El condensador
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the basic principles of capacitors, explaining how they store electrical charge between two metallic plates separated by an insulator. When a potential difference is applied, a field is created, and charge accumulates on the plates. The video covers key concepts like capacitance, charging time, and the relationship with circuit resistance, as well as the units used for measuring capacitance. It also touches on how capacitors behave differently in DC circuits and hints at further exploration of AC circuits. The video concludes with a practical circuit diagram demonstrating the capacitor in use.
Takeaways
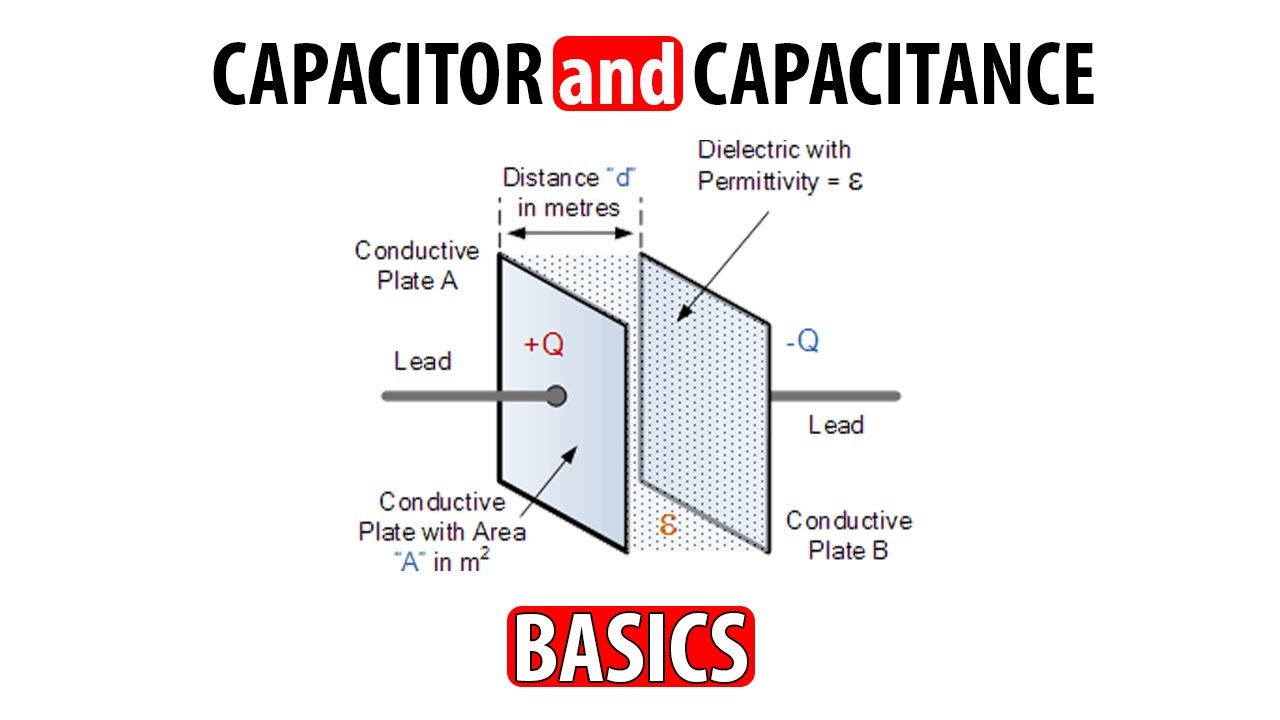
- 😀 A capacitor consists of two metallic plates separated by an insulating material, like air or other dielectrics.
- 😀 When a potential difference is applied, positive and negative charges accumulate on the plates, creating an electric field.
- 😀 Even after the power is turned off, the charges remain stored on the plates due to the electric field.
- 😀 A capacitor is defined by its ability to store electric charge, which is measured by its capacitance, denoted as 'C'.
- 😀 The capacitance value is measured in farads (F), but smaller units like microfarads (µF), nanofarads (nF), and picofarads (pF) are commonly used.
- 😀 In a DC circuit, the capacitor's charging time depends on the circuit's resistance and capacitance, following an exponential curve.
- 😀 The RC time constant (R * C) determines how quickly the capacitor charges, with approximately 63% of the charge accumulated in one time constant.
- 😀 Capacitors are typically used in DC circuits to store energy temporarily.
- 😀 A typical capacitor circuit is represented by two parallel plates and can be shown with a power source and switch in a diagram.
- 😀 The behavior of capacitors in AC (alternating current) circuits differs from their behavior in DC circuits and will be explored in future videos.
Q & A
What is a capacitor?
-A capacitor is an electronic component that stores electrical charge. It consists of two metal plates separated by an insulating material, called a dielectric.
How does a capacitor work?
-When a voltage difference is applied across the plates of a capacitor, positive charges accumulate on one plate and negative charges on the other. This creates an electric field between the plates, allowing the capacitor to store energy.
What happens when the voltage is removed from a capacitor?
-When the voltage is removed, the accumulated charges on the plates remain due to the electric field, meaning the capacitor continues to store energy even without a voltage applied.
What is the function of the dielectric material in a capacitor?
-The dielectric material, such as air or another insulating material, prevents the plates from touching each other, ensuring that the capacitor can store a charge by maintaining a separation between the conductive plates.
What is the relationship between resistance, capacitance, and charging time?
-The time it takes for a capacitor to charge depends on the circuit's resistance and capacitance. The time constant (τ) is calculated as the product of resistance (R) and capacitance (C), and it determines how quickly the capacitor charges.
How is the charge stored in a capacitor measured?
-The amount of charge a capacitor can store is measured by its capacitance, typically in farads (F). This is defined as the amount of charge stored per unit of voltage.
What units are commonly used to measure capacitance?
-Capacitance is typically measured in farads (F), with practical units being microfarads (µF), picofarads (pF), and nanofarads (nF), depending on the scale of the capacitor.
What is the significance of the time constant in capacitor charging?
-The time constant (τ = RC) determines how quickly a capacitor charges. After a time equal to three times the time constant, the capacitor is considered fully charged.
How is a capacitor represented in a circuit diagram?
-In a circuit diagram, a capacitor is represented by two parallel lines, symbolizing the conductive plates, and the connections to the circuit components.
What happens when a capacitor is used in an alternating current (AC) circuit?
-A capacitor behaves differently in an AC circuit, as the direction of current alternates, affecting how the capacitor charges and discharges. This difference will be explored in more detail in future content.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
What is Capacitor? What is Capacitance?

Electrical Engineering: Ch 6: Capacitors (1 of 26) Basics (What is a Capacitor?)

Capacitors and capacitance | Circuits | Physics | Khan Academy

Capacitors and Inductors (Circuits for Beginners #19)

Capacitores - Eletrostática

Lecture 3.1: Introduction to Capacitors (General Physics 2)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)