How to choose an appropriate statistical test
Summary
TLDRThis lecture explores how to choose the appropriate statistical test based on research questions, data scales, and study designs. It highlights the differences between parametric and non-parametric tests, emphasizing the importance of fulfilling normality assumptions. The discussion covers paired and unpaired study designs, detailing tests for comparing groups and examining relationships between variables. Examples include t-tests, ANOVA, chi-square tests, and correlation analyses, illustrating their applications in various scenarios. The lecture concludes by acknowledging the complexity of statistical choices, encouraging viewers to consider their specific research contexts.
Takeaways
- 😀 Choosing the right statistical test depends on your research question, the scale of data, and the study design.
- 📊 Continuous variables can be measured with instruments, while ordinal variables can be ordered naturally.
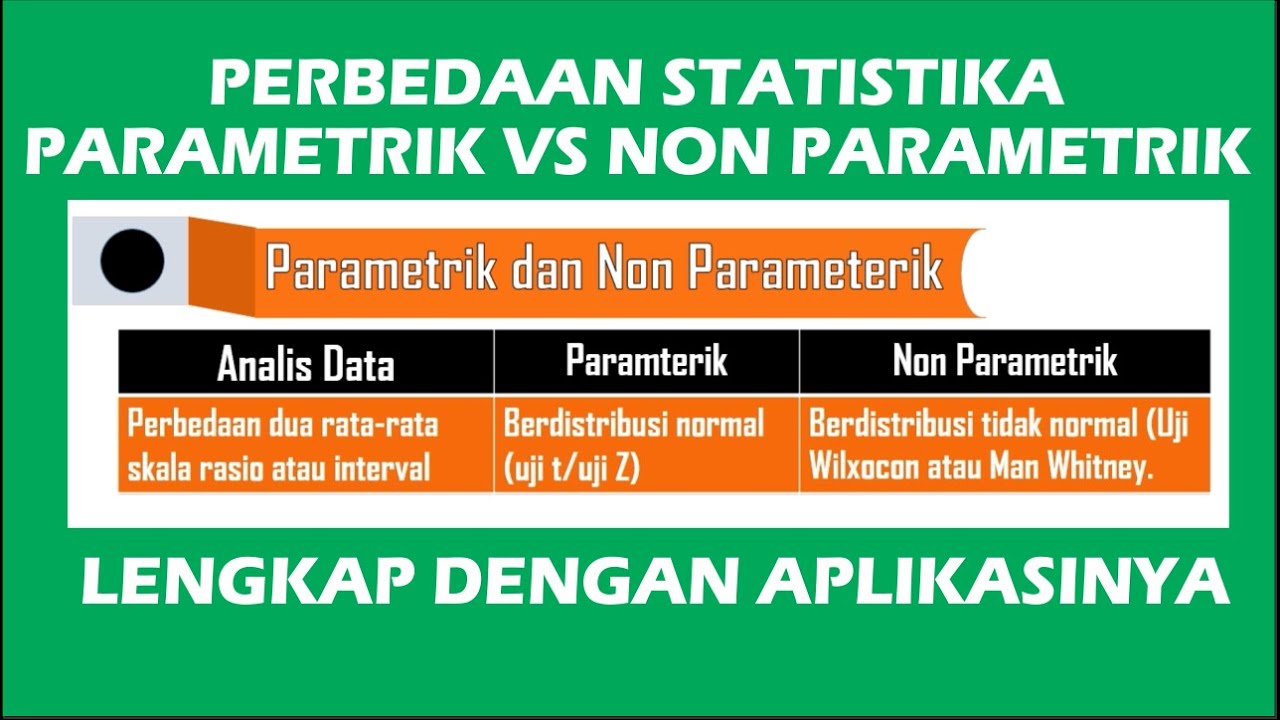
- 🔍 Parametric tests assume normal distribution, while non-parametric tests are used when those assumptions are not met.
- 👥 Paired designs compare two measurements from the same subjects, while unpaired designs involve independent groups.
- 🌱 Use a paired t-test for continuous data with a paired study design; if the data is skewed, consider non-parametric alternatives.
- 📈 For comparing more than two groups, a one-way ANOVA is appropriate if normality assumptions are met.
- 🧪 Chi-square tests are useful for analyzing relationships between categorical variables.
- 📉 Correlation tests like Pearson's and Spearman's assess relationships between continuous variables, depending on data assumptions.
- 📝 Always check assumptions of normality and symmetry before selecting a statistical test.
- 🔑 Statistical tests can control for external factors, and understanding their application is key to effective data analysis.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the lecture?
-The lecture focuses on how to choose the most appropriate statistical test based on research questions, data scales, assumptions, and study designs.
How do you determine if a parametric or non-parametric test should be used?
-You should use parametric tests if the data is normally distributed and meets assumptions; otherwise, non-parametric tests are more appropriate, especially in the presence of skewed data or extreme values.
What types of variables are discussed in the lecture?
-The lecture discusses continuous, ordinal, and nominal variables, each requiring different statistical approaches.
What is an example of a paired study design?
-An example of a paired study design is measuring blood pressure before and after a treatment in the same individuals.
What statistical test is recommended for comparing two independent groups with continuous data?
-An unpaired t-test is recommended for comparing two independent groups when the data is continuous.
What should you do if your data shows extreme values?
-If your data shows extreme values, you may consider using non-parametric tests, as they are more robust against such values.
What test can be used to analyze the relationship between two continuous variables?
-Pearson correlation can be used to analyze the relationship between two continuous variables if the assumptions for it are met; otherwise, Spearman correlation can be used.
When would you use the Wilcoxon signed-rank test?
-The Wilcoxon signed-rank test is used for paired data when the variable is continuous but does not fulfill normality assumptions.
What is the significance of the normal distribution in parametric tests?
-Parametric tests rely on the normal distribution to make inferences, which generally provides higher statistical power compared to non-parametric tests.
What is a one-way ANOVA used for?
-A one-way ANOVA is used to compare means among three or more independent groups when the assumptions of normality are fulfilled.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)