Macam-Macam Bentuk Permukaan Bumi dan Contohnya
Summary
TLDRThis educational video from Halo explores the diverse forms of Earth's relief, categorized into terrestrial and marine landscapes shaped by endogenous and exogenous forces. Key terrestrial features include mountains, hills, plateaus, and valleys, each defined by their formation processes and elevations. On the marine side, it covers underwater mountains, continental shelves, slopes, ridges, and deep-sea basins. The video highlights how geological processes like tectonics and erosion continuously reshape these landforms, offering viewers a comprehensive understanding of Earth's dynamic surface. This insightful overview aims to enhance viewers' knowledge of geography and geology.
Takeaways
- 😀 Relief refers to the various forms of Earth's surface, shaped by endogenic and exogenic processes.
- 😀 Endogenic forces originate from within the Earth, while exogenic forces come from external sources.
- 😀 Types of land relief include mountains, hills, plateaus, plains, and valleys.
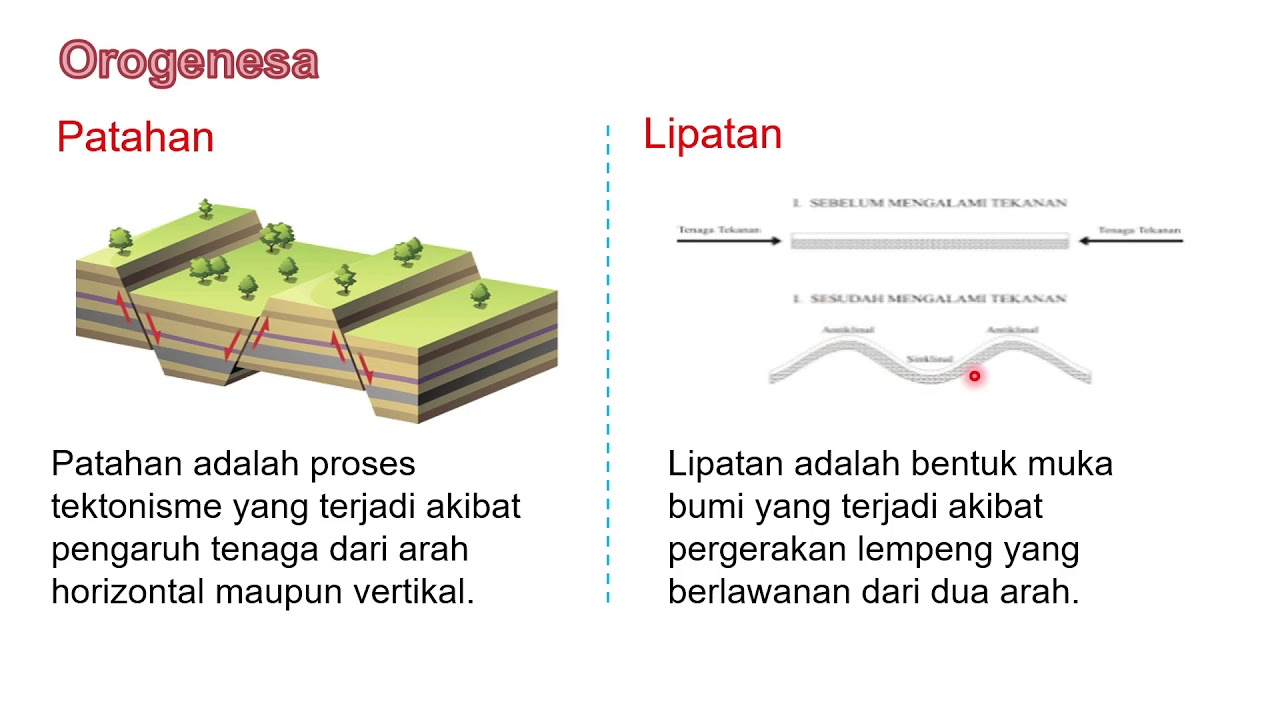
- 😀 Mountains are formed by tectonic and volcanic activity and consist of peaks, slopes, and bases.
- 😀 Indonesia is home to many significant mountains, such as Mount Merapi and Mount Agung.
- 😀 Hills differ from mountains in height, generally being lower and forming elongated ranges.
- 😀 Plateaus are flat, elevated areas formed through erosion, sedimentation, or volcanic activity.
- 😀 Lowlands are flat areas with elevations close to sea level, often used for settlements and agriculture.
- 😀 Valleys are depressions between hills or mountains, shaped by geological forces.
- 😀 Ocean relief features include underwater mountains, continental shelves, slopes, and deep-sea trenches.
Q & A
What are the two main types of landforms mentioned in the script?
-The two main types of landforms are land relief and ocean relief.
What is the difference between endogenous and exogenous forces?
-Endogenous forces originate from within the Earth, while exogenous forces come from outside the Earth.
How are mountains formed according to the script?
-Mountains are formed by endogenous forces such as tectonic and volcanic activity.
What are the three parts of a mountain?
-The three parts of a mountain are the peak, the slopes, and the foot of the mountain.
What characterizes highlands or plateaus?
-Highlands or plateaus are flat and extensive areas located at high elevations, typically between 200 to 1500 meters above sea level.
What is a valley, and how is it formed?
-A valley is a low area between hills or mountains, formed by endogenous forces such as folding or faulting.
What defines continental shelves?
-Continental shelves are shallow parts of the ocean floor that slope down from the land and are typically up to 200 meters deep.
Can you give examples of highlands found in Indonesia?
-Examples of highlands in Indonesia include Gayo Plateau in Aceh, Dieng Plateau in Central Java, and Malang Highlands in East Java.
What is a seamount?
-A seamount is an underwater mountain formed by volcanic activity, with its base on the ocean floor and its peak often visible above the water.
How do endogenous and exogenous forces affect the Earth's surface?
-Endogenous forces build up the Earth's surface through tectonic and volcanic activities, while exogenous forces wear it down through processes like erosion and weathering.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Os agentes INTERNOS e EXTERNOS do relevo (Endógenos e Exógenos) - Geografia Física

Belajar IPS Seru - Bentuk Muka Bumi Indonesia
Materi Tenaga Pembentuk Muka Bumi - Tenaga Endogen - Tektonisme

Kurikulum Merdeka Rangkuman IPS Kelas 8 Tema 2 Keragaman Aktivitas Ekonomi Masyarakat

Interior of the Earth - Chapter 3 Geography NCERT Class 11

GEO 2 6 FIN
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)