Understanding and building phylogenetic trees | High school biology | Khan Academy
Summary
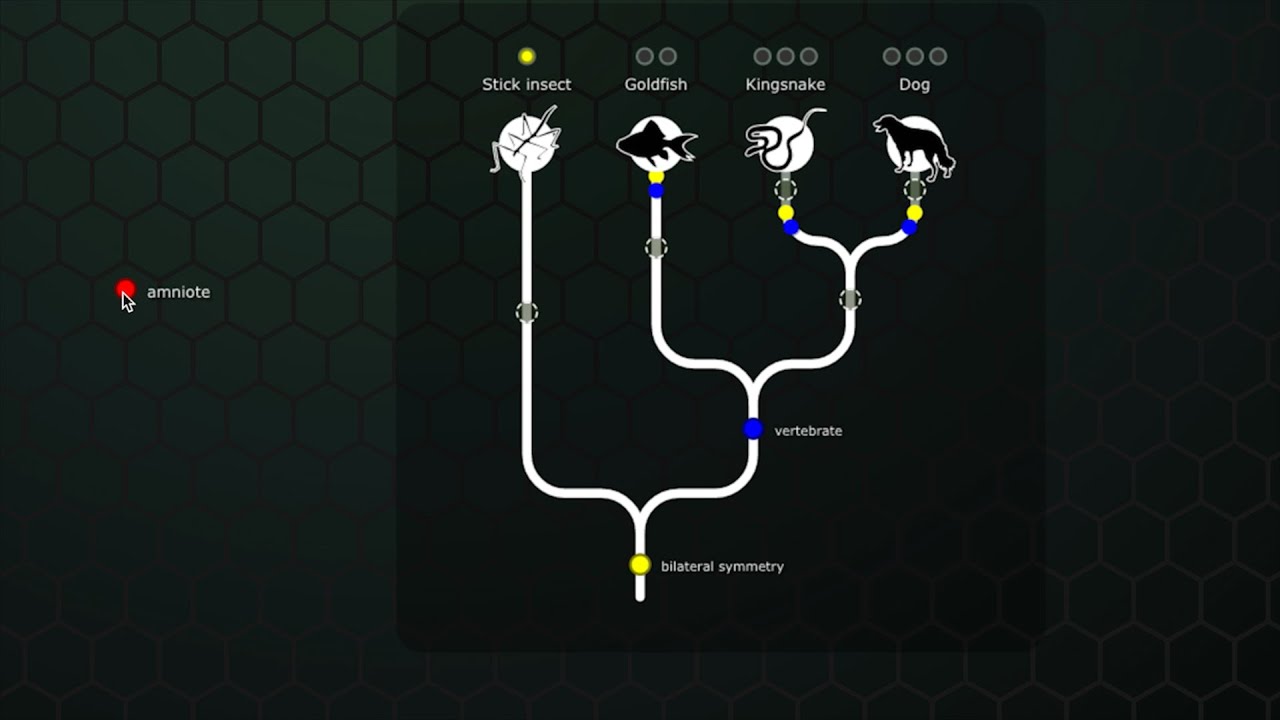
TLDRThis video explores the concept of a phylogenetic tree, illustrating how various species are related through common ancestors based on observable traits. By analyzing five species—lamprey, sea bass, antelope, bald eagle, and alligator—the presenter simplifies the complex evolutionary relationships, emphasizing the importance of parsimony in constructing hypotheses. Key traits such as jaws, lungs, gizzards, feathers, and fur are examined to demonstrate branching points in evolution. Ultimately, the video underscores the role of genetic evidence in refining these trees, revealing deeper connections among species.
Takeaways
- 😀 Understanding the relatedness of species is essential in studying biodiversity.
- 🧬 Phylogenetic trees illustrate how different species evolved from common ancestors.
- 🌳 The construction of a phylogenetic tree is based on observable traits.
- 🔍 Parsimony is a key principle, favoring the simplest explanations for evolutionary relationships.
- 🐟 The lamprey serves as an outgroup, lacking traits like jaws that other species possess.
- 🌬️ Jaws are identified as a derived trait that evolved in a common ancestor of certain species.
- 🌊 The sea bass diverges from the others due to its lack of lungs.
- 🐊 Bald eagles and alligators share a more recent common ancestor compared to the antelope.
- 🦅 Feathers are a derived trait specific to the bald eagle in this grouping.
- 🦙 Fur is a derived trait of the antelope, showcasing the diversity of adaptations among species.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video?
-The video focuses on constructing a phylogenetic tree to show how different species are related through common ancestors based on observable traits.
What does the term 'phylogenetic tree' refer to?
-A phylogenetic tree is a graphical representation that illustrates the evolutionary relationships among various species, showing how they diverged from common ancestors.
Why is the lamprey considered the outgroup in this analysis?
-The lamprey is considered the outgroup because it lacks the observable traits shared by the other species, indicating it diverged earlier from their common ancestor.
What does 'parsimony' mean in the context of constructing phylogenetic trees?
-In this context, parsimony refers to the principle of making the simplest explanation for observed traits, minimizing complexity in the hypothesis.
What trait distinguishes the sea bass from the other species discussed?
-The sea bass is distinguished by the absence of lungs, as it does not breathe air like the other species.
How are derived traits defined in this context?
-Derived traits are characteristics that have evolved in a species and are not present in their common ancestor.
What evolutionary significance do jaws have according to the video?
-Jaws are considered a derived trait that evolved in a lineage after diverging from the common ancestor shared with the lamprey.
What is the relationship between the bald eagle and the alligator based on the phylogenetic tree?
-The bald eagle and the alligator are more closely related to each other than to the antelope, sharing a more recent common ancestor.
Why might biologists look at molecular evidence when constructing phylogenetic trees?
-Molecular evidence, such as protein and DNA differences, provides a more accurate and detailed understanding of the evolutionary relationships among species.
What can be inferred about the fur of the antelope in relation to the phylogenetic tree?
-The fur of the antelope is a derived trait that likely evolved after the common ancestor of the antelope diverged from other species on the tree.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)