Why is Yemen at war? | Start Here
Summary
TLDRThe war in Yemen, described as the world's worst humanitarian crisis, has been fueled by a complex web of political and military forces. Once a prosperous country, Yemen has descended into chaos due to internal power struggles and the intervention of external powers like Saudi Arabia and Iran. The conflict, which involves multiple factions including the Houthis, former president Saleh's allies, and various armed groups, has led to widespread suffering, with millions of Yemenis in desperate need of aid. Despite efforts for peace, the war remains a brutal stalemate, with international powers contributing to the devastation. A diplomatic solution is the only hope for ending this nightmare.
Takeaways
- 😀 Yemen is facing the worst humanitarian crisis in the world, with millions struggling to survive amidst a brutal war.
- 😀 Yemen's complex conflict involves multiple players: former president Saleh, the Houthis, Saudi Arabia, and other regional powers.
- 😀 Ali Abdullah Saleh, Yemen's former president, ruled for 20 years before being forced out during the Arab Spring of 2011.
- 😀 After Saleh's removal, the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) helped install a new government, but Yemen continued to suffer under President Hadi.
- 😀 The Houthis, a Shia Muslim group from northern Yemen, began to rebel against the government, leading to their takeover of Yemen's capital, Sanaa, in 2014.
- 😀 Saudi Arabia formed a coalition to restore Hadi's government, citing concerns over Iran’s growing influence and regional stability.
- 😀 The Saudi-led coalition launched airstrikes against the Houthis and other targets, including hospitals and schools, resulting in widespread civilian casualties.
- 😀 The humanitarian crisis is exacerbated by blockades on Yemen’s ports, which prevent the delivery of essential supplies and aid.
- 😀 Yemen has a severe shortage of medical supplies, widespread cholera outbreaks, and 24 million people dependent on humanitarian aid.
- 😀 The war has evolved into a proxy conflict between Saudi Arabia and Iran, with both powers backing opposing factions in Yemen.
- 😀 Despite numerous peace talks and ceasefires brokered by the UN, the war remains at a stalemate with no clear resolution in sight.
Q & A
What is the current humanitarian crisis in Yemen?
-Yemen is facing the worst humanitarian crisis in the world, with 24 million people, nearly the entire population, in need of humanitarian aid. The crisis is worsened by relentless airstrikes, a blockade preventing supplies from entering the country, and the destruction of essential infrastructure such as hospitals and schools.
How did Yemen's political instability lead to the ongoing war?
-Yemen’s political instability began with the 2011 Arab Spring protests, which ousted long-time president Ali Abdullah Saleh. The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) helped install a new government under President Hadi, but it failed to address deep-rooted issues, leading to growing unrest. In 2014, the Houthi rebels took control of the capital, Sanaa, which led to President Hadi fleeing to Saudi Arabia, sparking a Saudi-led military intervention.
Who are the Houthis and what role do they play in the Yemen conflict?
-The Houthis are a Shia Muslim group from northern Yemen who feel marginalized by the central government. They played a significant role in the 2011 Arab Spring protests against Saleh and later took over Yemen’s capital in 2014. They are now one of the main factions in the ongoing war and control significant parts of the country, including the capital Sanaa.
Why did Saudi Arabia intervene in the war in Yemen?
-Saudi Arabia led an intervention in Yemen to restore the government of President Hadi, protect its southern border, prevent Yemen from fragmenting, and contain the influence of Iran in the region. The intervention has included a series of airstrikes, with the aim of defeating the Houthi rebels who had taken control of much of Yemen.
What has been the impact of the Saudi-led coalition's airstrikes in Yemen?
-The Saudi-led coalition's airstrikes have resulted in significant civilian casualties and widespread destruction of infrastructure. More than 19,000 airstrikes have been reported, targeting various sites, including hospitals and schools. Rights groups accuse the coalition of causing severe harm to civilians, exacerbating the humanitarian crisis.
How has the blockade imposed by the Saudi-led coalition affected Yemen?
-The Saudi-led coalition imposed a blockade around Yemen in 2015, severely restricting the movement of goods, including essential humanitarian aid. This has made it nearly impossible for supplies to enter the country, worsening the famine and disease outbreaks. The blockade has also led to shortages in medicines, food, and basic necessities.
What role does Iran play in the Yemen conflict?
-Iran is accused of supporting the Houthis, providing them with military aid and weapons, although Iran denies direct military involvement. Saudi Arabia and other coalition members view Iran's backing of the Houthis as a way to expand Iranian influence in the region, framing the conflict as a proxy war between Sunni-majority Saudi Arabia and Shia-majority Iran.
How have the Houthis responded to the Saudi-led intervention?
-The Houthis have continued to fight against the Saudi-led coalition despite heavy airstrikes and military pressure. In 2017, they broke with their former ally, Ali Abdullah Saleh, after he switched sides and sought peace talks with the coalition. The Houthis killed him soon after, and they now control much of northern Yemen, including the capital, Sanaa.
What is the current status of the war in Yemen?
-As of now, the war has reached a stalemate, with both sides unable to decisively win. The Houthis control significant territories in the north, while the Saudi-led coalition supports the Hadi government, which controls parts of the south. Despite numerous peace efforts, including UN-backed ceasefire negotiations, the conflict continues with no clear resolution in sight.
What are the main humanitarian needs in Yemen?
-Yemen’s humanitarian needs are vast, with millions in need of food, clean water, medical supplies, and shelter. The country faces widespread malnutrition, a cholera epidemic, and a lack of basic healthcare due to the destruction of hospitals and shortages of medical supplies. Around 11 million people, including many children, urgently require humanitarian assistance.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

What’s happening in Sudan’s civil war? | Start Here

How This Rebel Militia is Transforming the Middle East

The state of the Syrian refugee crisis
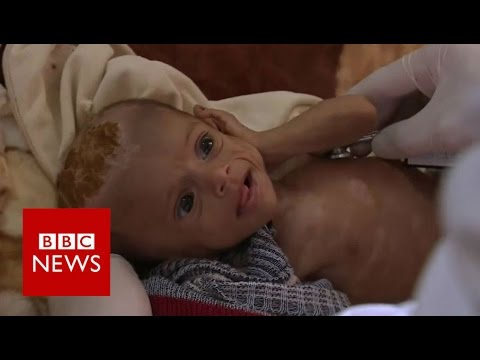
Yemen's war leaves children on the brink of famine - BBC News

Detik-detik Serangan Udara Israel Bombardir Gaza Tengah, Warga Berlarian

Explainer: Why is the humanitarian crisis in Yemen getting worse?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)