BELAJAR FOTOGRAFI DALAM 10 MENIT
Summary
TLDRIn this beginner-friendly photography tutorial, Glenn Prasetya breaks down the basics of photography in just 10 minutes. He covers the essential concepts of ISO, aperture (diaphragm), and shutter speed, explaining how each impacts exposure and image quality. Glenn emphasizes the importance of experimenting with these settings to improve one's skills. He offers practical advice on how to adjust these settings based on lighting conditions and subjects, and encourages viewers to practice by taking photos themselves. The video aims to help newcomers grasp the core concepts and start capturing better photos right away.
Takeaways
- 😀 ISO controls your camera’s sensitivity to light. Lower ISO (e.g., 100) captures less light, while higher ISO (e.g., 1600) captures more light but may introduce noise.
- 😀 In bright conditions, use a low ISO (e.g., 100) to avoid overexposure. In low light, increase the ISO to capture more light, but be mindful of noise.
- 😀 Aperture (Diafragma) controls the amount of light entering the camera. A larger aperture (e.g., f/2.8) lets in more light and creates a shallow depth of field, while a smaller aperture (e.g., f/16) lets in less light and keeps more of the image in focus.
- 😀 A wide aperture (small f-number) is ideal for portrait photography to blur the background, while a narrow aperture (large f-number) is great for landscape photography where you want everything in focus.
- 😀 Shutter speed controls how long the camera’s shutter is open. Fast shutter speeds (e.g., 1/500s) freeze motion, while slower speeds (e.g., 1/50s) can capture motion blur.
- 😀 Use a fast shutter speed (e.g., 1/500s or higher) when photographing fast-moving subjects to avoid motion blur.
- 😀 Slow shutter speeds (e.g., 1 second) are useful for capturing motion, like waterfalls or night photography, but require a tripod to avoid camera shake.
- 😀 ISO, aperture, and shutter speed work together in the 'Exposure Triangle' to determine your image’s exposure. Adjusting one will impact the others.
- 😀 In low light, if adjusting ISO and aperture doesn't work, increase the shutter speed to allow more light to hit the sensor.
- 😀 When shooting in bright conditions, reduce ISO, increase shutter speed, or use a smaller aperture to avoid overexposing the image.
- 😀 Practice is essential—experiment with different camera settings, make mistakes, and learn through experience. Don't be afraid to try new things.
Q & A
What is the importance of ISO in photography?
-ISO in photography refers to the camera sensor's sensitivity to light. A higher ISO allows the camera to capture more light in low-light conditions, but can also introduce grain (noise) into the image. Lower ISO values result in clearer, more detailed images, but require more light to achieve proper exposure.
How does ISO affect image quality?
-ISO affects the clarity of an image by introducing noise (grain) at higher values. While higher ISO values allow you to shoot in lower light, they can make the image appear grainy or less sharp. It's recommended to use the lowest ISO possible for clearer, more detailed images.
What is aperture and how does it affect exposure?
-Aperture refers to the size of the opening in the camera lens that controls the amount of light entering the camera. A larger aperture (lower f-number) lets in more light, which is useful in low-light conditions. A smaller aperture (higher f-number) lets in less light, resulting in a darker image.
How does aperture affect depth of field?
-Aperture also impacts depth of field, which is the range of distance that appears in focus in the image. A larger aperture (smaller f-number) results in a shallow depth of field, where the subject is in focus, but the background is blurred. A smaller aperture (higher f-number) increases the depth of field, making both the subject and background appear in focus.
What is shutter speed and how does it affect the image?
-Shutter speed is the amount of time the camera's shutter is open, allowing light to hit the sensor. Faster shutter speeds (e.g., 1/500 seconds) freeze motion, while slower shutter speeds (e.g., 1/30 seconds) allow more light in and can capture movement, potentially creating blur.
How does shutter speed affect motion blur?
-Slow shutter speeds allow more time for movement to be recorded on the sensor, resulting in motion blur. This is useful for capturing motion in a dynamic way, such as the movement of water in a waterfall. Fast shutter speeds freeze motion, preventing blur and capturing sharp images of fast-moving subjects.
What should you do if your image appears too dark?
-If your image is too dark, you can increase the ISO setting, open the aperture to a larger value (smaller f-number), or decrease the shutter speed to allow more light to reach the sensor. Be careful with increasing ISO too much, as it may introduce noise.
What can you do if your image appears too bright?
-If your image is too bright, reduce the ISO setting, close the aperture to a smaller value (higher f-number), or increase the shutter speed to reduce the amount of light hitting the sensor. Adjusting these settings will help balance the exposure.
How do you balance ISO, aperture, and shutter speed for proper exposure?
-To achieve proper exposure, you need to balance ISO, aperture, and shutter speed, which are known as the exposure triangle. If you change one of these settings, you may need to adjust the others to maintain correct exposure. For example, increasing ISO might require a faster shutter speed or smaller aperture to prevent overexposure.
How does shooting in low-light conditions affect your settings?
-In low-light conditions, you may need to increase the ISO to capture more light. You may also need to use a larger aperture (smaller f-number) to let more light in. If the image is still too dark, slowing down the shutter speed can help, but you should be cautious about camera shake, especially if shooting handheld.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
TIPS EDITING SEDERHANA UNTUK FOTOGRAFI PEMULA | 5 basic editing in photoshop for your photography
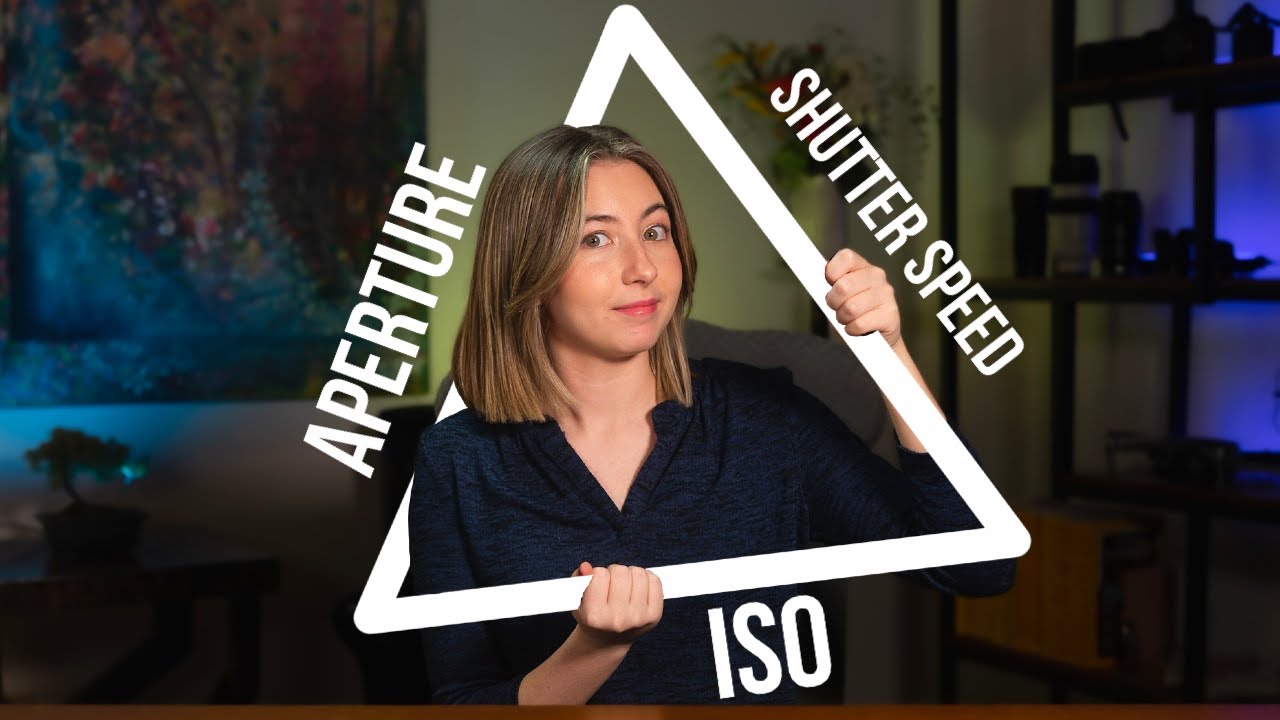
APERTURE, SHUTTER SPEED AND ISO/ THE EXPOSURE TRIANGLE MADE EASY!
TIPS FOTO PRODUK MENGGUNAKAN HP DENGAN PERALATAN SEADAANYA

How to Shoot Manual in 10 Minutes - Beginner Photography Tutorial

What is Photography?

I Tried Film Photography & Realized Our Problem...
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)