Mundell Fleming Model (3) : Nilai Tukar Tetap Fixed
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses the dynamics of fixed exchange rates, detailing how central banks manage currency values through buying and selling foreign currencies. It explains the implications of monetary and fiscal policies under a fixed exchange regime, including the effects of expansive fiscal policies on money supply and output, as well as responses to import restrictions. The analysis highlights how these policies can shift the LM curve and influence equilibrium in currency exchange, emphasizing differences between fixed and floating exchange rate systems. Overall, it illustrates the intricate relationship between exchange rates, government policies, and economic stability.
Takeaways
- 😀 Fixed exchange rates require central banks to intervene by buying or selling domestic currency to maintain set values.
- 😀 When exchange rates exceed fixed values, arbitrageurs can profit by selling foreign currency to the central bank.
- 😀 An increase in money supply by the central bank can lead to a rightward shift in the LM curve, influencing equilibrium exchange rates.
- 😀 If the exchange rate is below the fixed value, citizens will buy foreign currency from the central bank, causing money supply to decrease.
- 😀 Expansionary fiscal policy shifts the IS curve right, potentially increasing output and requiring adjustments in the LM curve to maintain fixed exchange rates.
- 😀 Under a fixed exchange rate regime, expansionary fiscal policy can lead to higher output but requires central bank action to stabilize currency values.
- 😀 Monetary policy that increases money supply causes the LM curve to shift right, affecting exchange rates and net exports.
- 😀 Import restrictions can shift the IS curve left or right, depending on their effects on output and net exports under different exchange rate regimes.
- 😀 In a fixed exchange rate environment, government interventions are necessary to counteract the effects of expansionary policies on currency stability.
- 😀 The overall impact of fiscal and monetary policies differs significantly between fixed and floating exchange rate regimes.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video regarding fixed exchange rates?
-The video explains how fixed exchange rates operate, including the role of central banks in maintaining these rates through buying and selling domestic and foreign currencies.
How does a central bank intervene when the exchange rate exceeds the fixed rate?
-When the exchange rate exceeds the fixed rate, the central bank buys foreign currency and sells its own, which increases the domestic money supply and can lead to a rightward shift in the LM curve.
What happens to the money supply when the exchange rate falls below the fixed rate?
-When the exchange rate falls below the fixed rate, the central bank sells foreign currency in exchange for domestic currency, reducing the money supply and shifting the LM curve to the left.
What are the consequences of an expansionary fiscal policy under a fixed exchange rate regime?
-Under an expansionary fiscal policy, the IS curve shifts right, which could increase the exchange rate. To maintain the fixed rate, the central bank must adjust the LM curve accordingly.
How does the video illustrate the interaction between fixed exchange rates and fiscal policy?
-It uses graphical representations to show how shifts in the IS and LM curves affect equilibrium exchange rates and output in the context of fixed exchange rates.
What is the impact of monetary policy under a fixed exchange rate regime?
-Expansionary monetary policy leads to an increase in the money supply, which can shift the LM curve to the right. However, the central bank's actions will ensure that the fixed exchange rate is maintained.
What role do arbitrageurs play in the context of fixed exchange rates?
-Arbitrageurs buy foreign currency in the forex market and sell it to the central bank for a profit when the market rate deviates from the fixed rate, which helps to balance the exchange rate.
What effect does import restriction have on the fixed exchange rate system?
-Import restrictions can shift the IS curve and potentially increase the exchange rate. To counteract this, the central bank may need to sell domestic currency to keep the rate stable.
Can fiscal policies effectively change output under a fixed exchange rate?
-Yes, the video suggests that while fiscal policies may not alter output in floating exchange rate systems, they can lead to changes in output under fixed exchange rates.
What is the difference in outcomes between floating and fixed exchange rate systems regarding fiscal policy?
-In a floating exchange rate system, fiscal policies typically do not affect output, whereas in a fixed exchange rate system, they can lead to changes in output and adjustments in the exchange rate.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
VALUTA ASING DAN DEVISA - EKONOMI - MATERI UTBK SBMPTN DAN SIMAK UI

What is a Central Bank? | Back to Basics

Foreign Exchange Risk Management: How to Get Paid in Foreign Currencies

Sistem Moneter Internasional dalam Mata Kuliah Bisnis Internasional
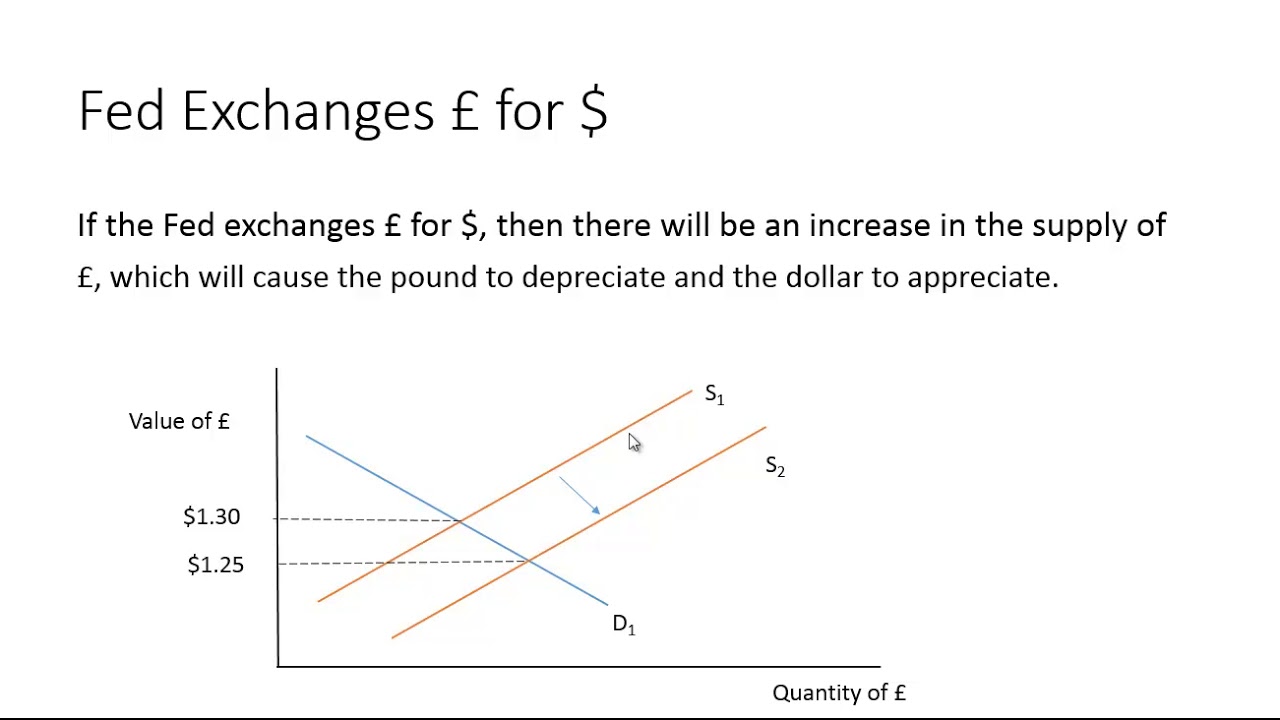
Foreign Exchange Government Intervention

What is Forex Market | How Forex Market Works | Foreign Exchange Market (हिंदी में )
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)