10.SINIF FİZİK 1.DÖNEM 1.YAZILI - 2024 - 2025
Summary
TLDRThis educational video focuses on electrical circuits, explaining the relationships between current, voltage, and the brightness of bulbs in both series and parallel configurations. It discusses how current divides among components and how voltage impacts brightness, emphasizing that parallel connections maintain consistent brightness across bulbs. The video aims to enhance understanding of fundamental electrical concepts, guiding students through practical applications and theoretical insights, while encouraging interaction through feedback on their learning experiences.
Takeaways
- 😀 Current splits in a circuit, with varying paths affecting the flow (2i and 1i).
- 😀 The brightest bulb corresponds to the highest current passing through it.
- 😀 Resistors and identical bulbs in a circuit can help determine brightness based on voltage.
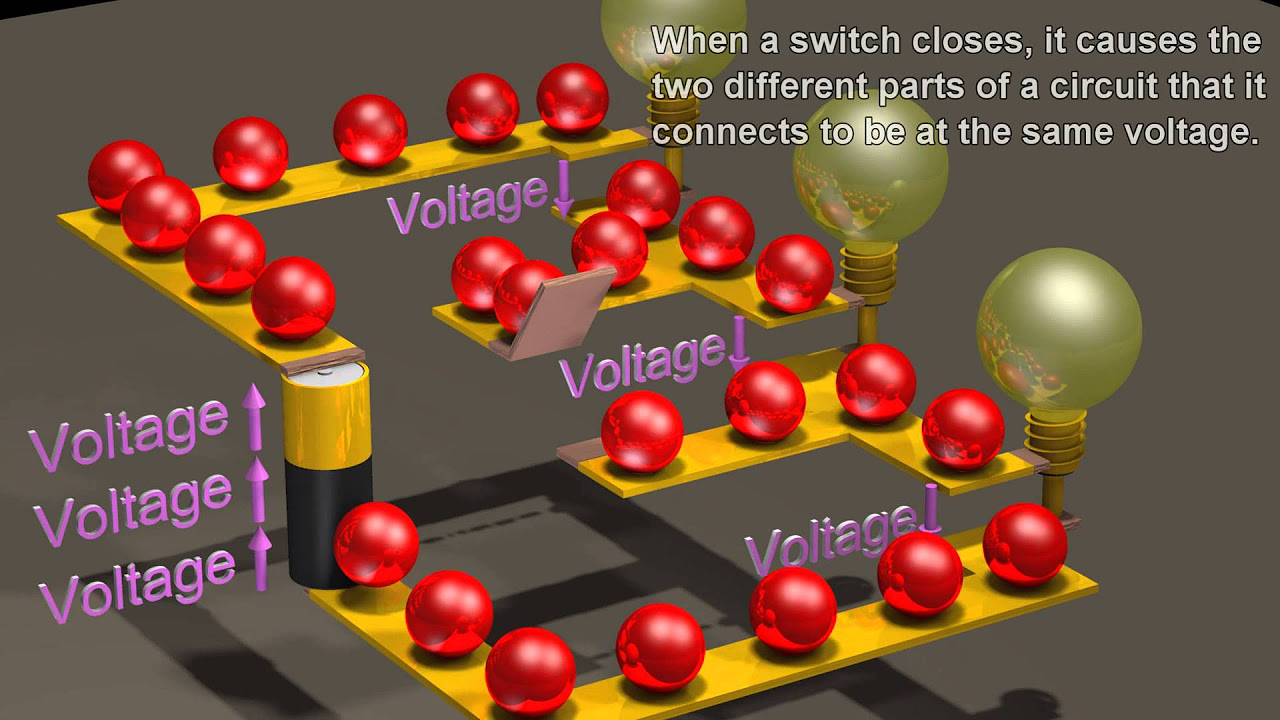
- 😀 Voltage across two points in a circuit is crucial for understanding brightness and current distribution.
- 😀 When bulbs are connected in parallel, their brightness remains consistent regardless of the configuration.
- 😀 If one bulb in a parallel circuit is removed, the others will still function with the same voltage.
- 😀 Series connections distribute voltage equally among bulbs, affecting their brightness.
- 😀 The total voltage in a series connection is the sum of the voltages across each component.
- 😀 A bulb's brightness increases with higher voltage applied to it.
- 😀 Understanding circuit connections is key to predicting how changes affect brightness and current.
Q & A
What is the significance of the current distribution in the circuit described?
-The current distribution is crucial as it determines how the current flows through different branches of the circuit, impacting the brightness of the connected lamps.
How does the arrangement of the lamps affect their brightness?
-In a parallel arrangement, the brightness of the lamps remains consistent regardless of how many lamps are connected, as they each receive the full voltage.
What happens to the current when lamps are added in series?
-When lamps are added in series, the total voltage is divided among them, resulting in reduced current for each lamp, which generally leads to dimmer brightness.
How can the voltage across two points in the circuit be calculated?
-The voltage across two points can be calculated based on the total voltage supplied and how it is divided across components, depending on whether they are in series or parallel.
What is the relationship between voltage and brightness in the context of this circuit?
-The brightness of a lamp is directly related to the voltage across it; higher voltage results in greater brightness.
What does it mean when the script mentions 'the internal resistance of the generator is negligible'?
-This means that the generator's internal resistance does not significantly affect the overall circuit performance, allowing for a more straightforward analysis of voltage and current.
Why is it stated that the brightness does not change with varying connections of lamps?
-This is true in a parallel configuration, where each lamp can maintain its brightness despite changes in the number of lamps because they share the same voltage source.
What can be inferred about the brightness of lamp X when it is connected in series versus parallel?
-Lamp X will be brighter when connected in parallel since it receives the full supply voltage, compared to being in series where the voltage is divided.
What factors determine the change in voltage across a lamp when configurations change?
-The arrangement of the lamps (series vs. parallel) and the total voltage provided by the source are the primary factors that determine the voltage across each lamp.
What conclusion can be drawn about the circuit's behavior based on the analysis provided?
-The analysis shows that understanding the relationship between current, voltage, and the configuration of components is essential for predicting the performance of electrical circuits.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Electric Circuits: Basics of the voltage and current laws.

DC Resistors & Batteries: Crash Course Physics #29

Series & Parallel Circuits EXPLAINED with Kirchhoff's Circuit Laws // HSC Physics

Aula 8 - Circuito em série e paralelo

Listrik Dinamis-Rangkaian Listrik (Hukum Ohm) (Part 3)

Series and Parallel Circuits | Electricity | Physics | FuseSchool
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)