Konsep dan Cara Kerja TCP/IP ( dasar jaringan komputer )
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an introduction to TCP/IP, explaining its role as a foundational protocol suite for computer networking. It covers key concepts such as data communication, network protocols, and the essential layers of TCP/IP: Physical, Link, Network, Transport, and Application. The speaker highlights the importance of each layer in ensuring reliable data transmission and solving common network issues like packet loss and routing. The video is aimed at beginners, offering a clear explanation of how TCP/IP works and its significance in modern computer networks.
Takeaways
- 😀 TCP/IP is a fundamental concept in networking that ensures data communication between computers through specific protocols.
- 😀 Data communication in networks involves transferring information like files, photos, or videos, and sharing hardware resources such as printers or scanners.
- 😀 Communication issues such as data corruption, misdelivery, and loss can arise, especially when devices are on different networks. These issues are mitigated by TCP/IP protocols.
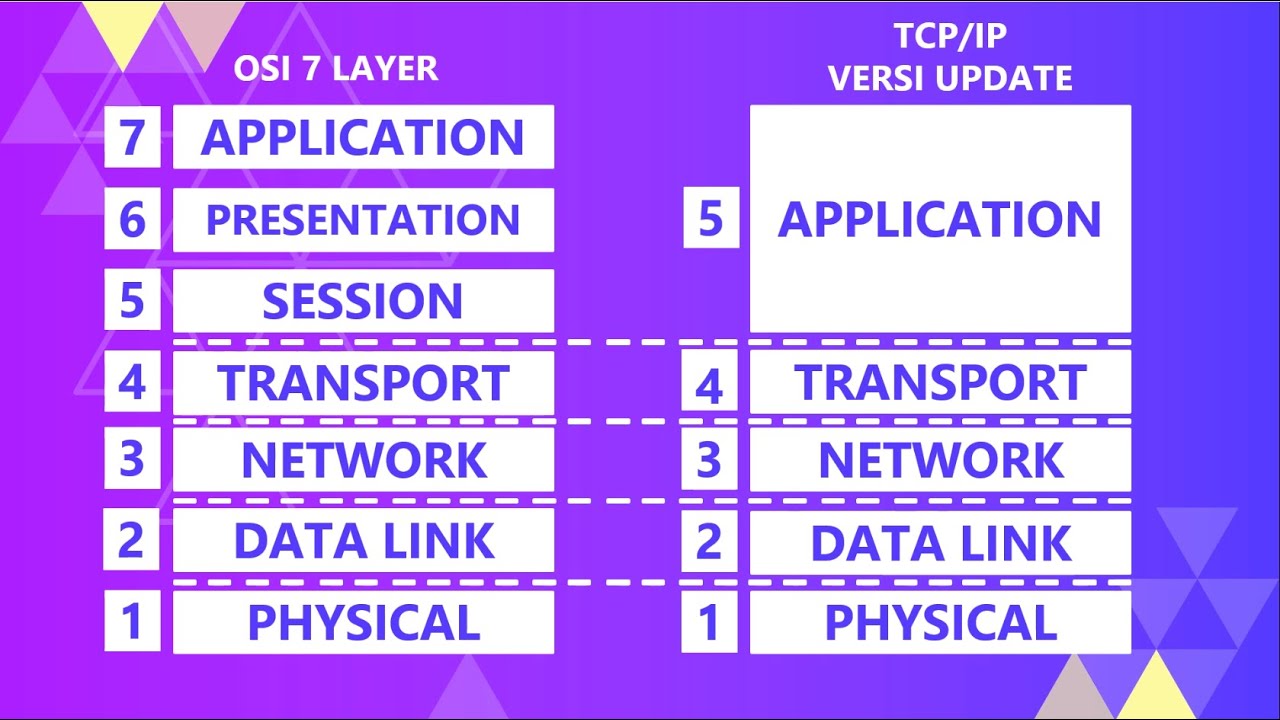
- 😀 TCP/IP protocols are structured in layers: Physical, Link, Network, Transport, and Application, each handling specific aspects of data transmission.
- 😀 The Physical Layer handles the hardware of networks, such as cables, routers, and access points, facilitating the physical connection between devices.
- 😀 The Link Layer ensures communication between devices on the same network using protocols like Ethernet for wired connections or Wi-Fi for wireless communication.
- 😀 The Network Layer is responsible for routing data between different networks using IP addresses, ensuring data travels across various networks correctly.
- 😀 The Transport Layer guarantees the integrity and reliability of data, using protocols like TCP (connection-oriented) and UDP (connectionless).
- 😀 The Application Layer handles data intended for specific applications (e.g., HTTP for web browsing, SMTP for email), ensuring the correct application processes the data.
- 😀 TCP is a connection-oriented protocol, ensuring reliable, error-free data transfer, while UDP is faster but does not guarantee data integrity, often used in real-time applications like live streaming.
- 😀 End-to-end communication in networking involves the systematic transmission of data through all layers, from the Application Layer to the Physical Layer, ensuring the correct routing and delivery of data.
Q & A
What is the significance of understanding TCP/IP in networking?
-Understanding TCP/IP is crucial because it forms the foundation for many advanced networking concepts. Without grasping these basics, it would be difficult to understand how data is communicated across networks and how various devices interact with one another.
How does data communication work in a computer network?
-Data communication involves transmitting data between computers over a network using a specific protocol. The data can include files, images, videos, or hardware resources. Proper protocols ensure data reaches the correct destination, even if devices use different languages or technologies.
What role do protocols play in network communication?
-Protocols are essential in network communication as they define the rules for data exchange between devices. They ensure that data is sent and received in a way that all devices on the network can understand and process, much like a common language for communication.
What are the layers of the TCP/IP model?
-The TCP/IP model consists of five layers: Physical, Link, Network, Transport, and Application. Each layer handles specific tasks, such as data transmission, routing, and ensuring data integrity, enabling flexible and efficient communication across networks.
What is the Physical Layer responsible for in the TCP/IP model?
-The Physical Layer handles the hardware components responsible for physically connecting devices, such as cables, wireless devices, and network interface cards. It ensures that signals are transmitted correctly over the chosen medium.
How does the Link Layer function in TCP/IP?
-The Link Layer is responsible for connecting devices within the same network, typically using protocols like Ethernet for wired connections or WiFi for wireless communication. It manages how data is packaged and transmitted across a local network.
What is the role of the Network Layer in TCP/IP communication?
-The Network Layer is responsible for routing data across different networks. It uses IP addresses to ensure that data packets are directed to the correct network and the correct destination device, even if they are geographically distant.
How do the Transport Layer protocols, TCP and UDP, differ?
-TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is connection-oriented, meaning it ensures reliable data delivery and maintains data integrity by verifying that the data has arrived intact. UDP (User Datagram Protocol), on the other hand, is connectionless and does not guarantee data delivery, making it faster but less reliable.
What does the Application Layer do in the TCP/IP model?
-The Application Layer interacts with end-user applications, such as web browsers, email clients, and file transfer tools. It ensures that data is properly formatted for the specific application and that the correct protocol (like HTTP or FTP) is used for communication.
Why is modularity important in the TCP/IP model?
-Modularity in TCP/IP makes the model flexible and efficient. Each layer works independently, handling specific tasks without needing to understand the workings of other layers. This modular approach allows for easier troubleshooting, updates, and the integration of new technologies into existing systems.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Standar Komunikasi Jaringan Komputer | Network Fundamental Learning Series #4

Jaringan Komputer dan Internet - Jaringan Komputer dan Manfaatnya - Informatika Kelas XII

System Design Concepts: Networking Essentials

Redes de computadores - Protocolo TCP IP - Informática para concursos - Professor Danilo Vilanova

Lec-3: TCP/IP Protocol Suite | Internet Protocol Suite | OSI vs TCP/IP
Apa itu Protokol TCP/IP?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)