What is a Clock?
Summary
TLDRThis lecture on digital electronics explains the fundamental role of clock signals in sequential circuits. The clock controls the timing of flip-flops, ensuring their outputs are stable and predictable. It covers the relationship between clock frequency and circuit speed, and introduces the concept of duty cycle, which is the ratio of time the clock is high to the total period. The video also touches on edge triggering, which determines when flip-flops update their state based on rising or falling clock edges. Understanding these principles is essential for designing synchronized digital circuits.
Please replace the link and try again.
Q & A
What is the role of the clock in sequential circuits?
-The clock in sequential circuits controls the timing of operations, ensuring that processes do not occur randomly. It dictates when the inputs are processed and when outputs are generated, providing synchronization to the circuit.
How does the clock signal work in digital circuits?
-The clock signal oscillates between a low state (0) and a high state (1). It repeats this cycle continuously, with the duration of the high phase being equal to the low phase, allowing the circuit to operate in a structured sequence.
What is the relationship between time period and frequency of a clock?
-The frequency (F) of the clock is the inverse of the time period (T). Mathematically, this is expressed as F = 1/T, meaning that if the time period is reduced, the frequency increases, making the circuit operate faster.
Why is it necessary to control the clock frequency in digital circuits?
-Controlling the clock frequency allows the circuit to operate at the desired speed. By increasing the frequency (decreasing the time period), the circuit can process inputs and produce outputs more quickly.
What is a flip-flop, and how does it interact with the clock signal?
-A flip-flop is a sequential circuit element that stores binary data. It only changes its state when the clock signal reaches a specific phase, typically when the clock is high or transitioning from low to high, depending on the design.
What is meant by the term 'duty cycle' in a clock signal?
-The duty cycle refers to the proportion of time the clock signal is high compared to the total time period. For a 50% duty cycle, the clock is high for half of the time period and low for the other half.
How does a clock signal with a 50% duty cycle function?
-A clock with a 50% duty cycle is high for half of its time period (T/2) and low for the other half. This means the high and low phases are of equal duration, making the signal balanced.
What is the difference between rising edge and falling edge triggering in flip-flops?
-Rising edge triggering occurs when the clock transitions from low to high, while falling edge triggering occurs when the clock transitions from high to low. Both types of edge triggering dictate when a flip-flop responds to the clock signal.
Why is it important for the output of a sequential circuit to be controlled by the clock?
-The clock ensures that the output of a sequential circuit does not change randomly. It forces the output to update only at specific times, reducing errors caused by stray signals or processes operating out of sync.
How does increasing the clock frequency affect the operation of a digital circuit?
-Increasing the clock frequency decreases the time period, which causes the circuit to perform tasks faster. This can speed up the processing and execution of the circuit's operations.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Introduction to Sequential Circuits | Digital Electronics

Introduction to Sequential Circuits | Important
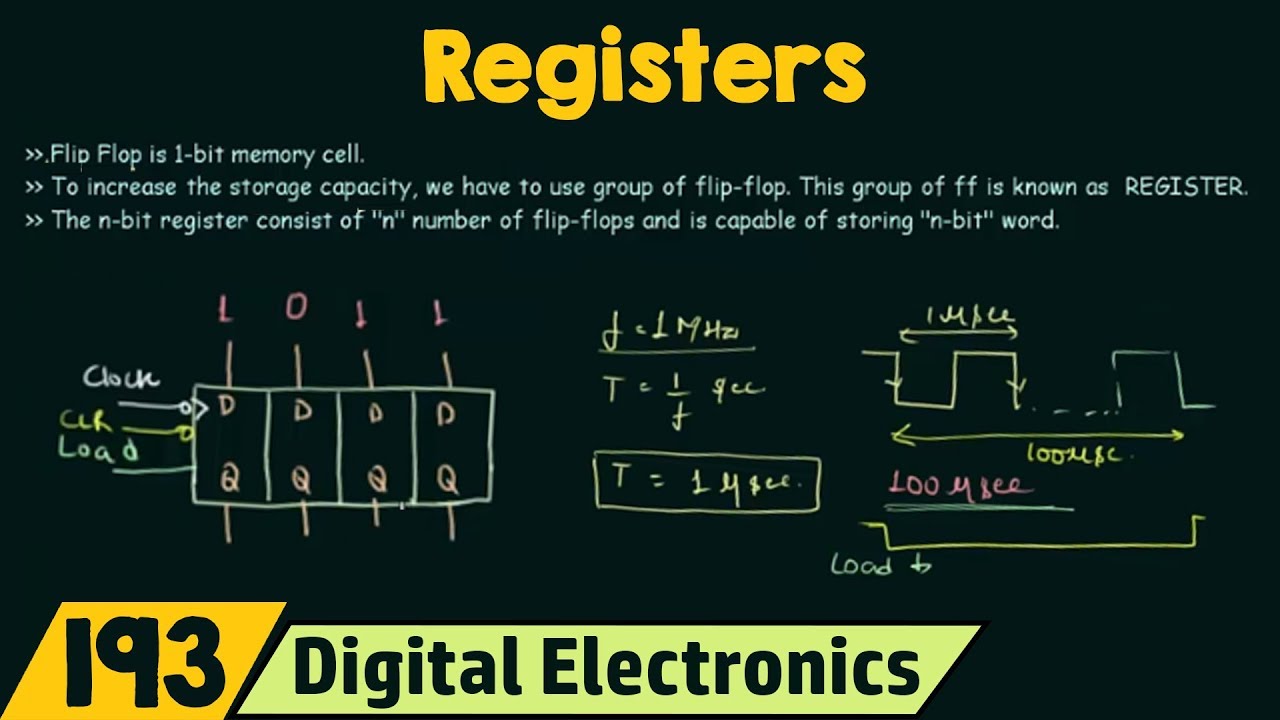
Introduction to Registers

Penjelasan D Flip Flop
Simulasi Rangkaian JK Flip-flop, RS Flip-flop, dan D Flip-flop ( Faishal Satria G 2211181006 )

Part 5.2 #Latches and #FlipFlops #SequentialCircuits in Digital Electronics in Hindi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)