Proteins: Primary and Secondary Structure | A-level Biology | OCR, AQA, Edexcel
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the hierarchical structure of proteins, detailing the primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures. The primary structure is defined by the unique sequence of amino acids, which determines a protein's function. The secondary structure includes alpha helices and beta pleated sheets, formed through hydrogen bonding between amino acids. These distinct shapes are crucial for protein function, exemplified by collagen's structural role and hemoglobin's oxygen transport capability. Understanding these structures is essential for grasping how proteins operate within biological systems.
Takeaways
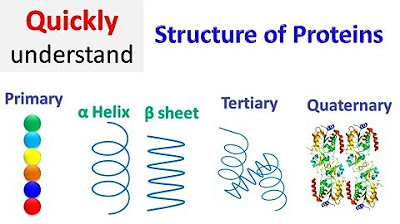
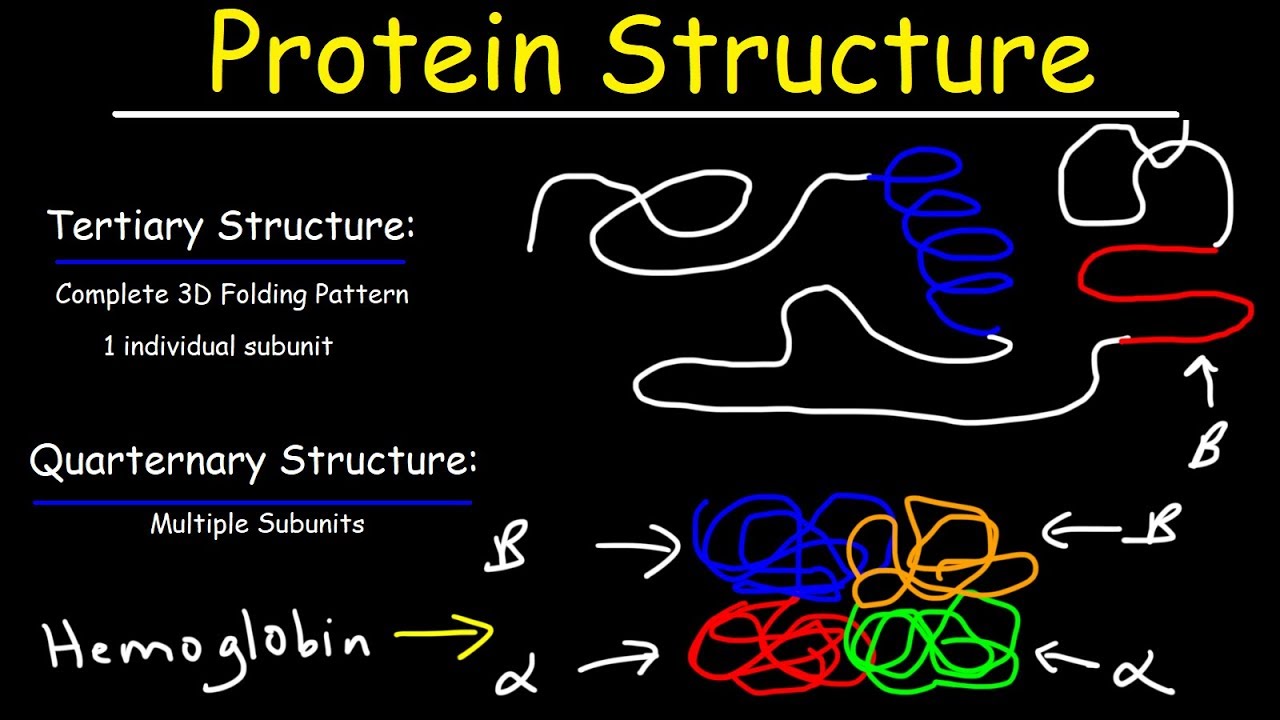
- 😀 Proteins have four structural levels: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary.
- 😀 The primary structure of a protein is its unique sequence of amino acids.
- 😀 There are 20 different amino acids, leading to trillions of possible combinations in proteins.
- 😀 The specific sequence of amino acids determines a protein's unique shape and function.
- 😀 Collagen and hemoglobin are examples of proteins with different structures and functions.
- 😀 The secondary structure involves folding into shapes like alpha helices and beta pleated sheets.
- 😀 Hydrogen bonds form between the NH and CO groups of amino acids, stabilizing secondary structures.
- 😀 Alpha helices appear as coiled shapes, while beta pleated sheets form zigzag patterns.
- 😀 The stability of secondary structures comes from numerous hydrogen bonds throughout the polypeptide.
- 😀 Understanding protein structure is crucial for grasping how proteins function in biological systems.
Q & A
What is the primary structure of a protein?
-The primary structure of a protein is the unique sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain, determining its specific shape and function.
How many naturally occurring amino acids are there?
-There are 20 different naturally occurring amino acids, each contributing to the vast diversity of protein structures.
What examples are given for proteins with different functions?
-Collagen is mentioned as a structural protein, while hemoglobin is highlighted for its role in oxygen transport.
What are the two main types of secondary structure in proteins?
-The two main types of secondary structure are the alpha helix and the beta pleated sheet.
What causes the formation of secondary structures like alpha helices and beta sheets?
-Secondary structures form due to hydrogen bonding between the amino acids in the polypeptide chain.
How does the structure of amino acids contribute to protein folding?
-Each amino acid contains a carboxyl group (CO) and an amino group (NH), which are involved in forming hydrogen bonds, leading to the folding of the chain into secondary structures.
What role do hydrogen bonds play in protein structure?
-Hydrogen bonds are weak interactions that stabilize the secondary structure of proteins, helping maintain their specific shapes.
Can you describe the alpha helix structure?
-The alpha helix is a coiled structure formed when the polypeptide chain twists and hydrogen bonds stabilize the coil.
What does the beta pleated sheet look like?
-The beta pleated sheet consists of amino acids arranged in a zig-zag formation, where segments can line up parallel to each other.
Why is it difficult to document all possible protein combinations?
-The vast number of possible combinations of the 20 amino acids allows for trillions of different sequences, making it nearly impossible to document all proteins.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)