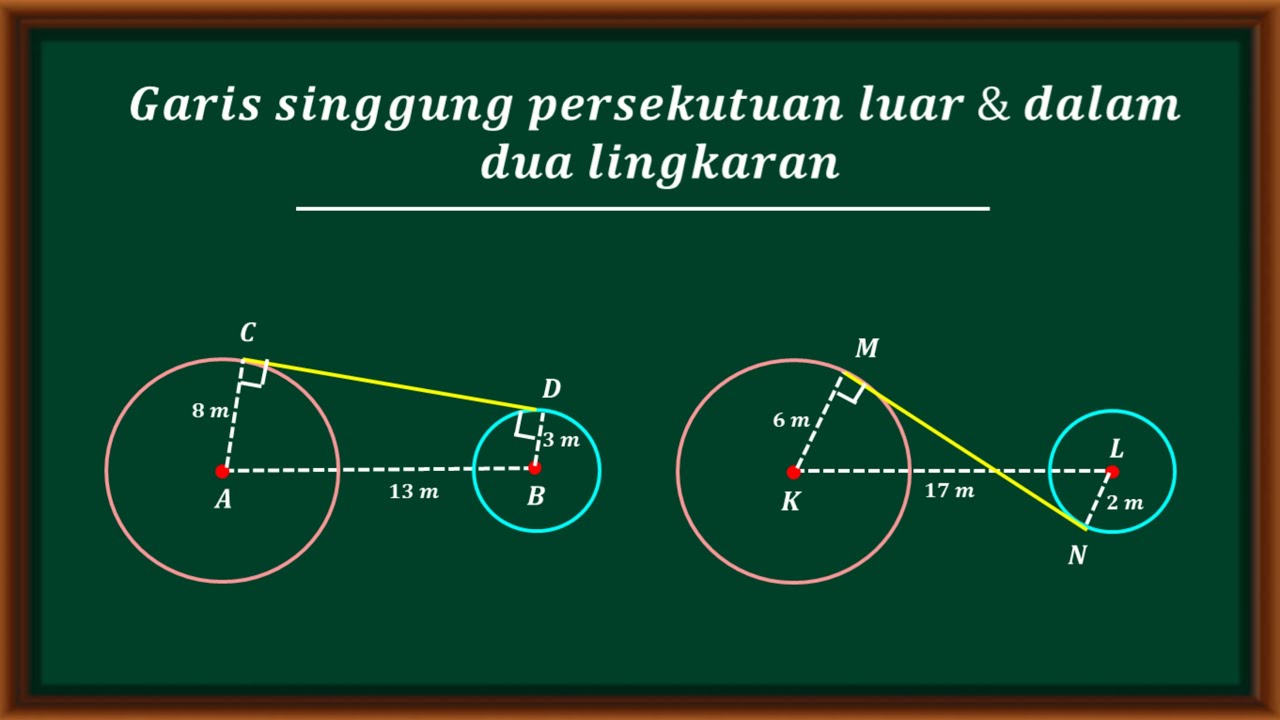
- 😀 For two circles, the formula for the length of a common internal tangent involves the Pythagorean Theorem and the difference in the radii.
- 😀 For two circles, the formula for the length of a common external tangent involves the Pythagorean Theorem and the sum of the radii of the circles.
Q & A
What is the definition of a tangent line to a circle?
-A tangent line to a circle is a straight line that touches the circle at exactly one point, called the point of tangency.
What is the relationship between a tangent line and the radius of a circle at the point of tangency?
-The tangent line is always perpendicular to the radius of the circle at the point of tangency, forming a right angle (90 degrees).
What is the significance of the Pythagorean theorem in the context of tangents to a circle?
-The Pythagorean theorem can be used to calculate the length of a tangent line from a point outside the circle. It relates the distance from the external point to the center of the circle, the radius of the circle, and the length of the tangent.
What formula is used to calculate the length of a tangent from an external point?
-The length of the tangent, AB, can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem: AB = √(AP² - BP²), where AP is the distance from the external point to the center of the circle and BP is the radius of the circle.
What does the term 'internal tangent' refer to in geometry?
-An internal tangent is a line that touches two circles at exactly one point, and the line lies between the circles, passing through the region between their centers.
How do you calculate the length of an internal tangent between two circles?
-The length of an internal tangent can be calculated using the formula: AB = √(PR² - (R1 + R2)²), where PR is the distance between the centers of the two circles, and R1 and R2 are the radii of the two circles.
What is an external tangent between two circles, and how is its length determined?
-An external tangent is a line that touches two circles at exactly one point, and the line lies outside both circles. Its length can be calculated using the formula: AB = √(PR² - (R1 - R2)²), where PR is the distance between the centers, and R1 and R2 are the radii of the two circles.
What is Pitot’s theorem, and what does it describe?
-Pitot’s theorem applies to a tangential quadrilateral, which is a quadrilateral where all sides are tangent to a circle. The theorem states that the sum of the lengths of opposite sides is equal: AB + CD = AD + BC.
How can Pitot’s theorem be used to solve problems involving tangents in a quadrilateral?
-Pitot’s theorem can be used to solve for missing side lengths in a tangential quadrilateral by setting up the equation AB + CD = AD + BC, where the lengths of the sides can be substituted to find unknown values.
How is the Pythagorean theorem applied to solve the length of a tangent line in the example where the radius is 7 cm and the distance from the external point is 25 cm?
-In this example, the Pythagorean theorem is used to calculate the length of the tangent, PB, with the formula PB = √(AP² - r²). Given AP = 25 cm and r = 7 cm, we calculate PB = √(25² - 7²) = √(625 - 49) = √576 = 24 cm.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Garis singgung persekutuan luar dan garis singgung persekutuan dalam dua lingkaran

Southeast Asian Mathematical Olympiad Competition (SEAMO) Training 2022 - Paper D

Persamaan Garis Singgung Lingkaran Yang Melalui Titik Pada Lingkaran : Matematika Peminatan Kelas 11

Materi Matematika Kelas 8: Lingkaran

Lingkaran Bagian 5 - Persamaan Garis Singgung Melalui Titik Pada Lingkaran

Persamaan Lingkaran Pusat (0, 0) dan jari jari r
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)